434 results
Cardiology across continents: an interactive, case-based learning series
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 April 2024, pp. 1-3
-
- Article
- Export citation
VaTEST III: Validation of 8 Potential Super-Earths from TESS Data
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 April 2024, pp. 1-22
-
- Article
- Export citation
Metrology for sub-Rayleigh-length target positioning in ~1022 W/cm2 laser-plasma experiments
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 March 2024, pp. 1-58
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Rediscovery of Swertia dilatata var. pilosa after 140 years
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Incidence and risk factors for catheter-associated urinary tract infection in 623 intensive care units throughout 37 Asian, African, Eastern European, Latin American, and Middle Eastern nations: A multinational prospective research of INICC
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 45 / Issue 5 / May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 January 2024, pp. 567-575
- Print publication:
- May 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Kinetics of citrate-induced selenite desorption from montmorillonite as affected by complexation with hydroxyaluminum and hydroxyaluminosilicate ions
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 55 / Issue 1 / February 2007
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 71-88
-
- Article
- Export citation
Field Localization and Density Cavitation in Low-Beta Plasmas
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 2021 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e3
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Genetic diversity and population structure analysis in early generations maize inbreds derived from local germplasm of Eastern Himalayan regions using microsatellite markers
-
- Journal:
- Plant Genetic Resources / Volume 21 / Issue 5 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 November 2023, pp. 418-425
-
- Article
- Export citation
The burden of mental disorders in Nepal between 1990 and 2019: Findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019
-
- Journal:
- Cambridge Prisms: Global Mental Health / Volume 10 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 September 2023, e61
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Evaluation of phenological development and agronomic traits in exotic common bean germplasm across multiple environments
-
- Journal:
- Plant Genetic Resources / Volume 21 / Issue 3 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 August 2023, pp. 195-203
-
- Article
- Export citation
Advocacy at the Eighth World Congress of Pediatric Cardiology and Cardiac Surgery
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 33 / Issue 8 / August 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 August 2023, pp. 1277-1287
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
14CO2 ACTIVITY IN AIR SAMPLES AND DILUTION FACTOR EVALUATION OF KAKRAPAR GUJARAT SITE, INDIA
-
- Journal:
- Radiocarbon / Volume 65 / Issue 4 / August 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 August 2023, pp. 819-831
- Print publication:
- August 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Introduction of rural psychiatry posting in MD curriculum: A qualitative study on residents’ perspective
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 66 / Issue S1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 July 2023, pp. S909-S910
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
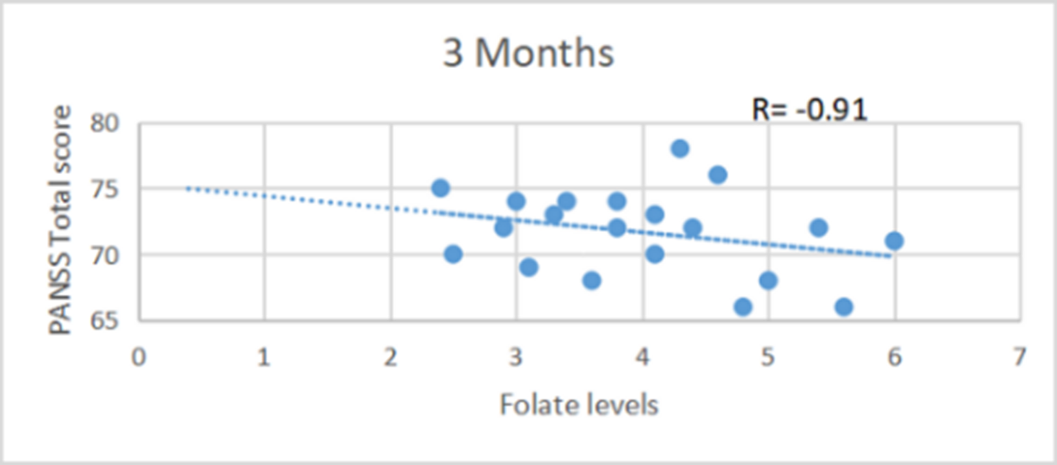
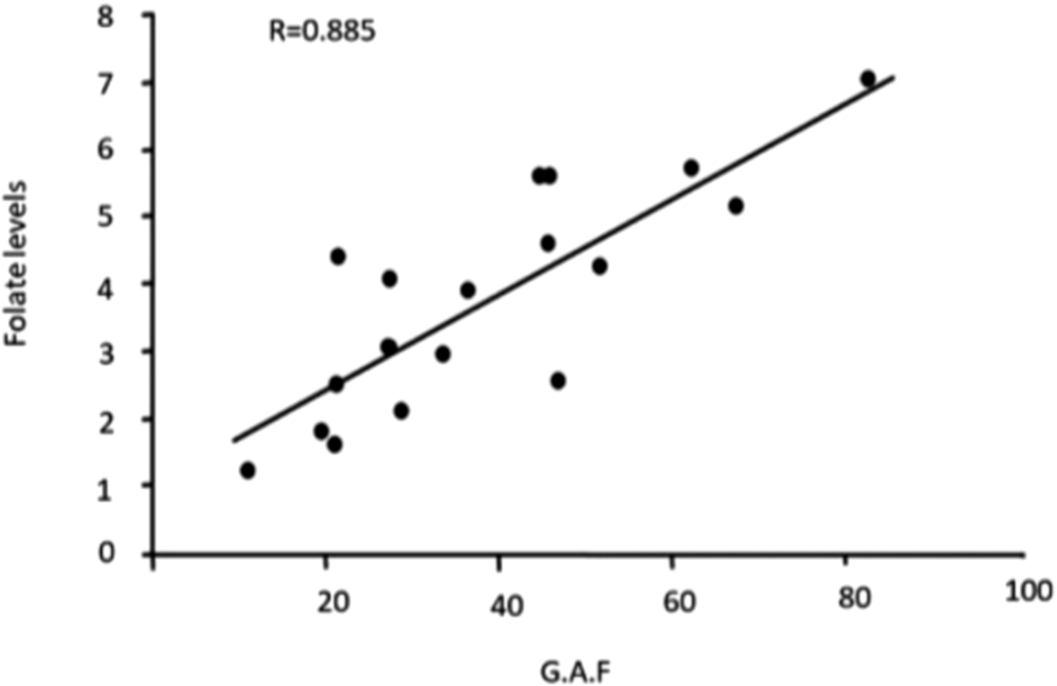
Role of Folic acid as adjuvant treatment in Schizophrenia: A randomized controlled trial
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 66 / Issue S1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 July 2023, pp. S634-S635
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Facing the COVID-19 pandemic – an assessment of students’ mental health and major coping strategies during the COVID-19 pandemic – an international study
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 66 / Issue S1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 July 2023, pp. S152-S153
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Psychometric Evaluation of the Computerized Battery for Neuropsychological Evaluation of Children (BENCI) among School Aged Children in the Context of HIV in an Urban Kenyan Setting
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 66 / Issue S1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 July 2023, p. S63
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Do variations in nasal irrigation recipes and storage effect the risk of bacterial contamination? – ERRATUM
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Laryngology & Otology / Volume 137 / Issue 8 / August 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 June 2023, pp. 942-944
- Print publication:
- August 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
P.042 Could Live Cell-Based Assay increase the acetylcholine receptor autoantibodies seropositivity in patients with clinical suspicion of myasthenia gravis?
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 50 / Issue s2 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 June 2023, p. S69
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
P.041 Guillain Barre syndrome could be a rare presenting finding of nodal and paranodal autoantibodies in immune-mediated neuropathies (IMN): A clinical utility of Cell based Assay
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 50 / Issue s2 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 June 2023, p. S69
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation



 R
R R
R R
R R
R R
R R
R R
R R
R