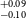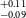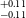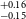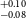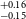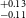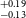25 results
VaTEST III: Validation of eight potential super-earths from TESS data
- Priyashkumar Mistry, Aniket Prasad, Mousam Maity, Kamlesh Pathak, Sarvesh Gharat, Georgios Lekkas, Surendra Bhattarai, Dhruv Kumar, Jack J. Lissauer, Joseph D. Twicken, Abderahmane Soubkiou, Francisco J. Pozuelos, Jon Jenkins, Keith Horne, Steven Giacalone, Khalid Barkaoui, Mathilde Timmermans, Cristilyn N. Watkins, Ramotholo Sefako, Karen A. Collins, David R. Ciardi, Catherine A. Clark, Boris S. Safonov, Avi Shporer, Joshua E. Schlieder, Zouhair Benkhaldoun, Chris Stockdale, Carl Ziegler, Emily A. Gilbert, Jehin Emmanuël, Felipe Murgas, Ian J. M. Crossfield, Martin Paegert, Michael B. Lund, Norio Narita, Richard P. Schwarz, Robert F. Goeke, Sergio B. Fajardo-Acosta, Steve B. Howell, Thiam-Guan Tan, Thomas Barclay, Yugo Kawai
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 41 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 April 2024, e030
-
- Article
- Export citation
-
NASA’s all-sky survey mission, the Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS), is specifically engineered to detect exoplanets that transit bright stars. Thus far, TESS has successfully identified approximately 400 transiting exoplanets, in addition to roughly 6 000 candidate exoplanets pending confirmation. In this study, we present the results of our ongoing project, the Validation of Transiting Exoplanets using Statistical Tools (VaTEST). Our dedicated effort is focused on the confirmation and characterisation of new exoplanets through the application of statistical validation tools. Through a combination of ground-based telescope data, high-resolution imaging, and the utilisation of the statistical validation tool known as TRICERATOPS, we have successfully discovered eight potential super-Earths. These planets bear the designations: TOI-238b (1.61
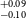 $^{+0.09} _{-0.10}$ R
$^{+0.09} _{-0.10}$ R $_\oplus$), TOI-771b (1.42
$_\oplus$), TOI-771b (1.42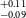 $^{+0.11} _{-0.09}$ R
$^{+0.11} _{-0.09}$ R $_\oplus$), TOI-871b (1.66
$_\oplus$), TOI-871b (1.66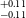 $^{+0.11} _{-0.11}$ R
$^{+0.11} _{-0.11}$ R $_\oplus$), TOI-1467b (1.83
$_\oplus$), TOI-1467b (1.83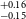 $^{+0.16} _{-0.15}$ R
$^{+0.16} _{-0.15}$ R $_\oplus$), TOI-1739b (1.69
$_\oplus$), TOI-1739b (1.69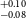 $^{+0.10} _{-0.08}$ R
$^{+0.10} _{-0.08}$ R $_\oplus$), TOI-2068b (1.82
$_\oplus$), TOI-2068b (1.82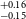 $^{+0.16} _{-0.15}$ R
$^{+0.16} _{-0.15}$ R $_\oplus$), TOI-4559b (1.42
$_\oplus$), TOI-4559b (1.42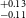 $^{+0.13} _{-0.11}$ R
$^{+0.13} _{-0.11}$ R $_\oplus$), and TOI-5799b (1.62
$_\oplus$), and TOI-5799b (1.62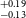 $^{+0.19} _{-0.13}$ R
$^{+0.19} _{-0.13}$ R $_\oplus$). Among all these planets, six of them fall within the region known as ‘keystone planets’, which makes them particularly interesting for study. Based on the location of TOI-771b and TOI-4559b below the radius valley we characterised them as likely super-Earths, though radial velocity mass measurements for these planets will provide more details about their characterisation. It is noteworthy that planets within the size range investigated herein are absent from our own solar system, making their study crucial for gaining insights into the evolutionary stages between Earth and Neptune.
$_\oplus$). Among all these planets, six of them fall within the region known as ‘keystone planets’, which makes them particularly interesting for study. Based on the location of TOI-771b and TOI-4559b below the radius valley we characterised them as likely super-Earths, though radial velocity mass measurements for these planets will provide more details about their characterisation. It is noteworthy that planets within the size range investigated herein are absent from our own solar system, making their study crucial for gaining insights into the evolutionary stages between Earth and Neptune.
Communicating with families of young people with hard-to-treat cancers: Healthcare professionals’ perspectives on challenges, skills, and training
- Lauren Kelada, Eden G. Robertson, Skye McKay, Brittany C. McGill, Rebecca Daly, Carolyn Mazariego, Natalie Taylor, Elijah Tyedmers, Nicole Armitage, Holly E. Evans, Claire E. Wakefield, David S. Ziegler
-
- Journal:
- Palliative & Supportive Care , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 January 2024, pp. 1-7
-
- Article
- Export citation
-
Objectives
Hard-to-treat childhood cancers are those where standard treatment options do not exist and the prognosis is poor. Healthcare professionals (HCPs) are responsible for communicating with families about prognosis and complex experimental treatments. We aimed to identify HCPs’ key challenges and skills required when communicating with families about hard-to-treat cancers and their perceptions of communication-related training.
MethodsWe interviewed Australian HCPs who had direct responsibilities in managing children/adolescents with hard-to-treat cancer within the past 24 months. Interviews were analyzed using qualitative content analysis.
ResultsWe interviewed 10 oncologists, 7 nurses, and 3 social workers. HCPs identified several challenges for communication with families including: balancing information provision while maintaining realistic hope; managing their own uncertainty; and nurses and social workers being underutilized during conversations with families, despite widespread preferences for multidisciplinary teamwork. HCPs perceived that making themselves available to families, empowering them to ask questions, and repeating information helped to establish and maintain trusting relationships with families. Half the HCPs reported receiving no formal training for communicating prognosis and treatment options with families of children with hard-to-treat cancers. Nurses, social workers, and less experienced oncologists supported the development of communication training resources, more so than more experienced oncologists.
Significance of resultsResources are needed which support HCPs to communicate with families of children with hard-to-treat cancers. Such resources may be particularly beneficial for junior oncologists and other HCPs during their training, and they should aim to prepare them for common challenges and foster greater multidisciplinary collaboration.
Antibiotic practice and stewardship in the management of neutropenic fever: A survey of US institutions
- Swarn Arya, Xiao Wang, Sonal Patel, Stephen Saw, Mary Decena, Rebecca Hirsh, David Pegues, Matthew Ziegler
-
- Journal:
- Antimicrobial Stewardship & Healthcare Epidemiology / Volume 3 / Issue S2 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 September 2023, p. s25
-
- Article
-
- You have access Access
- Open access
- Export citation
-
Background: Neutropenic fever management decisions are complex and result in prolonged duration of broad-spectrum antibiotics. Strategies for antibiotic stewardship in this context have been studied, including de-escalation of antibiotics prior to resolution of neutropenia, with unclear implementation. Here, we present the first survey study to describe real-world neutropenic fever management practices in US healthcare institutions, with particular emphasis on de-escalation strategies after initiation of broad-spectrum antibiotics. Methods: Using REDCap, we conducted a survey of US healthcare institutions through the SHEA Research Network (SRN). Questions pertained to antimicrobial prophylaxis and supportive care in the management of oncology patients and neutropenic fever management (including specific antimicrobial choices and clinical scenarios). Hematologic malignancy hospitalization (2020) and bone-marrow transplantation (2016–2020) volumes were obtained from CMS and Health Resources & Services Administration databases, respectively. Results: Overall, 23 complete responses were recorded (response rate, 35.4%). Collectively, these entities account for ~11.0% of hematologic malignancy hospitalizations and 13.3% bone marrow transplantations nationwide. Of 23 facilities, 19 had institutional guidelines for neutropenic fever management and 18 had institutional guidelines for prophylaxis, with similar definitions for neutropenic fever. Firstline treatment universally utilized antipseudomonal broad-spectrum IV antibiotics (20 of 23 use cephalosporin, 3 of 23 use penicillin agent, and no respondents use carbapenem). Fluoroquinolone prophylaxis was common for leukemia induction patients (18 of 23) but was mixed for bone-marrow transplantation (10 of 23). We observed significant heterogeneity in treatment decisions. For stable neutropenic fever patients with no clinical source of infection identified, 13 of 23 respondents continued IV antibiotics until ANC (absolute neutrophil count) recovery. The remainder had criteria for de-escalation back to prophylaxis prior to this (eg, a fever-free period). Respondents were more willing to de-escalate prior to ANC recovery in patients with identified clinical sources (14 of 23 de-escalations in patients with pneumonia) or microbiological sources (15 of 23 de-escalations in patients with bacteremia) after dedicated treatment courses. In free-text responses, several respondents described opportunities for more systemic de-escalation for antimicrobial stewardship in these scenarios. Conclusions: Our results illustrate the real-world management of neutropenic fever in US hospitals, including initiation of therapy, prophylaxis, and treatment duration. We found significant heterogeneity in de-escalation of empiric antibiotics relative to ANC recovery, highlighting a need for more robust evidence for and adoption of this practice.
Disclosures: None
Clostridioides difficile dynamic electronic order panel, an effective automated intervention to reduce inappropriate inpatient ordering
- Matthew J. Ziegler, Emilia J. Flores, Mika Epps, Kathleen Hopkins, Laurel Glaser, Nikhil K. Mull, David A. Pegues
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 44 / Issue 8 / August 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 March 2023, pp. 1294-1299
- Print publication:
- August 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access Access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
-
Background:
Ordering Clostridioides difficile diagnostics without appropriate clinical indications can result in inappropriate antibiotic prescribing and misdiagnosis of hospital onset C. difficile infection. Manual processes such as provider review of order appropriateness may detract from other infection control or antibiotic stewardship activities.
Methods:We developed an evidence-based clinical algorithm that defined appropriateness criteria for testing for C. difficile infection. We then implemented an electronic medical record–based order-entry tool that utilized discrete branches within the clinical algorithm including history of prior C. difficile test results, laxative or stool-softener administration, and documentation of unformed bowel movements. Testing guidance was then dynamically displayed with supporting patient data. We compared the rate of completed C. difficile tests after implementation of this intervention at 5 hospitals to a historic baseline in which a best-practice advisory was used.
Results:Using mixed-effects Poisson regression, we found that the intervention was associated with a reduction in the incidence rate of both C. difficile ordering (incidence rate ratio [IRR], 0.74; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.63–0.88; P = .001) and C. difficile–positive tests (IRR, 0.83; 95% CI, 0.76–0.91; P < .001). On segmented regression analysis, we identified a sustained reduction in orders over time among academic hospitals and a new reduction in orders over time among community hospitals.
Conclusions:An evidence-based dynamic order panel, integrated within the electronic medical record, was associated with a reduction in both C. difficile ordering and positive tests in comparison to a best practice advisory, although the impact varied between academic and community facilities.
Spatial and temporal effects on severe acute respiratory coronavirus virus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) contamination of the healthcare environment
- Part of
- Matthew J. Ziegler, Elizabeth Huang, Selamawit Bekele, Emily Reesey, Pam Tolomeo, Sean Loughrey, Michael Z. David, Ebbing Lautenbach, Brendan J. Kelly, for the CDC Prevention Epicenters Program
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 43 / Issue 12 / December 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 December 2021, pp. 1773-1778
- Print publication:
- December 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
-
Background:
The spatial and temporal extent of severe acute respiratory coronavirus virus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) environmental contamination has not been precisely defined. We sought to elucidate contamination of different surface types and how contamination changes over time.
Methods:We sampled surfaces longitudinally within COVID-19 patient rooms, performed quantitative RT-PCR for the detection of SARS-CoV-2 RNA, and modeled distance, time, and severity of illness on the probability of detecting SARS-CoV-2 using a mixed-effects binomial model.
Results:The probability of detecting SARS-CoV-2 RNA in a patient room did not vary with distance. However, we found that surface type predicted probability of detection, with floors and high-touch surfaces having the highest probability of detection: floors (odds ratio [OR], 67.8; 95% credible interval [CrI], 36.3–131) and high-touch elevated surfaces (OR, 7.39; 95% CrI, 4.31–13.1). Increased surface contamination was observed in room where patients required high-flow oxygen, positive airway pressure, or mechanical ventilation (OR, 1.6; 95% CrI, 1.03–2.53). The probability of elevated surface contamination decayed with prolonged hospitalization, but the probability of floor detection increased with the duration of the local pandemic wave.
Conclusions:Distance from a patient’s bed did not predict SARS-CoV-2 RNA deposition in patient rooms, but surface type, severity of illness, and time from local pandemic wave predicted surface deposition.
Severe acute respiratory coronavirus virus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) surface contamination in staff common areas and impact on healthcare worker infection: Prospective surveillance during the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic
- Part of
- Helen L. Zhang, Brendan J. Kelly, Michael Z. David, Ebbing Lautenbach, Elizabeth Huang, Selamawit Bekele, Pam Tolomeo, Emily Reesey, Sean Loughrey, David Pegues, Matthew J. Ziegler, for the CDC Prevention Epicenters Program
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 44 / Issue 1 / January 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 November 2021, pp. 110-113
- Print publication:
- January 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
-
We prospectively surveyed SARS-CoV-2 RNA contamination in staff common areas within an acute-care hospital. An increasing prevalence of surface contamination was detected over time. Adjusting for patient census or community incidence of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), the proportion of contaminated surfaces did not predict healthcare worker COVID-19 infection on study units.
Healthcare microenvironments define multidrug-resistant organism persistence
- Brendan J. Kelly, Selamawit Bekele, Sean Loughrey, Elizabeth Huang, Pam Tolomeo, Michael Z. David, Ebbing Lautenbach, Jennifer H. Han, Matthew J. Ziegler, for the CDC Prevention Epicenters Program
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 43 / Issue 9 / September 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 August 2021, pp. 1135-1141
- Print publication:
- September 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
-
Background:
Multidrug-resistant organisms (MDROs) colonizing the healthcare environment have been shown to contribute to risk for healthcare-associated infections (HAIs), with adverse effects on patient morbidity and mortality. We sought to determine how bacterial contamination and persistent MDRO colonization of the healthcare environment are related to the position of patients and wastewater sites.
Methods:We performed a prospective cohort study, enrolling 51 hospital rooms at the time of admitting a patient with an eligible MDRO in the prior 30 days. We performed systematic sampling and MDRO culture of rooms, as well as 16S rRNA sequencing to define the environmental microbiome in a subset of samples.
Results:The probability of detecting resistant gram-negative organisms, including Enterobacterales, Acinetobacter spp, and Pseudomonas spp, increased with distance from the patient. In contrast, Clostridioides difficile and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus were more likely to be detected close to the patient. Resistant Pseudomonas spp and S. aureus were enriched in these hot spots despite broad deposition of 16S rRNA gene sequences assigned to the same genera, suggesting modifiable factors that permit the persistence of these MDROs.
Conclusions:MDRO hot spots can be defined by distance from the patient and from wastewater reservoirs. Evaluating how MDROs are enriched relative to bacterial DNA deposition helps to identify healthcare micro-environments and suggests how targeted environmental cleaning or design approaches could prevent MDRO persistence and reduce infection risk.
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) research agenda for healthcare epidemiology
- Part of
- Lona Mody, Ibukunoluwa C. Akinboyo, Hilary M. Babcock, Werner E. Bischoff, Vincent Chi-Chung Cheng, Kathleen Chiotos, Kimberly C. Claeys, K. C. Coffey, Daniel J. Diekema, Curtis J. Donskey, Katherine D. Ellingson, Heather M. Gilmartin, Shruti K. Gohil, Anthony D. Harris, Sara C. Keller, Eili Y. Klein, Sarah L. Krein, Jennie H Kwon, Adam S. Lauring, Daniel J. Livorsi, Eric T. Lofgren, Katreena Merrill, Aaron M. Milstone, Elizabeth A. Monsees, Daniel J. Morgan, Luci P. Perri, Christopher D. Pfeiffer, Clare Rock, Sanjay Saint, Emily Sickbert-Bennett, Felicia Skelton, Katie J. Suda, Thomas R. Talbot, Valerie M. Vaughn, David J. Weber, Timothy L. Wiemken, Mohamed H. Yassin, Matthew J. Ziegler, Deverick J. Anderson
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 43 / Issue 2 / February 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 January 2021, pp. 156-166
- Print publication:
- February 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access Access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
-
This SHEA white paper identifies knowledge gaps and challenges in healthcare epidemiology research related to coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) with a focus on core principles of healthcare epidemiology. These gaps, revealed during the worst phases of the COVID-19 pandemic, are described in 10 sections: epidemiology, outbreak investigation, surveillance, isolation precaution practices, personal protective equipment (PPE), environmental contamination and disinfection, drug and supply shortages, antimicrobial stewardship, healthcare personnel (HCP) occupational safety, and return to work policies. Each section highlights three critical healthcare epidemiology research questions with detailed description provided in supplementary materials. This research agenda calls for translational studies from laboratory-based basic science research to well-designed, large-scale studies and health outcomes research. Research gaps and challenges related to nursing homes and social disparities are included. Collaborations across various disciplines, expertise and across diverse geographic locations will be critical.
Enhanced Environmental Cleaning to Reduce Rates of Clostridioides difficile Infection on Oncology Units
- Matthew Ziegler, David Pegues, Steven Gaynes, Ariel Desphy-Carter, Jacqueline Omorogbe, Cheryl Gilmar, Pam Tolomeo, Ebbing Lautenbach, Jennifer Han
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 41 / Issue S1 / October 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 November 2020, p. s213
- Print publication:
- October 2020
-
- Article
-
- You have access Access
- Export citation
-
Background: Clostridioides difficile infection (CDI) is a major contributor to morbidity and mortality in patients with hematologic malignancy. Due to both immunosuppression and frequent antibiotic exposures, up to one-third of inpatients receiving chemotherapy or stem-cell transplant develop CDI. Transmission of C. difficile in healthcare facilities occurs due to environmental surface contamination and hand carriage by healthcare workers from colonized and infected patients. We investigated the effectiveness of enhanced room cleaning in collaboration with environmental services (EVS) staff to prevent CDI transmission and infection.
Methods: From April 1, 2018, to September 30, 2018, a multimodal enhanced cleaning intervention was implemented on 2 oncology units at the Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania. This intervention included real-time feedback to EVS staff following ATP bioluminescence monitoring. Additionally, all rooms on the intervention units underwent UV disinfection after terminal cleaning. We performed a system-level cohort study, comparing rates of CDI on the 2 study units to historic and 2 concurrent control units. Historic and concurrent control units received UV disinfection only for rooms with prior occupants with MRSA or CDI. All units during the intervention period received education on the importance of environmental cleaning for infection prevention. Mixed-effects Poisson regression was used to adjust for system-level confounders. Results: A median of 1.34 CDI cases per 1,000 patient days (IQR, 1.20–3.62) occurred during the 12-month baseline period. There was a trend toward a reduced rate of CDI across all units during the intervention period (median, 1.19; IQR, 0.00–2.47; P = .13) compared with all units during the historical period. Using mixed-effects Poisson regression, accounting for the random effects of study units, the intervention was associated with an incidence rate ratio for C. difficile of 0.72 compared to control units (95% CI, 0.53–0.97; P = .03). Average room turnaround time (TAT) increased across all units during the study period, from 78 minutes (IQR 74–81) to 92 minutes (IQR, 85–96; P < .001). Within the intervention period, TAT was higher on intervention units (median, 94 minutes; IQR, 92–98) compared to concurrent control units (median, 85; IQR, 80–92; P = .005). Conclusions: Enhanced environmental cleaning, including UV disinfection of all patient rooms and ATP bioluminescent monitoring with real-time feedback, was associated with a reduction in the incidence of CDI.
Funding: None
Disclosures: None
Guideline implementation is effective at reducing proton pump inhibitor use in hematology-oncology units: A multidisciplinary intervention for reducing Clostridioides difficile risk
- Matthew J. Ziegler, Craig Freyer, Daniel Landsburg, David Pegues, Warren Bilker, Rebecca Hirsh, Colleen Kucharczuk, Cheryl Gilmar, Theresa Gorman, Melissa Palmer, Christina Harker, Erin Lightheart, Jennifer H. Han
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 40 / Issue 11 / November 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 August 2019, pp. 1294-1296
- Print publication:
- November 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation
-
We implemented a guideline for appropriate acid suppressant use in hematology-oncology patients. This intervention resulted in a sustained reduction in proton pump inhibitor (PPI) use without an increase in rates of gastrointestinal bleeding. Practice guidelines are effective in reducing PPI use, which is associated with risk of Clostridioides difficile infection.
31 Intracranial growing teratoma syndrome (IGTS): An international retrospective study
- George Michaiel, Douglas Strother, Nicholas Gottardo, Ute Bartels, Hallie Coltin, David D. Eisenstat, Juliette Hukin, Donna L. Johnston, Beverly Wilson, Shayna Zelcer, Jordan R. Hansford, Olivia Wells, Mohamed S. AbdelBaki, Mohammad H. Abu-Arja, Kristina A. Cole, Girish Dhall, Paul G. Fisher, Lindsey Hoffman, Sarah E.S. Leary, Emily E. Owens Pickle, Natasha P. Smiley, Amy Smith, Anna Vinitsky, Nicholas A. Vitanza, Avery Wright, Kee K. Yeo, Lionel M.L. Chow, Maria Kirby, Santosh Valvi, Magimairajan I. Vanan, Grace Wong, David Ziegler, Eric Bouffet, Lucie Lafay-Cousi
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 45 / Issue S3 / June 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 July 2018, p. S13
-
- Article
-
- You have access Access
- Export citation
-
BACKGROUND: IGTS is a rare phenomenon of paradoxical germ cell tumor (GCT) growth during or following treatment despite normalization of tumor markers. We sought to evaluate the frequency, clinical characteristics and outcome of IGTS in patients in 21 North-American and Australian institutions. METHODS: Patients with IGTS diagnosed from 2000-2017 were retrospectively evaluated. RESULTS: Out of 739 GCT diagnoses, IGTS was identified in 33 patients (4.5%). IGTS occurred in 9/191 (4.7%) mixed-malignant GCTs, 4/22 (18.2%) immature teratomas (ITs), 3/472 (0.6%) germinomas/germinomas with mature teratoma, and in 17 secreting non-biopsied tumours. Median age at GCT diagnosis was 10.9 years (range 1.8-19.4). Male gender (84%) and pineal location (88%) predominated. Of 27 patients with elevated markers, median serum AFP and Beta-HCG were 70 ng/mL (range 9.2-932) and 44 IU/L (range 4.2-493), respectively. IGTS occurred at a median time of 2 months (range 0.5-32) from diagnosis, during chemotherapy in 85%, radiation in 3%, and after treatment completion in 12%. Surgical resection was attempted in all, leading to gross total resection in 76%. Most patients (79%) resumed GCT chemotherapy/radiation after surgery. At a median follow-up of 5.3 years (range 0.3-12), all but 2 patients are alive (1 succumbed to progressive disease, 1 to malignant transformation of GCT). CONCLUSION: IGTS occurred in less than 5% of patients with GCT and most commonly after initiation of chemotherapy. IGTS was more common in patients with IT-only on biopsy than with mixed-malignant GCT. Surgical resection is a principal treatment modality. Survival outcomes for patients who developed IGTS are favourable.
Clinical Characteristics and Outcomes of Hematologic Malignancy Patients With Positive Clostridium difficile Toxin Immunoassay Versus Polymerase Chain Reaction Test Results
- Matthew Ziegler, Daniel Landsburg, David Pegues, Kevin Alby, Cheryl Gilmar, Kristen Bink, Theresa Gorman, Amy Moore, Brittaney Bonhomme, Jacqueline Omorogbe, Dana Tango, Pam Tolomeo, Jennifer H. Han
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 39 / Issue 7 / July 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 April 2018, pp. 863-866
- Print publication:
- July 2018
-
- Article
- Export citation
-
In a cohort of inpatients with hematologic malignancy and positive enzyme immunoassay (EIA) or polymerase chain reaction (PCR) Clostridium difficile tests, we found that clinical characteristics and outcomes were similar between these groups. The method of testing is unlikely to predict infection in this population, and PCR-positive results should be treated with concern.
Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol 2018;863–866
Diabetes prevalence is associated with serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D and 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D in US middle-aged Caucasian men and women: a cross-sectional analysis within the Prostate, Lung, Colorectal and Ovarian Cancer Screening Trial
- Kaye E. Brock, Wen-Yi Huang, David R. Fraser, Liang Ke, Marilyn Tseng, Rebecca S. Mason, Rachael Z. Stolzenberg-Solomon, D. Michal Freedman, Jiyoung Ahn, Ulrike Peters, Catherine McCarty, Bruce W. Hollis, Regina G. Ziegler, Mark P. Purdue, Barry I. Graubard
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 106 / Issue 3 / 14 August 2011
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 May 2011, pp. 339-344
- Print publication:
- 14 August 2011
-
- Article
-
- You have access Access
- HTML
- Export citation
-
Hypovitaminosis D may be associated with diabetes, hypertension and CHD. However, because studies examining the associations of all three chronic conditions with circulating 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25(OH)D) and 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D (1,25(OH)2D) are limited, we examined these associations in the US Prostate, Lung, Colorectal and Ovarian (PLCO) Cancer Screening Trial (n 2465). Caucasian PLCO participants selected as controls in previous nested case–control studies of 25(OH)D and 1,25(OH)2D were included in this analysis. Diabetes, CHD and hypertension prevalence, risk factors for these conditions and intake of vitamin D and Ca were collected from a baseline questionnaire. Results indicated that serum levels of 25(OH)D were low ( < 50 nmol/l) in 29 % and very low ( < 37 nmol/l) in 11 % of subjects. The prevalence of diabetes, hypertension and CHD was 7, 30 and 10 %, respectively. After adjustment for confounding by sex, geographical location, educational level, smoking history, BMI, physical activity, total dietary energy and vitamin D and Ca intake, only diabetes was significantly associated with lower 25(OH)D and 1,25(OH)2D levels. Caucasians who had 25(OH)D ≥ 80 nmol/l were half as likely to have diabetes (OR 0·5 (95 % CI 0·3, 0·9)) compared with those who had 25(OH)D < 37 nmol/l. Those in the highest quartile of 1,25(OH)2D ( ≥ 103 pmol/l) were less than half as likely to have diabetes (OR 0·3 (95 % CI 0·1, 0·7)) than those in the lowest quartile ( < 72 pmol/l). In conclusion, the independent associations of 25(OH)D and 1,25(OH)2D with diabetes prevalence in a large population are new findings, and thus warrant confirmation in larger, prospective studies.
Entrapment of DFPase in titania coatings from a biomimetically derived method
- Shaun Filocamo, Robert Stote, David Ziegler, Heidi Gibson
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 26 / Issue 8 / 28 April 2011
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 March 2011, pp. 1042-1051
- Print publication:
- 28 April 2011
-
- Article
- Export citation
-
Silicon oxide has been widely used to encapsulate biomolecules to preserve their activity in less than ideal environments. However, there are other inorganic oxides with inherent properties that would be advantageous in creating a multifunctional material. Titanium oxide exhibits properties that have applications in areas such as electronics, energy conversion, and decontamination. Herein is reported the formation of titania coatings fabricated on polymer beads using a biomimetic approach and characterized with scanning electron microscopy and energy dispersive x-ray spectroscopy. The approach involves the use of functionalized polymer beads, which initiate oxide formation from a water-soluble titanium complex. The method was used to encapsulate the enzyme diisopropylfluorophosphatase, in situ, within the oxide matrix under buffered aqueous conditions while retaining its enzymatic activity against diisopropylfluorophosphate. In addition, the biomimetically produced titania was shown to exhibit UV-assisted degradation activity against an ethidium bromide dye, upon liberation from the coating template.
Contributors
-
- By Rose Teteki Abbey, K. C. Abraham, David Tuesday Adamo, LeRoy H. Aden, Efrain Agosto, Victor Aguilan, Gillian T. W. Ahlgren, Charanjit Kaur AjitSingh, Dorothy B E A Akoto, Giuseppe Alberigo, Daniel E. Albrecht, Ruth Albrecht, Daniel O. Aleshire, Urs Altermatt, Anand Amaladass, Michael Amaladoss, James N. Amanze, Lesley G. Anderson, Thomas C. Anderson, Victor Anderson, Hope S. Antone, María Pilar Aquino, Paula Arai, Victorio Araya Guillén, S. Wesley Ariarajah, Ellen T. Armour, Brett Gregory Armstrong, Atsuhiro Asano, Naim Stifan Ateek, Mahmoud Ayoub, John Alembillah Azumah, Mercedes L. García Bachmann, Irena Backus, J. Wayne Baker, Mieke Bal, Lewis V. Baldwin, William Barbieri, António Barbosa da Silva, David Basinger, Bolaji Olukemi Bateye, Oswald Bayer, Daniel H. Bays, Rosalie Beck, Nancy Elizabeth Bedford, Guy-Thomas Bedouelle, Chorbishop Seely Beggiani, Wolfgang Behringer, Christopher M. Bellitto, Byard Bennett, Harold V. Bennett, Teresa Berger, Miguel A. Bernad, Henley Bernard, Alan E. Bernstein, Jon L. Berquist, Johannes Beutler, Ana María Bidegain, Matthew P. Binkewicz, Jennifer Bird, Joseph Blenkinsopp, Dmytro Bondarenko, Paulo Bonfatti, Riet en Pim Bons-Storm, Jessica A. Boon, Marcus J. Borg, Mark Bosco, Peter C. Bouteneff, François Bovon, William D. Bowman, Paul S. Boyer, David Brakke, Richard E. Brantley, Marcus Braybrooke, Ian Breward, Ênio José da Costa Brito, Jewel Spears Brooker, Johannes Brosseder, Nicholas Canfield Read Brown, Robert F. Brown, Pamela K. Brubaker, Walter Brueggemann, Bishop Colin O. Buchanan, Stanley M. Burgess, Amy Nelson Burnett, J. Patout Burns, David B. Burrell, David Buttrick, James P. Byrd, Lavinia Byrne, Gerado Caetano, Marcos Caldas, Alkiviadis Calivas, William J. Callahan, Salvatore Calomino, Euan K. Cameron, William S. Campbell, Marcelo Ayres Camurça, Daniel F. Caner, Paul E. Capetz, Carlos F. Cardoza-Orlandi, Patrick W. Carey, Barbara Carvill, Hal Cauthron, Subhadra Mitra Channa, Mark D. Chapman, James H. Charlesworth, Kenneth R. Chase, Chen Zemin, Luciano Chianeque, Philip Chia Phin Yin, Francisca H. Chimhanda, Daniel Chiquete, John T. Chirban, Soobin Choi, Robert Choquette, Mita Choudhury, Gerald Christianson, John Chryssavgis, Sejong Chun, Esther Chung-Kim, Charles M. A. Clark, Elizabeth A. Clark, Sathianathan Clarke, Fred Cloud, John B. Cobb, W. Owen Cole, John A Coleman, John J. Collins, Sylvia Collins-Mayo, Paul K. Conkin, Beth A. Conklin, Sean Connolly, Demetrios J. Constantelos, Michael A. Conway, Paula M. Cooey, Austin Cooper, Michael L. Cooper-White, Pamela Cooper-White, L. William Countryman, Sérgio Coutinho, Pamela Couture, Shannon Craigo-Snell, James L. Crenshaw, David Crowner, Humberto Horacio Cucchetti, Lawrence S. Cunningham, Elizabeth Mason Currier, Emmanuel Cutrone, Mary L. Daniel, David D. Daniels, Robert Darden, Rolf Darge, Isaiah Dau, Jeffry C. Davis, Jane Dawson, Valentin Dedji, John W. de Gruchy, Paul DeHart, Wendy J. Deichmann Edwards, Miguel A. De La Torre, George E. Demacopoulos, Thomas de Mayo, Leah DeVun, Beatriz de Vasconcellos Dias, Dennis C. Dickerson, John M. Dillon, Luis Miguel Donatello, Igor Dorfmann-Lazarev, Susanna Drake, Jonathan A. Draper, N. Dreher Martin, Otto Dreydoppel, Angelyn Dries, A. J. Droge, Francis X. D'Sa, Marilyn Dunn, Nicole Wilkinson Duran, Rifaat Ebied, Mark J. Edwards, William H. Edwards, Leonard H. Ehrlich, Nancy L. Eiesland, Martin Elbel, J. Harold Ellens, Stephen Ellingson, Marvin M. Ellison, Robert Ellsberg, Jean Bethke Elshtain, Eldon Jay Epp, Peter C. Erb, Tassilo Erhardt, Maria Erling, Noel Leo Erskine, Gillian R. Evans, Virginia Fabella, Michael A. Fahey, Edward Farley, Margaret A. Farley, Wendy Farley, Robert Fastiggi, Seena Fazel, Duncan S. Ferguson, Helwar Figueroa, Paul Corby Finney, Kyriaki Karidoyanes FitzGerald, Thomas E. FitzGerald, John R. Fitzmier, Marie Therese Flanagan, Sabina Flanagan, Claude Flipo, Ronald B. Flowers, Carole Fontaine, David Ford, Mary Ford, Stephanie A. Ford, Jim Forest, William Franke, Robert M. Franklin, Ruth Franzén, Edward H. Friedman, Samuel Frouisou, Lorelei F. Fuchs, Jojo M. Fung, Inger Furseth, Richard R. Gaillardetz, Brandon Gallaher, China Galland, Mark Galli, Ismael García, Tharscisse Gatwa, Jean-Marie Gaudeul, Luis María Gavilanes del Castillo, Pavel L. Gavrilyuk, Volney P. Gay, Metropolitan Athanasios Geevargis, Kondothra M. George, Mary Gerhart, Simon Gikandi, Maurice Gilbert, Michael J. Gillgannon, Verónica Giménez Beliveau, Terryl Givens, Beth Glazier-McDonald, Philip Gleason, Menghun Goh, Brian Golding, Bishop Hilario M. Gomez, Michelle A. Gonzalez, Donald K. Gorrell, Roy Gottfried, Tamara Grdzelidze, Joel B. Green, Niels Henrik Gregersen, Cristina Grenholm, Herbert Griffiths, Eric W. Gritsch, Erich S. Gruen, Christoffer H. Grundmann, Paul H. Gundani, Jon P. Gunnemann, Petre Guran, Vidar L. Haanes, Jeremiah M. Hackett, Getatchew Haile, Douglas John Hall, Nicholas Hammond, Daphne Hampson, Jehu J. Hanciles, Barry Hankins, Jennifer Haraguchi, Stanley S. Harakas, Anthony John Harding, Conrad L. Harkins, J. William Harmless, Marjory Harper, Amir Harrak, Joel F. Harrington, Mark W. Harris, Susan Ashbrook Harvey, Van A. Harvey, R. Chris Hassel, Jione Havea, Daniel Hawk, Diana L. Hayes, Leslie Hayes, Priscilla Hayner, S. Mark Heim, Simo Heininen, Richard P. Heitzenrater, Eila Helander, David Hempton, Scott H. Hendrix, Jan-Olav Henriksen, Gina Hens-Piazza, Carter Heyward, Nicholas J. Higham, David Hilliard, Norman A. Hjelm, Peter C. Hodgson, Arthur Holder, M. Jan Holton, Dwight N. Hopkins, Ronnie Po-chia Hsia, Po-Ho Huang, James Hudnut-Beumler, Jennifer S. Hughes, Leonard M. Hummel, Mary E. Hunt, Laennec Hurbon, Mark Hutchinson, Susan E. Hylen, Mary Beth Ingham, H. Larry Ingle, Dale T. Irvin, Jon Isaak, Paul John Isaak, Ada María Isasi-Díaz, Hans Raun Iversen, Margaret C. Jacob, Arthur James, Maria Jansdotter-Samuelsson, David Jasper, Werner G. Jeanrond, Renée Jeffery, David Lyle Jeffrey, Theodore W. Jennings, David H. Jensen, Robin Margaret Jensen, David Jobling, Dale A. Johnson, Elizabeth A. Johnson, Maxwell E. Johnson, Sarah Johnson, Mark D. Johnston, F. Stanley Jones, James William Jones, John R. Jones, Alissa Jones Nelson, Inge Jonsson, Jan Joosten, Elizabeth Judd, Mulambya Peggy Kabonde, Robert Kaggwa, Sylvester Kahakwa, Isaac Kalimi, Ogbu U. Kalu, Eunice Kamaara, Wayne C. Kannaday, Musimbi Kanyoro, Veli-Matti Kärkkäinen, Frank Kaufmann, Léon Nguapitshi Kayongo, Richard Kearney, Alice A. Keefe, Ralph Keen, Catherine Keller, Anthony J. Kelly, Karen Kennelly, Kathi Lynn Kern, Fergus Kerr, Edward Kessler, George Kilcourse, Heup Young Kim, Kim Sung-Hae, Kim Yong-Bock, Kim Yung Suk, Richard King, Thomas M. King, Robert M. Kingdon, Ross Kinsler, Hans G. Kippenberg, Cheryl A. Kirk-Duggan, Clifton Kirkpatrick, Leonid Kishkovsky, Nadieszda Kizenko, Jeffrey Klaiber, Hans-Josef Klauck, Sidney Knight, Samuel Kobia, Robert Kolb, Karla Ann Koll, Heikki Kotila, Donald Kraybill, Philip D. W. Krey, Yves Krumenacker, Jeffrey Kah-Jin Kuan, Simanga R. Kumalo, Peter Kuzmic, Simon Shui-Man Kwan, Kwok Pui-lan, André LaCocque, Stephen E. Lahey, John Tsz Pang Lai, Emiel Lamberts, Armando Lampe, Craig Lampe, Beverly J. Lanzetta, Eve LaPlante, Lizette Larson-Miller, Ariel Bybee Laughton, Leonard Lawlor, Bentley Layton, Robin A. Leaver, Karen Lebacqz, Archie Chi Chung Lee, Marilyn J. Legge, Hervé LeGrand, D. L. LeMahieu, Raymond Lemieux, Bill J. Leonard, Ellen M. Leonard, Outi Leppä, Jean Lesaulnier, Nantawan Boonprasat Lewis, Henrietta Leyser, Alexei Lidov, Bernard Lightman, Paul Chang-Ha Lim, Carter Lindberg, Mark R. Lindsay, James R. Linville, James C. Livingston, Ann Loades, David Loades, Jean-Claude Loba-Mkole, Lo Lung Kwong, Wati Longchar, Eleazar López, David W. Lotz, Andrew Louth, Robin W. Lovin, William Luis, Frank D. Macchia, Diarmaid N. J. MacCulloch, Kirk R. MacGregor, Marjory A. MacLean, Donald MacLeod, Tomas S. Maddela, Inge Mager, Laurenti Magesa, David G. Maillu, Fortunato Mallimaci, Philip Mamalakis, Kä Mana, Ukachukwu Chris Manus, Herbert Robinson Marbury, Reuel Norman Marigza, Jacqueline Mariña, Antti Marjanen, Luiz C. L. Marques, Madipoane Masenya (ngwan'a Mphahlele), Caleb J. D. Maskell, Steve Mason, Thomas Massaro, Fernando Matamoros Ponce, András Máté-Tóth, Odair Pedroso Mateus, Dinis Matsolo, Fumitaka Matsuoka, John D'Arcy May, Yelena Mazour-Matusevich, Theodore Mbazumutima, John S. McClure, Christian McConnell, Lee Martin McDonald, Gary B. McGee, Thomas McGowan, Alister E. McGrath, Richard J. McGregor, John A. McGuckin, Maud Burnett McInerney, Elsie Anne McKee, Mary B. McKinley, James F. McMillan, Ernan McMullin, Kathleen E. McVey, M. Douglas Meeks, Monica Jyotsna Melanchthon, Ilie Melniciuc-Puica, Everett Mendoza, Raymond A. Mentzer, William W. Menzies, Ina Merdjanova, Franziska Metzger, Constant J. Mews, Marvin Meyer, Carol Meyers, Vasile Mihoc, Gunner Bjerg Mikkelsen, Maria Inêz de Castro Millen, Clyde Lee Miller, Bonnie J. Miller-McLemore, Alexander Mirkovic, Paul Misner, Nozomu Miyahira, R. W. L. Moberly, Gerald Moede, Aloo Osotsi Mojola, Sunanda Mongia, Rebeca Montemayor, James Moore, Roger E. Moore, Craig E. Morrison O.Carm, Jeffry H. Morrison, Keith Morrison, Wilson J. Moses, Tefetso Henry Mothibe, Mokgethi Motlhabi, Fulata Moyo, Henry Mugabe, Jesse Ndwiga Kanyua Mugambi, Peggy Mulambya-Kabonde, Robert Bruce Mullin, Pamela Mullins Reaves, Saskia Murk Jansen, Heleen L. Murre-Van den Berg, Augustine Musopole, Isaac M. T. Mwase, Philomena Mwaura, Cecilia Nahnfeldt, Anne Nasimiyu Wasike, Carmiña Navia Velasco, Thulani Ndlazi, Alexander Negrov, James B. Nelson, David G. Newcombe, Carol Newsom, Helen J. Nicholson, George W. E. Nickelsburg, Tatyana Nikolskaya, Damayanthi M. A. Niles, Bertil Nilsson, Nyambura Njoroge, Fidelis Nkomazana, Mary Beth Norton, Christian Nottmeier, Sonene Nyawo, Anthère Nzabatsinda, Edward T. Oakes, Gerald O'Collins, Daniel O'Connell, David W. Odell-Scott, Mercy Amba Oduyoye, Kathleen O'Grady, Oyeronke Olajubu, Thomas O'Loughlin, Dennis T. Olson, J. Steven O'Malley, Cephas N. Omenyo, Muriel Orevillo-Montenegro, César Augusto Ornellas Ramos, Agbonkhianmeghe E. Orobator, Kenan B. Osborne, Carolyn Osiek, Javier Otaola Montagne, Douglas F. Ottati, Anna May Say Pa, Irina Paert, Jerry G. Pankhurst, Aristotle Papanikolaou, Samuele F. Pardini, Stefano Parenti, Peter Paris, Sung Bae Park, Cristián G. Parker, Raquel Pastor, Joseph Pathrapankal, Daniel Patte, W. Brown Patterson, Clive Pearson, Keith F. Pecklers, Nancy Cardoso Pereira, David Horace Perkins, Pheme Perkins, Edward N. Peters, Rebecca Todd Peters, Bishop Yeznik Petrossian, Raymond Pfister, Peter C. Phan, Isabel Apawo Phiri, William S. F. Pickering, Derrick G. Pitard, William Elvis Plata, Zlatko Plese, John Plummer, James Newton Poling, Ronald Popivchak, Andrew Porter, Ute Possekel, James M. Powell, Enos Das Pradhan, Devadasan Premnath, Jaime Adrían Prieto Valladares, Anne Primavesi, Randall Prior, María Alicia Puente Lutteroth, Eduardo Guzmão Quadros, Albert Rabil, Laurent William Ramambason, Apolonio M. Ranche, Vololona Randriamanantena Andriamitandrina, Lawrence R. Rast, Paul L. Redditt, Adele Reinhartz, Rolf Rendtorff, Pål Repstad, James N. Rhodes, John K. Riches, Joerg Rieger, Sharon H. Ringe, Sandra Rios, Tyler Roberts, David M. Robinson, James M. Robinson, Joanne Maguire Robinson, Richard A. H. Robinson, Roy R. Robson, Jack B. Rogers, Maria Roginska, Sidney Rooy, Rev. Garnett Roper, Maria José Fontelas Rosado-Nunes, Andrew C. Ross, Stefan Rossbach, François Rossier, John D. Roth, John K. Roth, Phillip Rothwell, Richard E. Rubenstein, Rosemary Radford Ruether, Markku Ruotsila, John E. Rybolt, Risto Saarinen, John Saillant, Juan Sanchez, Wagner Lopes Sanchez, Hugo N. Santos, Gerhard Sauter, Gloria L. Schaab, Sandra M. Schneiders, Quentin J. Schultze, Fernando F. Segovia, Turid Karlsen Seim, Carsten Selch Jensen, Alan P. F. Sell, Frank C. Senn, Kent Davis Sensenig, Damían Setton, Bal Krishna Sharma, Carolyn J. Sharp, Thomas Sheehan, N. Gerald Shenk, Christian Sheppard, Charles Sherlock, Tabona Shoko, Walter B. Shurden, Marguerite Shuster, B. Mark Sietsema, Batara Sihombing, Neil Silberman, Clodomiro Siller, Samuel Silva-Gotay, Heikki Silvet, John K. Simmons, Hagith Sivan, James C. Skedros, Abraham Smith, Ashley A. Smith, Ted A. Smith, Daud Soesilo, Pia Søltoft, Choan-Seng (C. S.) Song, Kathryn Spink, Bryan Spinks, Eric O. Springsted, Nicolas Standaert, Brian Stanley, Glen H. Stassen, Karel Steenbrink, Stephen J. Stein, Andrea Sterk, Gregory E. Sterling, Columba Stewart, Jacques Stewart, Robert B. Stewart, Cynthia Stokes Brown, Ken Stone, Anne Stott, Elizabeth Stuart, Monya Stubbs, Marjorie Hewitt Suchocki, David Kwang-sun Suh, Scott W. Sunquist, Keith Suter, Douglas Sweeney, Charles H. Talbert, Shawqi N. Talia, Elsa Tamez, Joseph B. Tamney, Jonathan Y. Tan, Yak-Hwee Tan, Kathryn Tanner, Feiya Tao, Elizabeth S. Tapia, Aquiline Tarimo, Claire Taylor, Mark Lewis Taylor, Bishop Abba Samuel Wolde Tekestebirhan, Eugene TeSelle, M. Thomas Thangaraj, David R. Thomas, Andrew Thornley, Scott Thumma, Marcelo Timotheo da Costa, George E. “Tink” Tinker, Ola Tjørhom, Karen Jo Torjesen, Iain R. Torrance, Fernando Torres-Londoño, Archbishop Demetrios [Trakatellis], Marit Trelstad, Christine Trevett, Phyllis Trible, Johannes Tromp, Paul Turner, Robert G. Tuttle, Archbishop Desmond Tutu, Peter Tyler, Anders Tyrberg, Justin Ukpong, Javier Ulloa, Camillus Umoh, Kristi Upson-Saia, Martina Urban, Monica Uribe, Elochukwu Eugene Uzukwu, Richard Vaggione, Gabriel Vahanian, Paul Valliere, T. J. Van Bavel, Steven Vanderputten, Peter Van der Veer, Huub Van de Sandt, Louis Van Tongeren, Luke A. Veronis, Noel Villalba, Ramón Vinke, Tim Vivian, David Voas, Elena Volkova, Katharina von Kellenbach, Elina Vuola, Timothy Wadkins, Elaine M. Wainwright, Randi Jones Walker, Dewey D. Wallace, Jerry Walls, Michael J. Walsh, Philip Walters, Janet Walton, Jonathan L. Walton, Wang Xiaochao, Patricia A. Ward, David Harrington Watt, Herold D. Weiss, Laurence L. Welborn, Sharon D. Welch, Timothy Wengert, Traci C. West, Merold Westphal, David Wetherell, Barbara Wheeler, Carolinne White, Jean-Paul Wiest, Frans Wijsen, Terry L. Wilder, Felix Wilfred, Rebecca Wilkin, Daniel H. Williams, D. Newell Williams, Michael A. Williams, Vincent L. Wimbush, Gabriele Winkler, Anders Winroth, Lauri Emílio Wirth, James A. Wiseman, Ebba Witt-Brattström, Teofil Wojciechowski, John Wolffe, Kenman L. Wong, Wong Wai Ching, Linda Woodhead, Wendy M. Wright, Rose Wu, Keith E. Yandell, Gale A. Yee, Viktor Yelensky, Yeo Khiok-Khng, Gustav K. K. Yeung, Angela Yiu, Amos Yong, Yong Ting Jin, You Bin, Youhanna Nessim Youssef, Eliana Yunes, Robert Michael Zaller, Valarie H. Ziegler, Barbara Brown Zikmund, Joyce Ann Zimmerman, Aurora Zlotnik, Zhuo Xinping
- Edited by Daniel Patte, Vanderbilt University, Tennessee
-
- Book:
- The Cambridge Dictionary of Christianity
- Published online:
- 05 August 2012
- Print publication:
- 20 September 2010, pp xi-xliv
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Optical Coating Properties for Enhanced Blown-Sand Abrasion Resistance
- Christopher Drew, Suzanne Bosselman, David Ziegler
-
- Journal:
- MRS Online Proceedings Library Archive / Volume 977 / 2006
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 February 2011, 977-FF04-25
- Print publication:
- 2006
-
- Article
- Export citation
-
Lenses and other transparent optical materials suffer rapid damage when subjected to blowing abrasive particulates. The time-scale of these impact event falls between typical scratch tests (less than 1m/s) and ballistic tests (100s of m/s) and has not been studied in depth to date. Polymeric lens materials like polycarbonate are usually treated with a scratch-resistant coating, which is commonly silica-based. The coating provides some protection, yet is not sufficient at resisting abrasion from blown sand in most commercial products. We demonstrate that silicone elastomeric coatings are superior to polycarbonate and silica glass at resisting damage by blown sand particles. Sand abrasion tests were conducted using a custom-built test apparatus that exposes the sample to 400 micron diameter quartz silica moving at 16.5 m/s (approx. 38 mph). Scanning electron microscopy revealed the presence of small cracks and pits in polycarbonate, coated polycarbonate, and silica glass after sand exposure. No such damage was observed in the silicone-coated samples after an identical exposure.
We speculate that the elastic tensile strain at the surface is an important predictor of the material response at the time-scale of the impact. A simple mathematical model was developed using a momentum balance pre- and post-impact, and was used to approximate the maximum deformation and impact time-scale. A semispherical interaction volume was used in the model with a radius of 1.5x the particle diameter, determined through profilometry experiments. The material’s resistance to deformation was measured experimentally through a static mechanical test using a spherical indenter to represent the particle. Tensile tests were performed on both materials to identify the maximum elastic strain.Additionally, dynamic mechanical tests were performed to confirm that the mechanical behavior at long time-scales was valid at shorter time-scales of the impacts. DMA curves were shifted using the WLF equation. Profilometry and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) imaging were used to confirm the presence or absence of blown-sand induced damage.
Impact of social management on reproductive, adrenal and behavioural activity in the cheetah (Acinonyx jubatus)
- Nadja C. Wielebnowski, Karen Ziegler, David E. Wildt, John Lukas, Janine L. Brown
-
- Journal:
- Animal Conservation forum / Volume 5 / Issue 4 / November 2002
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 November 2002, pp. 291-301
- Print publication:
- November 2002
-
- Article
- Export citation
-
Cheetahs (Acinonyx jubatus) held ex situ can provide an important resource for obtaining new biological information that usually cannot be gleaned from free-living individuals. However, consistent captive propagation of the cheetah, a prerequisite for establishing a self-sustaining population, has not been accomplished so far. This study examined the effect of a husbandry regimen commonly used in ex situ facilities on female cheetahs. Although generally solitary in the wild, zoos frequently house cheetahs in pairs or groups. Using non-invasive hormone monitoring and quantitative behavioural observations, we studied the impact of such enforced social conditions on behaviour and ovarian/adrenal activity. Eight female cheetahs were evaluated for two consecutive 6-month periods, first while maintained in pairs and then as individuals. Subsequently four females were regrouped into two new pairs and monitored for another 6 months. Females in five of six pairings demonstrated prolonged anoestrus and displayed agonistic behaviours. After pair separation all females rapidly resumed oestrous cyclicity. Females in the sixth pair continued cycling throughout the year while consistently displaying affiliative grooming and no agonistic behaviours. Faecal corticoid patterns varied significantly among individuals, but appeared unrelated to behavioural or ovarian hormone patterns. Thus, data appear to indicate that same-sex pair-maintenance of behaviourally incompatible female cheetahs may lead to suppressed ovarian cyclicity. This suppression appears linked to agonistic behaviours but not to any particular adrenal hormone excretion pattern. Results clearly demonstrate the value of applying knowledge about in situ social behaviour to ex situ management practices. Conversely, however, non-invasive hormone monitoring conducted ex situ may help us to identify physiological phenomena of potential relevance for future in situ studies.
Photoelectric Response from Nanofibous Membranes
- Kris J. Senecal, David P. Ziegler, Jinan He, Ravi Mosurkal, Heidi Schreuder-Gibson, Lynne A. Samuelson
-
- Journal:
- MRS Online Proceedings Library Archive / Volume 708 / 2001
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 March 2011, BB9.5
- Print publication:
- 2001
-
- Article
- Export citation
-
Electrospinning has been used to prepare nanofibrous composite membranes of semi-conducting particles (TiO2) and photovoltaic dyes. Electrospinning is a relatively simple technique where electrical forces are used on polymeric solutions to produce nanoscale fibers. The resulting nanofibrous membranes have surface areas that are roughly one to two orders of magnitude higher than conventional thin films. It is believed that this higher surface will allow for more efficient light harvesting in photovoltaic devices. Our research has focused on the fabrication of organic/inorganic hybrid solar cells featuring dye sensitized nanocrystalline semiconductor particles using electrospinning. Phthalocyanine and N3 (cisdi(thiocyanato)bis(2,2'-bipyridyl-4,4'-dicarboxylate) ruthenium(II)) photoactive dyes were electrospun with semi-conductive TiO2 nanoparticles into a matrix polymer, polyacrylonitrile (PAN). Electron microscopy and elemental analysis of the electrospun membranes shows that each component is present and uniformly dispersed in the nanofibrous membranes. In general, the dye membranes electrospun with the TiO2 nanoparticles exhibited a greater photoelectric response than the membranes with dye only. The N3 dye membranes however showed the greatest photoresponse in comparison to the phthalocyanine dyes, with or without the TiO2 nanoparticles. Photoelectric responses on the order of 30 μA and 280 mV were achieved with dye-sensitized membranes and are believed to be the first demonstration of a photoelectric response from an electrospun nanofibrous membrane.
Template-Mediated Biomineralization of Hemozoin
- David W. Wright, James Ziegler
-
- Journal:
- MRS Online Proceedings Library Archive / Volume 599 / 1999
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 February 2011, 293
- Print publication:
- 1999
-
- Article
- Export citation
-
A critical target for the development of new antimalarial treatments is the detoxification pathway of free heme released during the catabolism of host hemoglobin in the digestive vacuole of the malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum. We have synthesized and examined two peptide dendrimers (BNT I and II) based on the tandem repeat motif of HRP II from P. falciparum for their abilities to both bind heme substrates and to form the critical detoxification polymer hemozoin. Each substrate was capable of binding significant amounts of the natural substrate Fe(III)PPIX along with other substrates such as Zn(II)PPIX and the metal free PPIX. Further, it was shown that the dendrimeric BNT I and II were capable of supporting the aggregation of hemozoin and that this process could be inhibited by the known antimalarial drug, chloroquine.
World Politics and the Evolution of War. By John J. Weltman. Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press, 1995. 263p. $14.95.
- David W. Ziegler
-
- Journal:
- American Political Science Review / Volume 89 / Issue 3 / September 1995
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 September 2013, pp. 813-814
- Print publication:
- September 1995
-
- Article
- Export citation