605 results

Casebook of Dementia
- A Reference Guide for Primary Care
- Coming soon
-
- Expected online publication date:
- May 2024
- Print publication:
- 31 May 2024
-
- Book
- Export citation
Acceptability of virtual psychiatric consultations for routine follow-ups post COVID-19 pandemic for people with intellectual disabilities: cross-sectional study
-
- Journal:
- BJPsych Open / Volume 10 / Issue 3 / May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 April 2024, e90
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Haplorchis infections in intermediate hosts from a clonorchiasis endemic area in Meinung, Taiwan, Republic of China
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Helminthology / Volume 76 / Issue 2 / June 2002
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 April 2024, pp. 185-188
-
- Article
- Export citation
Adjunctive Cariprazine for Major Depressive Disorder: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
-
- Journal:
- CNS Spectrums / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 April 2024, pp. 1-37
-
- Article
- Export citation
The effect of older age on outcomes of rTMS treatment for treatment-resistant depression
-
- Journal:
- International Psychogeriatrics , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 March 2024, pp. 1-6
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Holocene climate variability – CORRIGENDUM
-
- Journal:
- Quaternary Research , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 March 2024, p. 1
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Incidence of mental health diagnoses during the COVID-19 pandemic: a multinational network study
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology and Psychiatric Sciences / Volume 33 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 March 2024, e9
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Associations among loneliness, internal locus of control and subjective accelerated ageing in older adults who received the booster vaccination
-
- Journal:
- BJPsych Open / Volume 10 / Issue 2 / March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 February 2024, e54
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Research into land atmosphere interactions supports the sustainable development agenda
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Global Sustainability / Volume 7 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 February 2024, e12
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Social cognition and social motivation in schizophrenia and bipolar disorder: are impairments linked to the disorder or to being socially isolated?
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 February 2024, pp. 1-9
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
P103: Middle Cerebral Artery Stenosis is Associated with Severity of Depression in Elderly Patients: Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA) Findings
-
- Journal:
- International Psychogeriatrics / Volume 35 / Issue S1 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 February 2024, pp. 168-169
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Exploring the prospective acceptability of a healthy food incentive program from the perspective of people with type 2 diabetes and experiences of household food insecurity in Alberta, Canada
-
- Journal:
- Public Health Nutrition / Volume 27 / Issue 1 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 February 2024, e66
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Nation-Wide Variation in Presence of Legislation or Protocols for EMS Care of Operational Canines
-
- Journal:
- Prehospital and Disaster Medicine / Volume 39 / Issue 1 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 February 2024, pp. 59-64
- Print publication:
- February 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
EMDR v. other psychological therapies for PTSD: a systematic review and individual participant data meta-analysis
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 January 2024, pp. 1-9
-
- Article
- Export citation
32 Prediction of Seizure Outcome with Presurgical IAT, MRI, and PET in Patients with Temporal Lobe Epilepsy Undergoing Surgery
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 29 / Issue s1 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 December 2023, pp. 31-32
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
OP85 Cost Effectiveness Of Prednisolone To Treat Bell’s Palsy In Children: An Economic Evaluation Alongside A Randomized Controlled Trial
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Technology Assessment in Health Care / Volume 39 / Issue S1 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 December 2023, p. S23
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
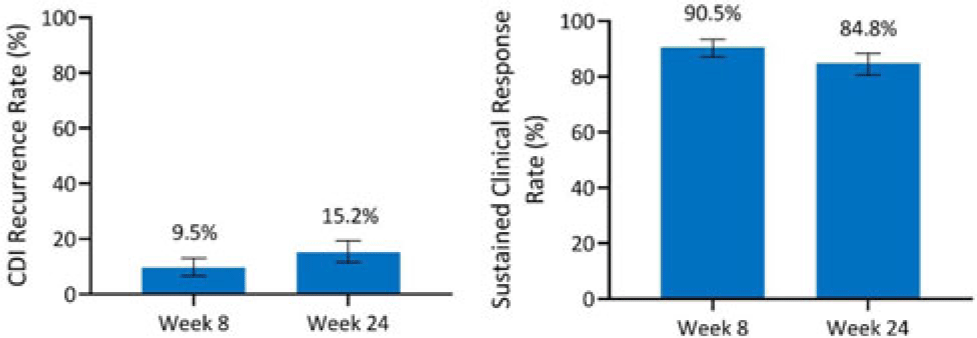
Integrated efficacy analysis from phase 3 studies of investigational microbiome therapeutic, SER-109, in recurrent Clostridioides difficile infection
-
- Journal:
- Antimicrobial Stewardship & Healthcare Epidemiology / Volume 3 / Issue S2 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 September 2023, p. s5
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
A causal roadmap for generating high-quality real-world evidence
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 7 / Issue 1 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 September 2023, e212
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Advocacy at the Eighth World Congress of Pediatric Cardiology and Cardiac Surgery
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 33 / Issue 8 / August 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 August 2023, pp. 1277-1287
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Experiences and perceived outcomes of a grocery gift card programme for households at risk of food insecurity
-
- Journal:
- Public Health Nutrition / Volume 26 / Issue 11 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 August 2023, pp. 2460-2469
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation