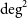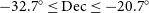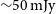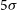329 results
Evolutionary map of the universe (EMU): Observations of filamentary structures in the Abell S1136 galaxy cluster
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 41 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 May 2024, e050
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Characteristics of healthcare personnel with SARS-CoV-2 infection: 10 emerging infections program sites in the United States, April 2020–December 2021
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 May 2024, pp. 1-9
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Polarized Single-Crystal Fourier-Transform Infrared Microscopy of Ouray Dickite and Keokuk Kaolinite
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 38 / Issue 6 / December 1990
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 April 2024, pp. 573-583
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Adsorption of Protamine and Papain Proteins on Saponite
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 56 / Issue 5 / October 2008
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 494-504
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Double trouble: Kennedy Disease and Immune-Mediated Necrotizing Myopathy in a Cree Male
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 October 2023, pp. 1-3
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The Southern-sky MWA Rapid Two-metre (SMART) pulsar survey—II. Survey status, pulsar census, and first pulsar discoveries – ADDENDUM
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 40 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 July 2023, e031
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Residential social vulnerability among healthcare personnel with and without severe acute respiratory coronavirus virus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection in Five US states, May–December 2020
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 45 / Issue 1 / January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 July 2023, pp. 82-88
- Print publication:
- January 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
P.046 Real-world survival effectiveness of edaravone in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: a propensity score weighted, registry-based, Canada-wide cohort study
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 50 / Issue s2 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 June 2023, p. S70
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
A framework for assessing clinical trial site readiness
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 7 / Issue 1 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 May 2023, e151
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
MWAX: A new correlator for the Murchison Widefield Array
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 40 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 April 2023, e019
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The Southern-sky MWA Rapid Two-metre (SMART) pulsar survey—II. Survey status, pulsar census, and first pulsar discoveries
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 40 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 April 2023, e020
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The Southern-sky MWA Rapid Two-metre (SMART) pulsar survey—I. Survey design and processing pipeline
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 40 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 April 2023, e021
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
James Sharpe’s Contributions to Neurology and Neuro-ophthalmology: A Posthumous Tribute 10 Years On
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 51 / Issue 1 / January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 January 2023, pp. 117-121
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A Comparison of Commonly Used Ear Tags on the Ear Damage of Sheep
-
- Journal:
- Animal Welfare / Volume 10 / Issue 2 / May 2001
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 January 2023, pp. 141-151
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Creating a Digital Psychoeducation Programme for bipolar disorder in the COVID-19 pandemic
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 65 / Issue S1 / June 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 September 2022, p. S569
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
GaLactic and Extragalactic All-sky Murchison Widefield Array survey eXtended (GLEAM-X) I: Survey description and initial data release
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 39 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 August 2022, e035
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Trends in Clostridioides difficile infection rates in Canadian hospitals during the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 44 / Issue 7 / July 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 August 2022, pp. 1180-1183
- Print publication:
- July 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The MeerTime Pulsar Timing Array: A census of emission properties and timing potential
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 39 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 July 2022, e027
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Pure Vision-Based Motion Tracking for Data-Driven Design – A Simple, Flexible, and Cost-Effective Approach for Capturing Static and Dynamic Interactions
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Design Society / Volume 2 / May 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 May 2022, pp. 485-494
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Early-time searches for coherent radio emission from short GRBs with the Murchison Widefield Array
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 39 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 February 2022, e003
-
- Article
- Export citation