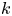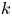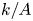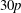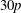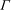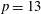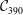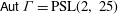21 results
Disrupted dynamic functional connectivity of hippocampal subregions mediated the slowed information processing speed in late-life depression
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 53 / Issue 14 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 February 2023, pp. 6500-6510
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Suppression of flow reversals via manipulating corner rolls in plane Rayleigh–Bénard convection
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 946 / 10 September 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 August 2022, A44
-
- Article
- Export citation
Cardiovascular diseases and related risk factors accelerated cognitive deterioration in patients with late-life depression: a one-year prospective study
-
- Journal:
- International Psychogeriatrics / Volume 31 / Issue 10 / October 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 January 2019, pp. 1483-1489
-
- Article
- Export citation
The Phase II Murchison Widefield Array: Design overview
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 35 / 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 November 2018, e033
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Anisotropic crystal–melt interfacial energy and stiffness of aluminum
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 30 / Issue 11 / 14 June 2015
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 May 2015, pp. 1827-1835
- Print publication:
- 14 June 2015
-
- Article
- Export citation
Uncertainty in simulating biomass yield and carbon–water fluxes from grasslands under climate change
-
- Journal:
- Advances in Animal Biosciences / Volume 6 / Issue 1 / March 2015
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2015, pp. 49-51
- Print publication:
- March 2015
-
- Article
- Export citation
Information System Innovation as a Social Action: The Case of Career and Vocational Helping Systems
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Pacific Rim Psychology / Volume 8 / Issue 2 / December 2014
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 December 2014, pp. 71-82
- Print publication:
- December 2014
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
PENTAVALENT SYMMETRIC GRAPHS OF ORDER
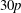 $\def \xmlpi #1{}\def \mathsfbi #1{\boldsymbol {\mathsf {#1}}}\let \le =\leqslant \let \leq =\leqslant \let \ge =\geqslant \let \geq =\geqslant \def \Pr {\mathit {Pr}}\def \Fr {\mathit {Fr}}\def \Rey {\mathit {Re}}30p$
$\def \xmlpi #1{}\def \mathsfbi #1{\boldsymbol {\mathsf {#1}}}\let \le =\leqslant \let \leq =\leqslant \let \ge =\geqslant \let \geq =\geqslant \def \Pr {\mathit {Pr}}\def \Fr {\mathit {Fr}}\def \Rey {\mathit {Re}}30p$
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 90 / Issue 3 / December 2014
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 August 2014, pp. 353-362
- Print publication:
- December 2014
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Chapter 7 - Early-onset mental disorders and their links to chronic physical conditions in adulthood
- from Section 2: - Mental disorders and personal disadvantages
-
-
- Book:
- The Burdens of Mental Disorders
- Print publication:
- 09 May 2013, pp 87-96
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Contributors
-
-
- Book:
- The Burdens of Mental Disorders
- Print publication:
- 09 May 2013, pp ix-xii
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Detrital zircon provenance of the Lower Yangtze foreland basin deposits: constraints on the evolution of the early Palaeozoic Wuyi–Yunkai orogenic belt in South China
-
- Journal:
- Geological Magazine / Volume 150 / Issue 6 / November 2013
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 March 2013, pp. 959-974
-
- Article
- Export citation
GASKAP—The Galactic ASKAP Survey
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 30 / 2013
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 January 2013, e003
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Contributors
-
-
- Book:
- Case Studies in Epilepsy
- Published online:
- 05 December 2012
- Print publication:
- 22 November 2012, pp viii-x
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
A Generalized Stationary Algorithm for Resonant Tunneling: Multi-Mode Approximation and High Dimension
-
- Journal:
- Communications in Computational Physics / Volume 10 / Issue 4 / October 2011
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 August 2015, pp. 882-898
- Print publication:
- October 2011
-
- Article
- Export citation
Electronic Impact of Inclusions in Diamond
-
- Journal:
- MRS Online Proceedings Library Archive / Volume 1203 / 2009
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 January 2011, 1203-J17-19
- Print publication:
- 2009
-
- Article
- Export citation
Influence of DSS-8 on the remineralisation of Dentine
-
- Journal:
- MRS Online Proceedings Library Archive / Volume 1187 / 2009
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 January 2011, 1187-KK05-34
- Print publication:
- 2009
-
- Article
- Export citation
Effects on Hardness and Elastic Modulus for DSS-8 Peptide Treatment on Remineralization of Human Dental Tissues
-
- Journal:
- MRS Online Proceedings Library Archive / Volume 1132 / 2008
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 March 2011, 1132-Z09-05
- Print publication:
- 2008
-
- Article
- Export citation
Diamond Amplified Photocathodes
-
- Journal:
- MRS Online Proceedings Library Archive / Volume 1039 / 2007
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 February 2011, 1039-P09-02
- Print publication:
- 2007
-
- Article
- Export citation
A Novel Simple Route to Synthesize Aqueous Niobium and Tantalum Precursors for Ferroelectric and Photocatalytic Applications
-
- Journal:
- MRS Online Proceedings Library Archive / Volume 942 / 2006
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 February 2011, 0942-W04-03
- Print publication:
- 2006
-
- Article
- Export citation
Chemical Vapor Deposition of ZrxTi1-xO and HfxTi1-xO Thin Films Using the Composite Anhydrous Nitrate Precursors
-
- Journal:
- MRS Online Proceedings Library Archive / Volume 917 / 2006
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 February 2011, 0917-E05-13
- Print publication:
- 2006
-
- Article
- Export citation