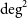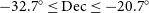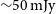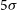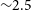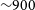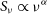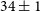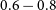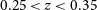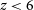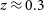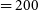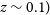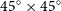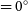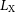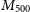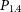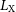316 results
The Southern-sky MWA Rapid Two-metre (SMART) pulsar survey—II. Survey status, pulsar census, and first pulsar discoveries – ADDENDUM
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 40 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 July 2023, e031
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
P.046 Real-world survival effectiveness of edaravone in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: a propensity score weighted, registry-based, Canada-wide cohort study
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 50 / Issue s2 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 June 2023, p. S70
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
The Southern-sky MWA Rapid Two-metre (SMART) pulsar survey—II. Survey status, pulsar census, and first pulsar discoveries
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 40 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 April 2023, e020
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The Southern-sky MWA Rapid Two-metre (SMART) pulsar survey—I. Survey design and processing pipeline
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 40 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 April 2023, e021
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Northern Ireland farm-level management factors for recurrent bovine tuberculosis herd breakdowns
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 150 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 October 2022, e176
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
GaLactic and Extragalactic All-sky Murchison Widefield Array survey eXtended (GLEAM-X) I: Survey description and initial data release
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 39 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 August 2022, e035
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The MeerTime Pulsar Timing Array: A census of emission properties and timing potential
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 39 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 July 2022, e027
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Pure Vision-Based Motion Tracking for Data-Driven Design – A Simple, Flexible, and Cost-Effective Approach for Capturing Static and Dynamic Interactions
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Design Society / Volume 2 / May 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 May 2022, pp. 485-494
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Medication-Facilitated Advanced Airway Management with First-Line Use of a Supraglottic Device – A One-Year Quality Assurance Review
-
- Journal:
- Prehospital and Disaster Medicine / Volume 37 / Issue 4 / August 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 May 2022, pp. 561-565
- Print publication:
- August 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Higher total faecal short-chain fatty acid concentrations correlate with increasing proportions of butyrate and decreasing proportions of branched-chain fatty acids across multiple human studies
-
- Journal:
- Gut Microbiome / Volume 3 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 March 2022, e2
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Early-time searches for coherent radio emission from short GRBs with the Murchison Widefield Array
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 39 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 February 2022, e003
-
- Article
- Export citation
The formation of planetary systems with SPICA
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 38 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 November 2021, e055
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Low-frequency integrated radio spectra of diffuse, steep-spectrum sources in galaxy clusters: palaeontology with the MWA and ASKAP
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 38 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 October 2021, e053
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Metabolomic profiling of the Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension diet provides novel insights for the nutritional epidemiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 128 / Issue 3 / 14 August 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 September 2021, pp. 487-497
- Print publication:
- 14 August 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
A broadband radio view of transient jet ejecta in the black hole candidate X-ray binary MAXI J1535–571
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 38 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 September 2021, e045
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
The MAGPI survey: Science goals, design, observing strategy, early results and theoretical framework
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 38 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 July 2021, e031
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
MWA and ASKAP observations of atypical radio-halo-hosting galaxy clusters: Abell 141 and Abell 3404
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 38 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 July 2021, e031
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Murchison Widefield Array rapid-response observations of the short GRB 180805A
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 38 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 June 2021, e026
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
What is quantitative plant biology?
-
- Journal:
- Quantitative Plant Biology / Volume 2 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 May 2021, e10
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Diffuse galaxy cluster emission at 168 MHz within the Murchison Widefield Array Epoch of Reionization 0-h field
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 38 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 March 2021, e010
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation