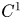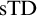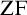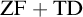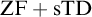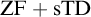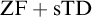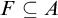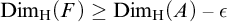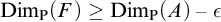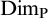129 results
Phylogenetic trends in TZ staining analysis of six deep dormancy seeds
-
- Journal:
- Seed Science Research , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 April 2024, pp. 1-13
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Trauma diagnostic-related target proteins and their detection techniques
-
- Journal:
- Expert Reviews in Molecular Medicine / Volume 26 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 April 2024, e7
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Comparative epidemiology of outbreaks caused by SARS-CoV-2 Delta and Omicron variants in China
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 152 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 March 2024, e43
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A comprehensive diagnostic of liquid sheet targets for laser ion acceleration
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 March 2024, pp. 1-17
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Smoothed particle hydrodynamics modelling of particle-size segregation in granular flows
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 977 / 25 December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 January 2024, A47
-
- Article
- Export citation
Clinical parameter-based prediction model for neurosyphilis risk stratification
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 152 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 January 2024, e21
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Fabrication and Optimization Design of Multilayer Flyer Plates for Laser-Driven Loading
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 2022 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e23
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Effect of Mechanical Activation on the Pozzolanic Activity of Muscovite
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 67 / Issue 3 / June 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 209-216
-
- Article
- Export citation
Bioinformatics Analysis of Competing Endogenous RNA Network and Immune Infiltration in Atrial Fibrillation
-
- Journal:
- Genetics Research / Volume 2022 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e50
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Antibiotic use in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: a population-based study in Hong Kong
-
- Journal:
- Antimicrobial Stewardship & Healthcare Epidemiology / Volume 3 / Issue 1 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 November 2023, e205
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Brain network integration underpins differential susceptibility of adolescent anxiety – ERRATUM
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 54 / Issue 1 / January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 October 2023, p. 219
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Testing guidelines for distinctness, uniformity and stability in Oxalis
-
- Journal:
- Plant Genetic Resources / Volume 21 / Issue 4 / August 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 October 2023, pp. 304-311
-
- Article
- Export citation
Brain network integration underpins differential susceptibility of adolescent anxiety
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 54 / Issue 1 / January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 October 2023, pp. 193-202
-
- Article
- Export citation
“The Wild West:” Nurse Experiences of Responding to the 2017 Las Vegas Mass Shooting
-
- Journal:
- Disaster Medicine and Public Health Preparedness / Volume 17 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 September 2023, e492
-
- Article
- Export citation
Ethnic differences in eating patterns and their associations with obesity among adults in West China
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 131 / Issue 2 / 28 January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 August 2023, pp. 321-332
- Print publication:
- 28 January 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
A universal velocity transformation for boundary layers with pressure gradients
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 970 / 10 September 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 August 2023, A3
-
- Article
- Export citation
SOME CONSEQUENCES OF
 ${\mathrm {TD}}$ AND
${\mathrm {TD}}$ AND 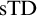 ${\mathrm {sTD}}$
${\mathrm {sTD}}$
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Symbolic Logic / Volume 88 / Issue 4 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 May 2023, pp. 1573-1589
- Print publication:
- December 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Efficacy of dynamic interpersonal therapy for major depressive disorder in China: results of a multicentered, three-arm, randomized, controlled trial
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 53 / Issue 15 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 April 2023, pp. 7242-7254
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Habitat selection and population status of breeding Wood Snipe Gallinago nemoricola in an alpine meadow in Sichuan, China
-
- Journal:
- Bird Conservation International / Volume 33 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 March 2023, e54
-
- Article
- Export citation
Characterisation and position-aiding performance analysis of Doppler observation from android smartphones
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Navigation / Volume 76 / Issue 2-3 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 April 2023, pp. 375-393
- Print publication:
- March 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation