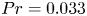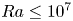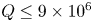2706 results
Spirituality and behavioural addictions: narrative review
-
- Journal:
- BJPsych International , FirstView
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 May 2024, pp. 1-3
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Detection of inducible nitric oxide synthase in Schistosoma japonicum and S. mansoni
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Helminthology / Volume 78 / Issue 1 / March 2004
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 April 2024, pp. 47-50
-
- Article
- Export citation
Impaired topology and connectivity of grey matter structural networks in major depressive disorder: evidence from a multi-site neuroimaging data-set
-
- Journal:
- The British Journal of Psychiatry / Volume 224 / Issue 5 / May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 April 2024, pp. 170-178
- Print publication:
- May 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Influence of Silicon and Phosphorus on Structural and Magnetic Properties of Synthetic Goethite and Related Oxides
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 36 / Issue 2 / April 1988
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 April 2024, pp. 165-175
-
- Article
- Export citation
Shifting the paradigm of research-to-policy impact: Infrastructure for improving researcher engagement and collective action
-
- Journal:
- Development and Psychopathology , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 March 2024, pp. 1-14
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Voter Backlash and Elite Misperception: The Logic of Violence in Electoral Competition. By Steven C. Rosenzweig. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2023. 200p. $110.00 cloth.
-
- Journal:
- Perspectives on Politics , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 March 2024, pp. 1-2
-
- Article
- Export citation
Incubation experiments using nitrogen isotope discrimination to estimate ammonia emission from amended sheep manure treatments
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Agricultural Science / Volume 162 / Issue 1 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 March 2024, pp. 67-76
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Nef cones of fiber products and an application to the cone conjecture
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Forum of Mathematics, Sigma / Volume 12 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 March 2024, e28
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
An advanced solid-state RF power source maximizing energy efficiency for optimal superconducting RF cavity charging
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Microwave and Wireless Technologies , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 February 2024, pp. 1-10
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The Kinetics of the Smectite to Illite Transformation in Cretaceous Bentonites, Cerro Negro, New Mexico
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 47 / Issue 3 / June 1999
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 February 2024, pp. 286-296
-
- Article
- Export citation
Jonathan Finn, Beyond the Finish Line: Images, Evidence and the History of the Photo-finish Montreal: McGill-Queen's University Press, 2020. Pp. xii + 212. ISBN 978-0-2280-0343-4. CD$43.95 (cloth).
-
- Journal:
- The British Journal for the History of Science , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 February 2024, pp. 1-3
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
A novel neck brace to characterize neck mobility impairments following neck dissection in head and neck cancer patients – ADDENDUM
-
- Journal:
- Wearable Technologies / Volume 5 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 February 2024, e7
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Effects of horizontal magnetic fields on turbulent Rayleigh–Bénard convection in a cuboid vessel with aspect ratio Γ = 5
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 980 / 10 February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 January 2024, A24
-
- Article
- Export citation
How adolescents’ lives were disrupted over the course of the COVID-19 pandemic: A longitudinal investigation in 12 cultural groups in 9 nations from March 2020 to July 2022
-
- Journal:
- Development and Psychopathology , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 January 2024, pp. 1-17
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Racial and ethnic differences in the degree of participation and retention in a decentralized cohort study of COVID-19 immunization in patients with inflammatory bowel diseases
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 8 / Issue 1 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 January 2024, e31
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Clinical parameter-based prediction model for neurosyphilis risk stratification
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 152 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 January 2024, e21
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Abnormal intrinsic brain functional network dynamics in first-episode drug-naïve adolescent major depressive disorder
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 January 2024, pp. 1-10
-
- Article
- Export citation
The Clinical Relevance and Functional Implications of Thymosin Beta-10 in Glioma
-
- Journal:
- Genetics Research / Volume 2023 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e35
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation