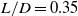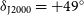1129 results
Phylogenetic trends in TZ staining analysis of six deep dormancy seeds
-
- Journal:
- Seed Science Research , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 April 2024, pp. 1-13
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The role of prosodic sensitivity and executive functions in L2 reading: The moderated mediation effect – ERRATUM
-
- Journal:
- Bilingualism: Language and Cognition , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 April 2024, p. 1
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The dry sky: future scenarios for humanity's modification of the atmospheric water cycle
-
- Journal:
- Global Sustainability / Volume 7 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 March 2024, e11
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The role of prosodic sensitivity and executive functions in L2 reading: The moderated mediation effect
-
- Journal:
- Bilingualism: Language and Cognition , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 March 2024, pp. 1-12
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A five-year quasi-experimental study to evaluate the impact of empiric antibiotic order sets on antibiotic use metrics among hospitalized adult patients
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 45 / Issue 5 / May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 January 2024, pp. 609-617
- Print publication:
- May 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Atmospheric water recycling an essential feature of critical natural asset stewardship
-
- Journal:
- Global Sustainability / Volume 7 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 January 2024, e2
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Disturbance observer-based fixed-time control for hypersonic morphing vehicles with uncertainties
-
- Journal:
- The Aeronautical Journal , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 January 2024, pp. 1-31
-
- Article
- Export citation
Functional neuroimaging biomarkers of anhedonia response to escitalopram plus adjunct aripiprazole treatment for major depressive disorder
-
- Journal:
- BJPsych Open / Volume 10 / Issue 1 / January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 January 2024, e18
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Fabrication of Anthocyanin/Montmorillonite Hybrid Pigments to Enhance Their Environmental Stability and Application in Allochroic Composite Films
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 69 / Issue 1 / February 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 142-151
-
- Article
- Export citation
9 Serum Neurofilament is Associated with Diffusion Kurtosis Imaging in Chronic Mild-Moderate Traumatic Brain Injury
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 29 / Issue s1 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 December 2023, p. 121
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
17 The Chinese Version of Craft Story Recall: A Preliminary Study on the Diagnostic Values of Mild Cognitive Impairment and Dementia.
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 29 / Issue s1 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 December 2023, pp. 700-701
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
4 Associations Between Glycemia and Cognitive Performance in Adults with Type 1 Diabetes (T1D) using Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) and Ecological Momentary Assessment (EMA)
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 29 / Issue s1 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 December 2023, pp. 792-793
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
The impact of lowering the study design significance threshold to 0.005 on sample size in randomized cancer clinical trials
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 8 / Issue 1 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 December 2023, e9
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The Rapid ASKAP Continuum Survey V: Cataloguing the sky at 1 367.5 MHz and the second data release of RACS-mid
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 41 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 December 2023, e003
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Aircraft fleet availability optimisation: a reinforcement learning approach
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- The Aeronautical Journal / Volume 127 / Issue 1318 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 November 2023, pp. 2204-2218
-
- Article
- Export citation
Host response of Nicotiana benthamiana to the parasitism of five populations of root-lesion nematode, Pratylenchus coffeae, from China
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Helminthology / Volume 97 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 September 2023, e73
-
- Article
- Export citation
Transdiagnostic indicators predict developmental changes in cognitive control resting-state networks
-
- Journal:
- Development and Psychopathology , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 August 2023, pp. 1-11
-
- Article
- Export citation
Is deep learning superior to traditional techniques in machine health monitoring applications
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- The Aeronautical Journal / Volume 127 / Issue 1318 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 August 2023, pp. 2105-2117
-
- Article
- Export citation
Multi-fidelity and multi-objective aerodynamic short nacelle shape optimisation under different flight conditions
-
- Journal:
- The Aeronautical Journal / Volume 128 / Issue 1321 / March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 August 2023, pp. 517-546
-
- Article
- Export citation
The Rapid ASKAP Continuum Survey IV: continuum imaging at 1367.5 MHz and the first data release of RACS-mid
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 40 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 August 2023, e034
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation