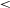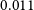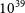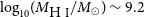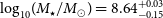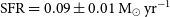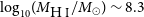360 results
VaTEST III: Validation of eight potential super-earths from TESS data
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 41 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 April 2024, e030
-
- Article
- Export citation
Metrology for sub-Rayleigh-length target positioning in ~1022 W/cm2 laser-plasma experiments
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 March 2024, pp. 1-58
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Evaluation of phenological development and agronomic traits in exotic common bean germplasm across multiple environments
-
- Journal:
- Plant Genetic Resources / Volume 21 / Issue 3 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 August 2023, pp. 195-203
-
- Article
- Export citation
Advocacy at the Eighth World Congress of Pediatric Cardiology and Cardiac Surgery
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 33 / Issue 8 / August 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 August 2023, pp. 1277-1287
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
14CO2 ACTIVITY IN AIR SAMPLES AND DILUTION FACTOR EVALUATION OF KAKRAPAR GUJARAT SITE, INDIA
-
- Journal:
- Radiocarbon / Volume 65 / Issue 4 / August 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 August 2023, pp. 819-831
- Print publication:
- August 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
A miniaturized CPW-fed CSRR-loaded quad-port MIMO antenna for 5.5/6.5 GHz wireless applications
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Microwave and Wireless Technologies , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 July 2023, pp. 1-10
-
- Article
- Export citation
Students’ emotional well-being and religiosity during the COVID-19 pandemic- an international study in 7 countries
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 66 / Issue S1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 July 2023, p. S406
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Facing the COVID-19 pandemic – an assessment of students’ mental health and major coping strategies during the COVID-19 pandemic – an international study
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 66 / Issue S1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 July 2023, pp. S152-S153
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Association of α-klotho levels with serum copper and cadmium levels in schizophrenia
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 66 / Issue S1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 July 2023, p. S257
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Comparing the distribution of neuropsychiatric symptoms among individuals with depression and mild cognitive impairment
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 66 / Issue S1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 July 2023, p. S173
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
“Geochronology and geochemistry of pelitic granulite from the South Delhi Terrane of the Aravalli Delhi Mobile Belt, NW India: implications for petrogenesis and geodynamic model”
-
- Journal:
- Geological Magazine / Volume 160 / Issue 7 / July 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 July 2023, pp. 1301-1320
-
- Article
- Export citation
The host galaxy of FRB 20171020A revisited
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 40 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 July 2023, e029
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Do variations in nasal irrigation recipes and storage effect the risk of bacterial contamination? – ERRATUM
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Laryngology & Otology / Volume 137 / Issue 8 / August 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 June 2023, pp. 942-944
- Print publication:
- August 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
P.017 Convergent and contrasting modulation of saccade and pupil responses by several neurodegenerative diseases during free viewing of video clips
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 50 / Issue s2 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 June 2023, p. S62
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
P.054 Older subjects with insomnia disorder and comorbid pain at baseline: response to Lemborexant
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 50 / Issue s2 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 June 2023, p. S73
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
P.053 Efficacy of lemborexant in adults with insomnia is supported by improvements in both objective and subjective measures
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 50 / Issue s2 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 June 2023, pp. S72-S73
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
P.051 Effect of lemborexant on cognition in patients with comorbid insomnia disorder and mild obstructive sleep apnea
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 50 / Issue s2 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 June 2023, p. S72
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
P.047 Effect of lemborexant on sleep architecture in subjects with comorbid insomnia and mild obstructive sleep apnea from a phase 3 trial
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 50 / Issue s2 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 June 2023, p. S71
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Radio wave propagation analysis with dominant path model using MIMO antenna element for vehicular base station application
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Microwave and Wireless Technologies / Volume 15 / Issue 10 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 June 2023, pp. 1789-1800
-
- Article
- Export citation
Characterization of chickpea cultivars and trait specific germplasm for grain protein content and amino acids composition and identification of potential donors for genetic improvement of its nutritional quality
-
- Journal:
- Plant Genetic Resources / Volume 20 / Issue 6 / December 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 May 2023, pp. 383-393
-
- Article
- Export citation