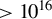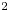389 results
Learn to flap: foil non-parametric path planning via deep reinforcement learning
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 984 / 10 April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 March 2024, A9
-
- Article
- Export citation
Numerical simulation of droplet impingement and film flow for three-dimensional wings
-
- Journal:
- The Aeronautical Journal , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 January 2024, pp. 1-21
-
- Article
- Export citation
Competition among the two-plasmon decay of backscattered light, filamentation of the electron-plasma wave and side stimulated Raman scattering
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 11 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 August 2023, e76
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Accelerated protons with energies up to 70 MeV based on the optimized SG-II Peta-watt laser facility
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 11 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 June 2023, e63
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
H2 bubble motion reversals during water electrolysis
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 958 / 10 March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 March 2023, A43
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Effective aero-optical suppression by steady wall blowing and wall suction schemes for supersonic turbulent boundary layer
-
- Journal:
- The Aeronautical Journal / Volume 127 / Issue 1312 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 November 2022, pp. 1037-1047
-
- Article
- Export citation
Stimulatory and inhibitory effects of light on Cereus repandus (Cactaceae) seed germination are strongly dependent on spectral quality
-
- Journal:
- Seed Science Research / Volume 32 / Issue 3 / September 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 September 2022, pp. 166-174
-
- Article
- Export citation
Prediction and copy number variation identification of ZNF146 gene related to growth traits in Chinese cattle
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Agricultural Science / Volume 160 / Issue 5 / October 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 August 2022, pp. 404-412
-
- Article
- Export citation
Sand erosion modeling in generic compressor rig testing
-
- Journal:
- The Aeronautical Journal / Volume 126 / Issue 1302 / August 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 August 2022, pp. 1303-1323
-
- Article
- Export citation
Study on the monitoring and classification of winter wheat freezing injury in spring based on 3S technology
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Agricultural Science / Volume 159 / Issue 9-10 / November 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 March 2022, pp. 623-635
-
- Article
- Export citation
Cognitive impairment and development of dementia in very late-onset schizophrenia-like psychosis: a systematic review
-
- Journal:
- Irish Journal of Psychological Medicine / Volume 40 / Issue 4 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 June 2021, pp. 616-628
- Print publication:
- December 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Path planning method for unmanned underwater vehicles eliminating effect of currents based on artificial potential field
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Navigation / Volume 74 / Issue 5 / September 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 April 2021, pp. 955-967
- Print publication:
- September 2021
-
- Article
- Export citation
Unsteady simulations of migration and deposition of fly-ash particles in the first-stage turbine of an aero-engine
-
- Journal:
- The Aeronautical Journal / Volume 125 / Issue 1291 / September 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 April 2021, pp. 1566-1586
-
- Article
- Export citation
Research on the design of smart morphing long-endurance UAVs
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- The Aeronautical Journal / Volume 125 / Issue 1283 / January 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 September 2020, pp. 22-41
-
- Article
- Export citation
EFFICIENT DYNAMIC HEDGING FOR LARGE VARIABLE ANNUITY PORTFOLIOS WITH MULTIPLE UNDERLYING ASSETS
-
- Journal:
- ASTIN Bulletin: The Journal of the IAA / Volume 50 / Issue 3 / September 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 August 2020, pp. 913-957
- Print publication:
- September 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation
Prevalence of depression, anxiety and suicide among men who have sex with men in China: a systematic review and meta-analysis
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology and Psychiatric Sciences / Volume 29 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 June 2020, e136
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Epidemiological characteristics of COVID-19 patients in convalescence period
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 148 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 June 2020, e108
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Analysis of forward approach for upper bounding end-to-end transmission delays over distributed real-time avionics networks
-
- Journal:
- The Aeronautical Journal / Volume 124 / Issue 1279 / September 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 April 2020, pp. 1399-1435
-
- Article
- Export citation