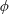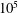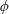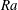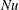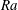93 results
Microplastics alter soil carbon cycling: Effects on carbon storage, CO2 and CH4 emission and microbial community
-
- Journal:
- Cambridge Prisms: Plastics / Volume 2 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 March 2024, e5
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Preparation of Organo-Montmorillonites and the Relationship Between Microstructure and Swellability
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 65 / Issue 6 / December 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 417-430
-
- Article
- Export citation
Tuning the Acidity of Montmorillonite by H3PO4-Activation and Supporting WO3 for Catalytic Dehydration of Glycerol to Acrolein
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 70 / Issue 3 / June 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 460-479
-
- Article
- Export citation
Mitigation of stimulated Raman scattering in a high-power fiber master oscillator power amplifier laser based on a dual-structure fiber grating
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 11 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 September 2023, e92
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
RNA N6-methyladenosine of DHAPAT and PAP involves in regulation of diapause of Bombyx mori via the lipid metabolism pathway
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of Entomological Research / Volume 113 / Issue 5 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 August 2023, pp. 665-675
-
- Article
- Export citation
Accelerated protons with energies up to 70 MeV based on the optimized SG-II Peta-watt laser facility
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 11 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 June 2023, e63
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Utilizing phase-shifted long-period fiber grating to suppress spectral broadening of a high-power fiber MOPA laser system
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 9 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 July 2021, e39
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Claire Kramsch in conversation with Zhu Hua
-
- Journal:
- Language Teaching / Volume 55 / Issue 2 / April 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 March 2021, pp. 211-216
- Print publication:
- April 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
X-ray powder diffraction data for nicotine 3,5-dihydroxybenzoate dihydrate, C10H15N2⋅C7H5O4⋅2H2O
-
- Journal:
- Powder Diffraction / Volume 36 / Issue 1 / March 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 January 2021, pp. 25-28
-
- Article
- Export citation
FNDC5 polymorphism influences the association between sarcopenia and liver fibrosis in adults with biopsy-proven non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 126 / Issue 6 / 28 September 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 November 2020, pp. 813-824
- Print publication:
- 28 September 2021
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
CURB-65 may serve as a useful prognostic marker in COVID-19 patients within Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 148 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 October 2020, e241
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Retrospective analysis of clinical features in 134 coronavirus disease 2019 cases
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 148 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 September 2020, e199
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Forecasting the incidence of acute haemorrhagic conjunctivitis in Chongqing: a time series analysis
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 148 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 August 2020, e193
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
From Rayleigh–Bénard convection to porous-media convection: how porosity affects heat transfer and flow structure
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 895 / 25 July 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 May 2020, A18
-
- Article
- Export citation
Effects of dairy products, calcium and vitamin D on ovarian cancer risk: a meta-analysis of twenty-nine epidemiological studies
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 124 / Issue 10 / 28 November 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 March 2020, pp. 1001-1012
- Print publication:
- 28 November 2020
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Improved Corrosion Resistance and Increased Hardness of Copper Substrates from Cu-Ni/Ni-P Composite Coatings
-
- Journal:
- MRS Advances / Volume 5 / Issue 40-41 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 April 2020, pp. 2129-2137
- Print publication:
- 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation
Synaptotagmin 1 regulates cortical granule exocytosis during mouse oocyte activation
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Serum folate concentrations at diagnosis are associated with hepatocellular carcinoma survival in the Guangdong Liver Cancer Cohort study
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 121 / Issue 12 / 28 June 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 June 2019, pp. 1376-1388
- Print publication:
- 28 June 2019
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Fabrication of kW-level chirped and tilted fiber Bragg gratings and filtering of stimulated Raman scattering in high-power CW oscillators
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 7 / 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 May 2019, e31
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation