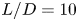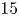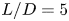613 results
Global, regional and national burdens of depression in adolescents and young adults aged 10–24 years, from 1990 to 2019: findings from the 2019 Global Burden of Disease study
-
- Journal:
- The British Journal of Psychiatry , FirstView
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 April 2024, pp. 1-10
-
- Article
- Export citation
Efficacy of catheter ablation in ganglionated plexus for malignant vasovagal syncope children
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 April 2024, pp. 1-6
-
- Article
- Export citation
Structure-function coupling and hierarchy-specific antidepressant response in major depressive disorder
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 April 2024, pp. 1-10
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Vortex dynamics and boundary layer transition in flow around a rectangular cylinder with different aspect ratios at medium Reynolds number
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 982 / 10 March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 February 2024, A5
-
- Article
- Export citation
Milk proteomic analysis reveals differentially expressed proteins in high-yielding and low-yielding Guanzhong dairy goats at peak lactation
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Dairy Research , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 February 2024, pp. 1-7
-
- Article
- Export citation
Demography as a confounding factor to explain highly diverged loci between cultivated and wild rice
-
- Journal:
- Plant Genetic Resources / Volume 22 / Issue 1 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 February 2024, pp. 45-49
-
- Article
- Export citation
Quantifying stakeholders’ preference for implantable medical devices in China: a discrete choice experiment
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Technology Assessment in Health Care / Volume 40 / Issue 1 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 January 2024, e8
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Rabies vaccination adherence and associated factors among rabies-exposed patients in Shenzhen, China: a hospital-based cross-sectional study
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 152 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 January 2024, e15
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Inverse association between maternal serum concentrations of trace elements and risk of spontaneous preterm birth: a nested case–control study in China
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 131 / Issue 8 / 28 April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 January 2024, pp. 1425-1435
- Print publication:
- 28 April 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Updating glacier inventories on the periphery of Antarctica and Greenland using multi-source data
-
- Journal:
- Annals of Glaciology , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 January 2024, pp. 1-18
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Removal of Fe from Kaolin using Dissimilatory Fe(III)-Reducing Bacteria
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 58 / Issue 4 / August 2010
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 515-521
-
- Article
- Export citation
Treatment of Municipal Landfill Leachate with Organically Modified Bentonite
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 59 / Issue 5 / October 2011
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 518-524
-
- Article
- Export citation
Effects of Fe and V States on the Fenton Catalytic Activity of Natural Rutile
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 66 / Issue 3 / June 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 261-273
-
- Article
- Export citation
Identification of a Novel 15q21.1 Microdeletion in a Family with Marfan Syndrome
-
- Journal:
- Genetics Research / Volume 2022 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e65
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Compact Thomson Scattering Source Based on a Mixed Injection Assisted Laser Wakefield Accelerator
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 2022 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e9
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Genetic Analysis of Prunus salicina L. by Random Amplified Polymorphic DNA (RAPD) and Intersimple Sequence Repeat (ISSR)
-
- Journal:
- Genetics Research / Volume 2022 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e63
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Two Origins of Illite at the Dexing Porphyry Cu Deposit, East China: Implications for Ore-Forming Fluid Constraint on Illite Crystallinity
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 50 / Issue 3 / June 2002
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 381-387
-
- Article
- Export citation
Study of the Interaction Between Bentonite and a Strain of Bacillus Mucilaginosus
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 59 / Issue 5 / October 2011
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 538-545
-
- Article
- Export citation
Simultaneous Immobilization of Zn(II) and Cr(III) in Spinel Crystals from Beneficial Utilization of Waste Brownfield-Site Soils
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 67 / Issue 4 / August 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 315-324
-
- Article
- Export citation
Preventive effects of caffeine on nicotine plus high-fat diet-induced hepatic steatosis and gain weight: a possible explanation for why obese smokers with high coffee consumption tend to be leaner
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 131 / Issue 8 / 28 April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 December 2023, pp. 1342-1351
- Print publication:
- 28 April 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation