2486 results

The Theological Imagination
- Perception and Interpretation in Life, Art, and Faith
- Coming soon
-
- Expected online publication date:
- November 2024
- Print publication:
- 30 November 2024
-
- Book
- Export citation
8 - How to Facilitate ESG Investor Engagement
-
-
- Book:
- Board-Shareholder Dialogue
- Published online:
- 31 August 2024
- Print publication:
- 30 September 2024, pp 242-269
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
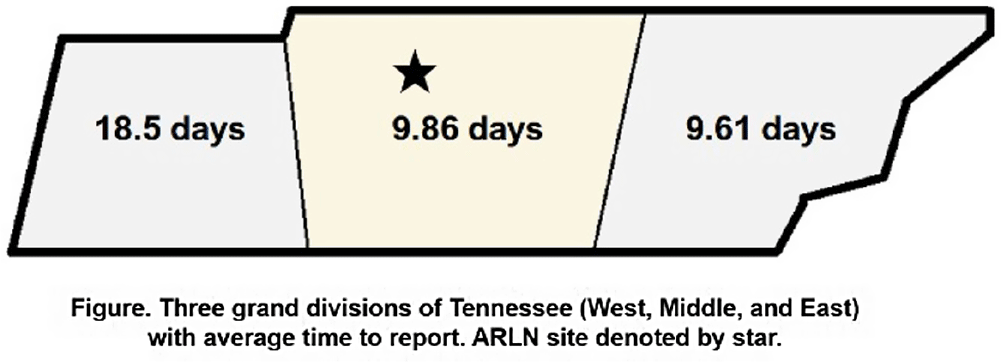
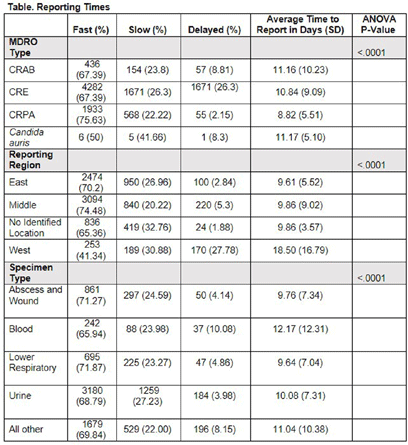
Variability of MDRO Reporting Across Tennessee Microbiology Laboratories
-
- Journal:
- Antimicrobial Stewardship & Healthcare Epidemiology / Volume 4 / Issue S1 / July 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 September 2024, p. s153
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Impact of a tracheal aspirate culture diagnostic test stewardship intervention in a tertiary care PICU
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 September 2024, pp. 1-9
-
- Article
- Export citation
The Interlayer Bonding in One-Layer Kaolin Structures
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 22 / Issue 1 / February 1974
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 July 2024, pp. 139-140
-
- Article
- Export citation
The Stability of Fluorine Analogues of Kaolinite
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 26 / Issue 1 / February 1978
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 July 2024, pp. 76-78
-
- Article
- Export citation
Fostering societal participation of marginalised people in street-outreach services in the Netherlands
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Social Policy , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 June 2024, pp. 1-22
-
- Article
- Export citation
Chapter 10 - Technological Fantasies
-
-
- Book:
- The Cambridge Companion to American Utopian Literature and Culture since 1945
- Published online:
- 09 May 2024
- Print publication:
- 16 May 2024, pp 185-200
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
A pivot point in Maya history: fire-burning event at K'anwitznal (Ucanal) and the making of a new era of political rule
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
423 Innovation in MS Patient Care: Linking Cognitive Health and Myelin Integrity
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 8 / Issue s1 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 April 2024, pp. 125-126
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
239 Promoting Health Equity in South Los Angeles: A Place-Based Initiative in the Nickerson Gardens Housing Development
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 8 / Issue s1 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 April 2024, p. 72
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
440 Muscle Protein Synthesis and Whole-Body Protein Balance Following Ingestion of Beef or a Soy Protein Based Meat Alternative
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 8 / Issue s1 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 April 2024, pp. 130-131
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
540 Diversifying SC CTSI’s Message: Successfully Leveraging Multi-Platform Social Media for Multi-Audience Dissemination
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 8 / Issue s1 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 April 2024, p. 161
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
97 BUILD EXITO: a successful collaborative training program for STEM undergraduates to improve workforce diversity
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 8 / Issue s1 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 April 2024, pp. 26-27
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Interaction of Aliphatic Amines with Montmorillonite to Enhance Adsorption of Organic Pollutants
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 33 / Issue 4 / August 1985
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 April 2024, pp. 301-311
-
- Article
- Export citation
Alleviating the burden of depression: a simulation study on the impact of mental health services
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology and Psychiatric Sciences / Volume 33 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 April 2024, e19
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Chalcolithic Tattooing: Historical and Experimental Evaluation of the Tyrolean Iceman's Body Markings
-
- Journal:
- European Journal of Archaeology , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 March 2024, pp. 1-22
-
- Article
- Export citation
16 - Christian Poetry
- from Part IV - The New Christian World
-
-
- Book:
- The Cambridge History of Old Norse-Icelandic Literature
- Published online:
- 08 February 2024
- Print publication:
- 29 February 2024, pp 334-353
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Social connections and risk of incident mild cognitive impairment, dementia, and mortality in 13 longitudinal cohort studies of ageing
-
- Journal:
- International Psychogeriatrics / Volume 35 / Issue S1 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 February 2024, pp. 16-17
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Conceptual framework for social health: identification of modifiable and protective and risk factors
-
- Journal:
- International Psychogeriatrics / Volume 35 / Issue S1 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 February 2024, p. 15
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation