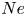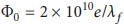442 results
11 - “Internet Plus Health Care” as an Impetus for China’s Health System Reform
- from Part III - The Shape of the Elephant for Digital Home Diagnostics
-
-
- Book:
- Digital Health Care outside of Traditional Clinical Settings
- Published online:
- 25 April 2024
- Print publication:
- 02 May 2024, pp 156-168
-
- Chapter
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Antimicrobial peptide cecropin B functions in pathogen resistance of Mythimna separata
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of Entomological Research , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 April 2024, pp. 1-12
-
- Article
- Export citation
Relationship between syncopal symptoms and head-up tilt test modes
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 April 2024, pp. 1-6
-
- Article
- Export citation
Deblending overlapping galaxies in DECaLS using Transformer-Based algorithm: a method combining multiple bands and data types
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 March 2024, pp. 1-20
-
- Article
- Export citation
Coulomb-driven electroconvection turbulence in two-dimensional cavity
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 980 / 10 February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 January 2024, A22
-
- Article
- Export citation
Assessment of Combined Karyotype Analysis and Chromosome Microarray Analysis in Prenatal Diagnosis: A Cohort Study of 3710 Pregnancies
-
- Journal:
- Genetics Research / Volume 2022 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e1
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Relationship between CYP2C19 Polymorphism and Clopidogrel Resistance in Patients with Coronary Heart Disease and Ischemic Stroke in China
-
- Journal:
- Genetics Research / Volume 2022 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e17
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Preparation and Properties of Sepiolite-Based 3D Flame-Retardant Aerogel
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 70 / Issue 6 / December 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 865-881
-
- Article
- Export citation
Stopping Power Modulation by Pump Waves of Charged Particles Moving above Two-Dimensional Electron Gases
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 2021 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e14
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Effect of Viscosity on Stopping Power for a Charged Particle Moving above Two-Dimensional Electron Gas
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 2022 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e19
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A Pulsed Synchronous Linear Accelerator for Low-Energy Proton
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 2022 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e3
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Reduced Concentrations of NSE, S100β, Aβ, and Proinflammatory Cytokines in Elderly Patients Receiving Ultrasound-Guided Combined Lumbar Plexus-Sciatic Nerve Block during Hip Replacement
-
- Journal:
- Genetics Research / Volume 2022 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e73
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The Properties of Clay Minerals in Soil Particles from Two Ultisols, China
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 65 / Issue 4 / August 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 273-285
-
- Article
- Export citation
Effect of the SiO2/Al2O3 Molar Ratio on the Microstructure and Properties of Clay-based Geopolymers: A Comparative Study of Kaolinite-based and Halloysite-based Geopolymers
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 70 / Issue 6 / December 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 882-902
-
- Article
- Export citation
Overexpressed Histocompatibility Minor 13 was Associated with Liver Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression and Prognosis
-
- Journal:
- Genetics Research / Volume 2022 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e23
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The egg ribonuclease SjCP1412 accelerates liver fibrosis caused by Schistosoma japonicum infection involving damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs)
-
- Journal:
- Parasitology / Volume 151 / Issue 3 / March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 December 2023, pp. 260-270
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Suboptimal antimicrobial discharge prescriptions at a tertiary referral children’s hospital
-
- Journal:
- Antimicrobial Stewardship & Healthcare Epidemiology / Volume 3 / Issue 1 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 December 2023, e223
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Effects of phase boundary and shear on diffusive instability – CORRIGENDUM
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 975 / 25 November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 November 2023, E2
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Rayleigh–Bénard instability in the presence of phase boundary and shear – CORRIGENDUM
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 975 / 25 November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 November 2023, E3
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Mental health symptoms and their associated factors among pharmacists in psychiatric hospitals during the early stage of the COVID-19 pandemic
-
- Journal:
- Cambridge Prisms: Global Mental Health / Volume 10 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 November 2023, e77
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation