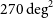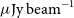46 results
Not all consequences should be accepted: Letter to the Editor Reply to “Reportable infections following colon surgery in a large public healthcare system in New York City: the consequences of being a level 1 trauma center”
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 March 2024, pp. 1-2
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Naturalistic assessment of reaction time variability in older adults at risk for Alzheimer’s disease
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 30 / Issue 5 / June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 January 2024, pp. 428-438
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Chapter 6 - Ibn Ṭūlūn’s Pacification Campaign: Sedition, Authority, and Empire in Abbasid Egypt
- from Part I - Political and Administrative Connections
-
-
- Book:
- Egypt and the Eastern Mediterranean World
- Published online:
- 01 December 2022
- Print publication:
- 15 December 2022, pp 169-202
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
The Evolutionary Map of the Universe Pilot Survey – ADDENDUM
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 39 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 November 2022, e055
-
- Article
- Export citation
ʿUthman ibn ʿAffan: Legend or Liability? Heather N. Keaney (London: Oneworld Academic, 2021). Pp. 159. $30.00 cloth. ISBN: 9781786076977
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Middle East Studies / Volume 54 / Issue 2 / May 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 May 2022, pp. 407-408
- Print publication:
- May 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
Securely sharing DSMB reports to speed decision making from multiple, concurrent, independent studies of similar treatments in COVID-19
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 6 / Issue 1 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 April 2022, e49
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The Evolutionary Map of the Universe pilot survey
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 38 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 September 2021, e046
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Chapter 14 - Slavery in the Islamic Middle East (c. 600–1000 CE)
- from Part IV - The Islamic World
-
-
- Book:
- The Cambridge World History of Slavery
- Published online:
- 09 September 2021
- Print publication:
- 12 August 2021, pp 337-361
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
1 - The early Islamic empire and the introduction of military slavery
- from Part I - Foundations, c.600–1000 ce
-
-
- Book:
- The Cambridge History of War
- Published online:
- 25 September 2020
- Print publication:
- 01 October 2020, pp 17-49
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Part I - Beyond Warfare: Armies, Tribes and Lords
-
- Book:
- The Cambridge World History of Violence
- Published online:
- 13 March 2020
- Print publication:
- 26 March 2020, pp 17-120
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Part II - The Violence of Governments and Rulers
-
- Book:
- The Cambridge World History of Violence
- Published online:
- 13 March 2020
- Print publication:
- 26 March 2020, pp 121-204
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Index
-
- Book:
- The Cambridge World History of Violence
- Published online:
- 13 March 2020
- Print publication:
- 26 March 2020, pp 676-708
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Copyright page
-
- Book:
- The Cambridge World History of Violence
- Published online:
- 13 March 2020
- Print publication:
- 26 March 2020, pp iv-iv
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Contributors to Volume II
-
- Book:
- The Cambridge World History of Violence
- Published online:
- 13 March 2020
- Print publication:
- 26 March 2020, pp xii-xiv
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Part III - Social, Interpersonal and Collective Violence
-
- Book:
- The Cambridge World History of Violence
- Published online:
- 13 March 2020
- Print publication:
- 26 March 2020, pp 205-346
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Part IV - Religious, Sacred and Ritualised Violence
-
- Book:
- The Cambridge World History of Violence
- Published online:
- 13 March 2020
- Print publication:
- 26 March 2020, pp 347-512
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Figures and Table
-
- Book:
- The Cambridge World History of Violence
- Published online:
- 13 March 2020
- Print publication:
- 26 March 2020, pp ix-xi
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Contents
-
- Book:
- The Cambridge World History of Violence
- Published online:
- 13 March 2020
- Print publication:
- 26 March 2020, pp v-viii
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Introduction to Volume II
-
-
- Book:
- The Cambridge World History of Violence
- Published online:
- 13 March 2020
- Print publication:
- 26 March 2020, pp 1-16
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Part V - Depictions of Violence
-
- Book:
- The Cambridge World History of Violence
- Published online:
- 13 March 2020
- Print publication:
- 26 March 2020, pp 513-675
-
- Chapter
- Export citation