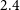1545 results
19 - Erotic Art in World History
-
-
- Book:
- The Cambridge World History of Sexualities
- Published online:
- 26 April 2024
- Print publication:
- 16 May 2024, pp 410-442
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Neural network-based robust adaptive super-twisting sliding mode fault-tolerant control for a class of tilt tri-rotor UAVs with unmodeled dynamics
-
- Journal:
- The Aeronautical Journal , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 April 2024, pp. 1-20
-
- Article
- Export citation
Chapter 18 - Radiculopathy
- from Section 2 - Clinical Neurosurgical Diseases
-
-
- Book:
- Neuroscience for Neurosurgeons
- Published online:
- 04 January 2024
- Print publication:
- 25 January 2024, pp 254-266
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
5 Associations Between Regional Perfusion and Locus Coeruleus MRI Contrast are Moderated by Plasma Alzheimer’s Disease Biomarkers in Older Adults
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 29 / Issue s1 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 December 2023, pp. 610-611
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Generation of energetic electrons by an electron cyclotron wave through stochastic heating in a spherical tokamak
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Plasma Physics / Volume 89 / Issue 6 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 November 2023, 905890603
-
- Article
- Export citation
Host response of Nicotiana benthamiana to the parasitism of five populations of root-lesion nematode, Pratylenchus coffeae, from China
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Helminthology / Volume 97 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 September 2023, e73
-
- Article
- Export citation
Interactions enhance dispersion in fluctuating channels via emergent flows
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 972 / 10 October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 September 2023, A8
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Non-Galilean Taylor–Culick law governs sheet dynamics in unsteady fragmentation
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 969 / 25 August 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 August 2023, A19
-
- Article
- Export citation
Design-oriented dynamic model of deployable fin under time-varying elevated temperature environment
-
- Journal:
- The Aeronautical Journal / Volume 128 / Issue 1322 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 August 2023, pp. 631-654
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
The Rapid ASKAP Continuum Survey IV: continuum imaging at 1367.5 MHz and the first data release of RACS-mid
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 40 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 August 2023, e034
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
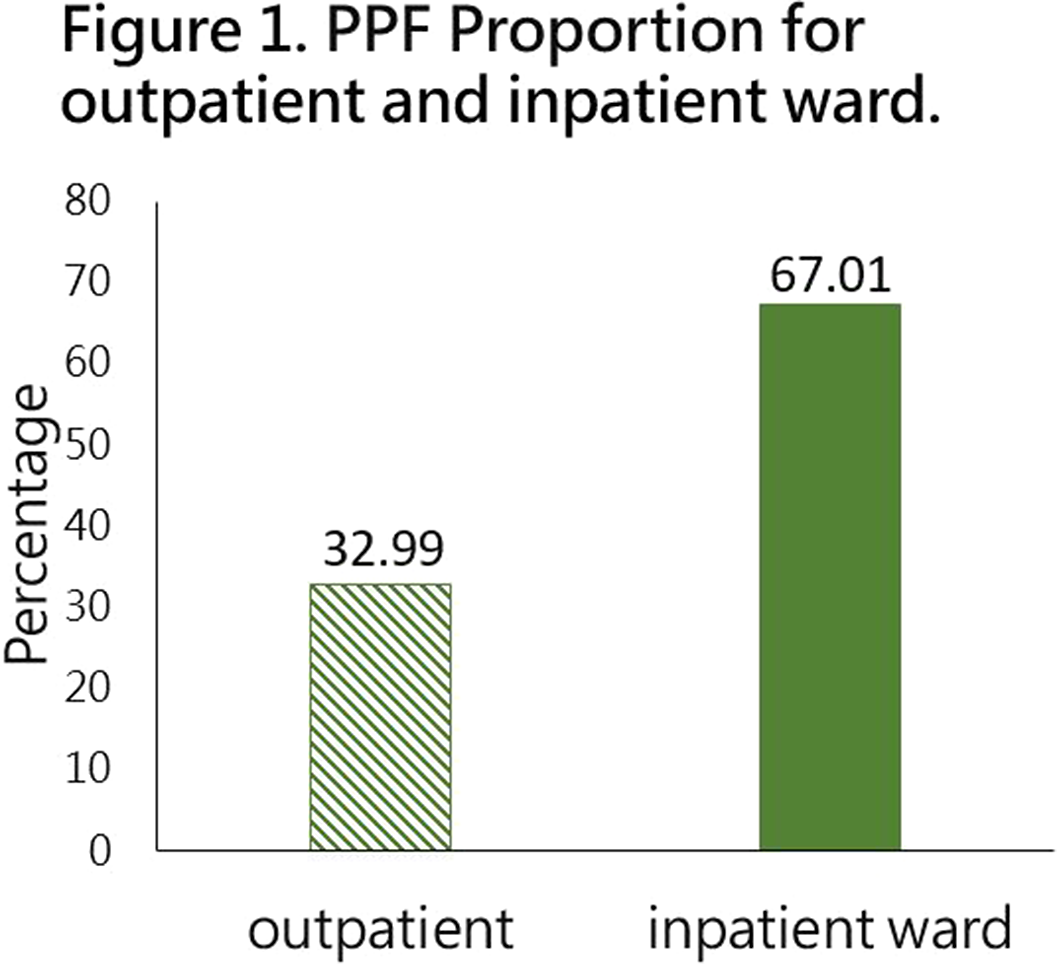
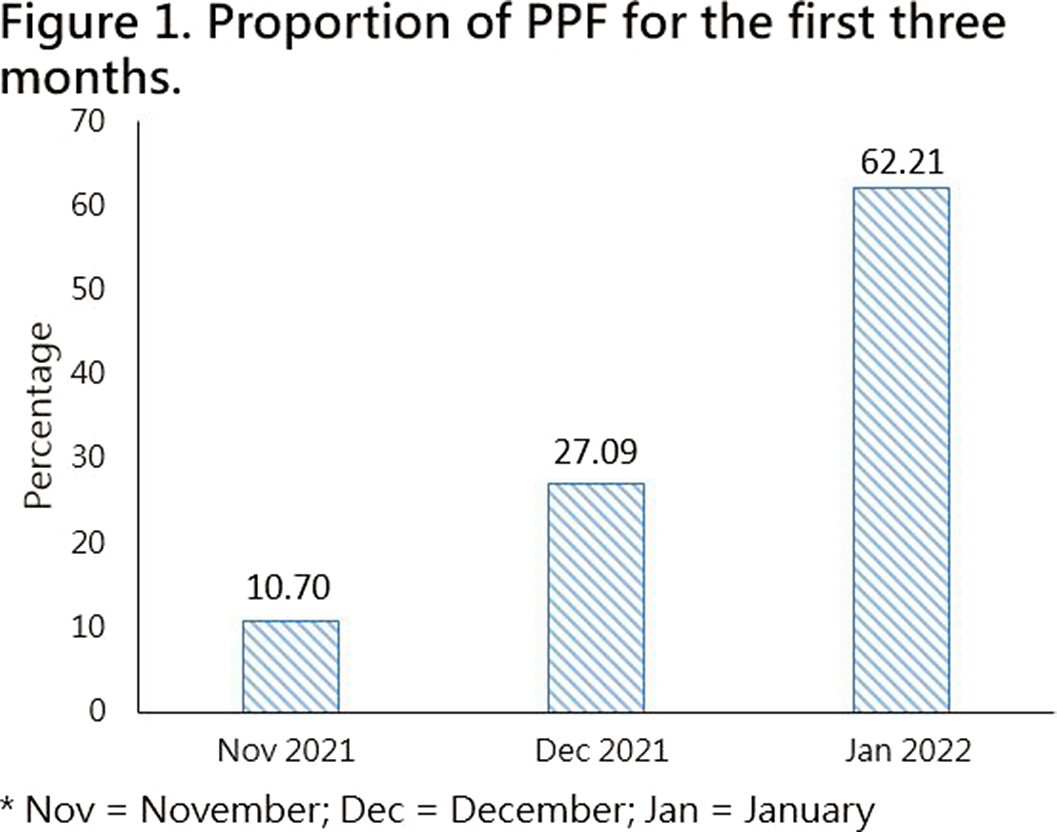
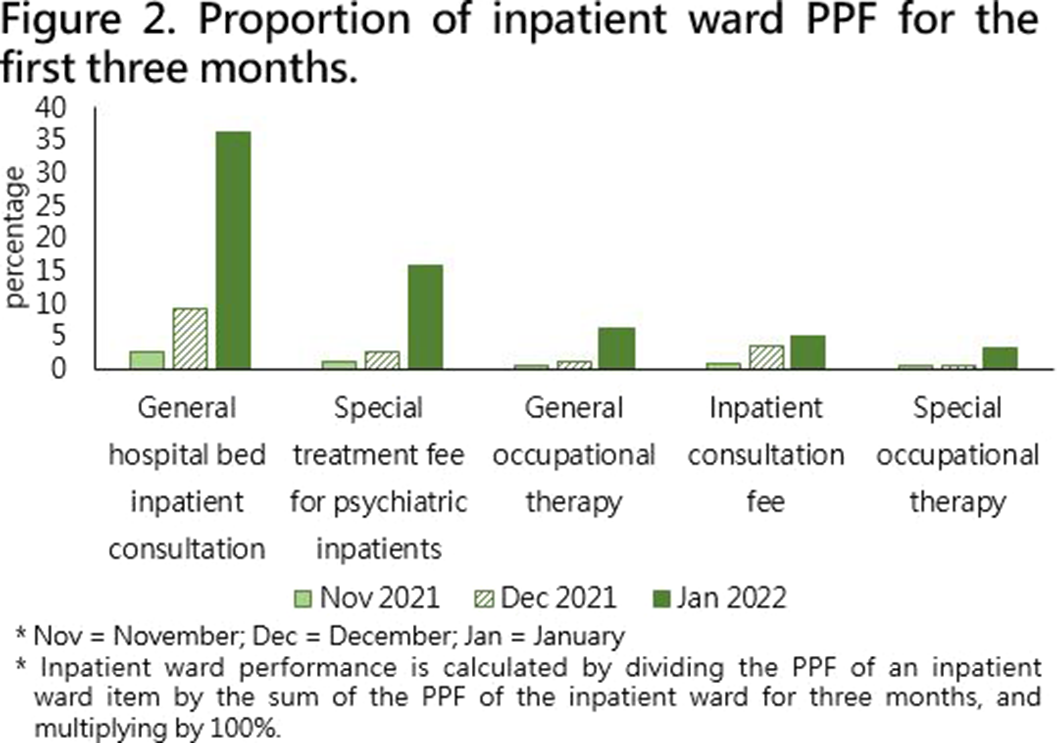
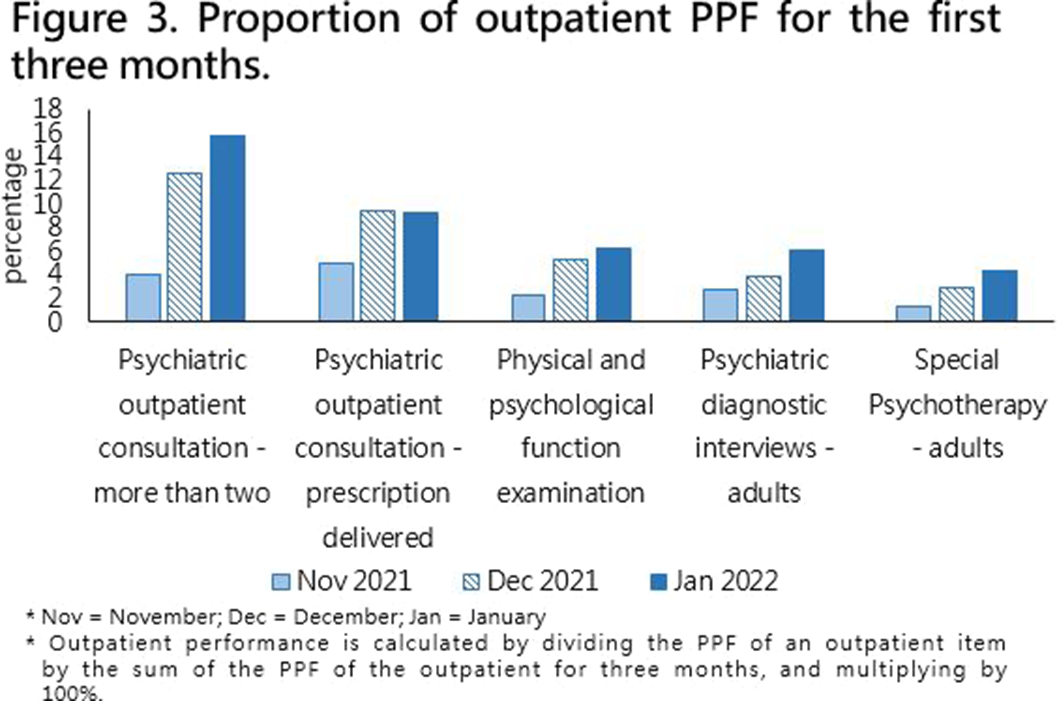
Taiwan National Health Insurance and the Difference between Proportional Physician Fee of Outpatient and Inpatient Ward in General Hospital during the COVID-19 pandemic : Case Report
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 66 / Issue S1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 July 2023, pp. S310-S311
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Facing the COVID-19 pandemic – an assessment of students’ mental health and major coping strategies during the COVID-19 pandemic – an international study
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 66 / Issue S1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 July 2023, pp. S152-S153
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Linked patterns of symptoms and cognition with brain controllability in major depressive disorder
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 66 / Issue S1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 July 2023, p. S420
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Characteristics of Adults Hospitalized for a Major Depressive Disorder: Results from the Multicenter OASIS-D Study
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 66 / Issue S1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 July 2023, pp. S346-S347
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Measuring photometric redshifts for high-redshift radio source surveys
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 40 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 July 2023, e039
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Taiwan National Health Insurance and Proportional Physician Fee of Psychiatrist in General Hospital during the COVID-19 pandemic : Case Report
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 66 / Issue S1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 July 2023, pp. S1029-S1030
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Amisulpride Augmentation in Schizophrenia Patients with Poor Response to Olanzapine: A 4-week, Randomized, Rater-Blind, Controlled, Pilot Study
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 66 / Issue S1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 July 2023, p. S1093
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
10 - Data Assimilation in the Near-Earth Electron Radiation Environment
- from Part II - ‘Fluid’ Earth Applications: From the Surface to the Space
-
-
- Book:
- Applications of Data Assimilation and Inverse Problems in the Earth Sciences
- Published online:
- 20 June 2023
- Print publication:
- 06 July 2023, pp 157-172
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Adaptive reinforcement learning control for a class of missiles with aerodynamic uncertainties and unmodeled dynamics
-
- Journal:
- The Aeronautical Journal / Volume 128 / Issue 1320 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 July 2023, pp. 292-308
-
- Article
- Export citation
TAXI! Do Mutual Funds Pursue and Exploit Information on Local Companies?
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Financial and Quantitative Analysis , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 July 2023, pp. 1-36
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation