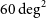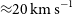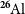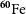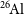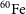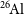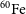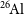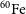395 results
Barriers to Surgical Intervention and Factors Influencing Motor Outcomes in Patients with Severe Peripheral Nerve Injury: A Province Wide Cohort Study
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 November 2023, pp. 1-9
-
- Article
- Export citation
Facing the COVID-19 pandemic – an assessment of students’ mental health and major coping strategies during the COVID-19 pandemic – an international study
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 66 / Issue S1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 July 2023, pp. S152-S153
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Culturally adapted psychoeducation for bipolar disorder in a low-resource setting: protocol for a multicentre randomized controlled trial
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 66 / Issue S1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 July 2023, p. S384
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Accelerated protons with energies up to 70 MeV based on the optimized SG-II Peta-watt laser facility
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 11 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 June 2023, e63
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
WALLABY pilot survey: The diversity of HI structural parameters in nearby galaxies
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 40 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 June 2023, e032
-
- Article
- Export citation
A.5 Neurovascular complications of veno-venous extracorporeal membrane oxygenation in critically ill COVID-19 patients
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 50 / Issue s2 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 June 2023, p. S49
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
P.104 Grade 3 meningioma survival, recurrence and functional outcomes in an international multicenter cohort
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 50 / Issue s2 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 June 2023, p. S85
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
WALLABY Pilot Survey: Public release of HI kinematic models for more than 100 galaxies from phase 1 of ASKAP pilot observations
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 39 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 November 2022, e059
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
WALLABY pilot survey: Public release of H i data for almost 600 galaxies from phase 1 of ASKAP pilot observations
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 39 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 November 2022, e058
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on maternal mental health during pregnancy: The CONCEPTION study – Phase I
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 65 / Issue S1 / June 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 September 2022, pp. S209-S210
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Prediction and copy number variation identification of ZNF146 gene related to growth traits in Chinese cattle
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Agricultural Science / Volume 160 / Issue 5 / October 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 August 2022, pp. 404-412
-
- Article
- Export citation
Acceleration of 60 MeV proton beams in the commissioning experiment of the SULF-10 PW laser
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 10 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 August 2022, e26
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
P.153 Traumatic spinal cord injuries among indigenous and non-indigenous peoples of Canada
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 49 / Issue s1 / June 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 June 2022, p. S47
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Degree of adherence to plant-based diet and total and cause-specific mortality: prospective cohort study in the Million Veteran Program
-
- Journal:
- Public Health Nutrition / Volume 26 / Issue 2 / February 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 March 2022, pp. 381-392
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The baby and the bathwater: On the need for substantive–methodological synergy in organizational research
-
- Journal:
- Industrial and Organizational Psychology / Volume 14 / Issue 4 / December 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 December 2021, pp. 497-504
-
- Article
- Export citation
The radioactive nuclei
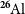 $^{\textbf{26}}\mathrm{Al}$
and
$^{\textbf{26}}\mathrm{Al}$
and 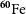 $^{\textbf{60}}\mathrm{Fe}$
in the Cosmos and in the solar system
$^{\textbf{60}}\mathrm{Fe}$
in the Cosmos and in the solar system
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 38 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 December 2021, e062
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The influence of background turbulence on Ahmed-body wake bistability
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 926 / 10 November 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 September 2021, R1
-
- Article
- Export citation
Nomenclature for Pediatric and Congenital Cardiac Care: Unification of Clinical and Administrative Nomenclature – The 2021 International Paediatric and Congenital Cardiac Code (IPCCC) and the Eleventh Revision of the International Classification of Diseases (ICD-11)
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 31 / Issue 7 / July 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 July 2021, pp. 1057-1188
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Characterization of a hospital-based gastroenteritis outbreak caused by GII.6 norovirus in Jinshan, China
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 148 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 December 2020, e289
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Neutron Star Extreme Matter Observatory: A kilohertz-band gravitational-wave detector in the global network
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 37 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 November 2020, e047
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation