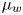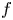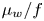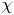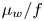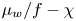66 results
Chinese stalagmite δ18O records reveal the diverse moisture trajectories during the middle to late last glacial period
-
- Journal:
- Geological Magazine , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 February 2024, pp. 1-13
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The egg ribonuclease SjCP1412 accelerates liver fibrosis caused by Schistosoma japonicum infection involving damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs)
-
- Journal:
- Parasitology / Volume 151 / Issue 3 / March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 December 2023, pp. 260-270
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Modelling the wall friction coefficient for a simple shear granular flow in view of the degradation mechanism
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 969 / 25 August 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 August 2023, A7
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
X-ray diffraction performance of thermally distorted crystals
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 11 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 July 2023, e69
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Observations of dust fragmentations in the Experimental Advanced Superconducting Tokamak
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Plasma Physics / Volume 89 / Issue 2 / April 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 April 2023, 175890202
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Petrogenesis of Eocene Wangdui adakitic pluton in the western Gangdese belt, southern Tibet: implications for crustal thickening
-
- Journal:
- Geological Magazine / Volume 159 / Issue 8 / August 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 May 2022, pp. 1335-1354
-
- Article
- Export citation
Inverse nodal problems on quantum tree graphs
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 153 / Issue 1 / February 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 December 2021, pp. 275-288
- Print publication:
- February 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Cardiovascular and metabolic risk of antipsychotics in children and young adults: a multinational self-controlled case series study
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology and Psychiatric Sciences / Volume 30 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 October 2021, e65
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Effects of different ventilation on cerebral oxygen saturation and cerebral blood flow before and after modified ultrafiltration in infants during ventricular septal defect repair
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 31 / Issue 3 / March 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 February 2021, pp. 371-376
-
- Article
- Export citation
4 - Advanced Diversity Techniques
-
- Book:
- Advanced Wireless Transmission Technologies
- Published online:
- 10 January 2020
- Print publication:
- 30 January 2020, pp 55-83
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
6 - Multiuser Scheduling
-
- Book:
- Advanced Wireless Transmission Technologies
- Published online:
- 10 January 2020
- Print publication:
- 30 January 2020, pp 146-178
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Dedication
-
- Book:
- Advanced Wireless Transmission Technologies
- Published online:
- 10 January 2020
- Print publication:
- 30 January 2020, pp v-vi
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
9 - Cognitive Transmission
-
- Book:
- Advanced Wireless Transmission Technologies
- Published online:
- 10 January 2020
- Print publication:
- 30 January 2020, pp 256-302
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
12 - Application: Massive MIMO Transmission
-
- Book:
- Advanced Wireless Transmission Technologies
- Published online:
- 10 January 2020
- Print publication:
- 30 January 2020, pp 367-390
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Contents
-
- Book:
- Advanced Wireless Transmission Technologies
- Published online:
- 10 January 2020
- Print publication:
- 30 January 2020, pp vii-x
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
10 - Application: Hybrid FSO/RF Transmission
-
- Book:
- Advanced Wireless Transmission Technologies
- Published online:
- 10 January 2020
- Print publication:
- 30 January 2020, pp 303-334
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
7 - Multiuser MIMO Transmissions
-
- Book:
- Advanced Wireless Transmission Technologies
- Published online:
- 10 January 2020
- Print publication:
- 30 January 2020, pp 179-225
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
11 - Application: Sensor Transmission with RF Energy Harvesting
-
- Book:
- Advanced Wireless Transmission Technologies
- Published online:
- 10 January 2020
- Print publication:
- 30 January 2020, pp 335-366
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
8 - Relay Transmission
-
- Book:
- Advanced Wireless Transmission Technologies
- Published online:
- 10 January 2020
- Print publication:
- 30 January 2020, pp 226-255
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
2 - Transmission Technologies for Flat Fading Channels
-
- Book:
- Advanced Wireless Transmission Technologies
- Published online:
- 10 January 2020
- Print publication:
- 30 January 2020, pp 20-40
-
- Chapter
- Export citation