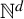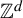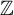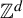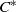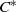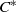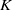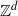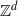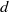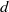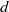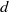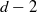59 results
Bohr chaoticity of principal algebraic actions and Riesz product measures
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Ergodic Theory and Dynamical Systems , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 March 2024, pp. 1-27
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
New examples of Bernoulli algebraic actions
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Ergodic Theory and Dynamical Systems / Volume 42 / Issue 9 / September 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 May 2021, pp. 2923-2934
- Print publication:
- September 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
4 - Fiscal Rules in the World
- from Part II - Better Institutions for Better Fiscal Policy
-
-
- Book:
- Rethinking Fiscal Policy after the Crisis
- Published online:
- 19 May 2017
- Print publication:
- 18 May 2017, pp 103-137
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Site formation and chronology of the New Paleolithic Site Sima de Las Palomas de Teba, Southern Spain
-
- Journal:
- Quaternary Research / Volume 85 / Issue 2 / March 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 January 2017, pp. 313-331
-
- Article
- Export citation
Evidence for Holocene environmental changes in the northern Fertile Crescent provided by pedogenic carbonate coatings
-
- Journal:
- Quaternary Research / Volume 67 / Issue 3 / May 2007
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 January 2017, pp. 315-327
-
- Article
- Export citation
8 - Fiscal Institutions in Resource-rich Economies
-
-
- Book:
- Understanding and Avoiding the Oil Curse in Resource-rich Arab Economies
- Published online:
- 05 July 2016
- Print publication:
- 14 July 2016, pp 225-283
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Chapter 5 - Gathering of the Dead? The Early Neolithic Sanctuaries of Göbekli Tepe, Southeastern Turkey
- from Part II - Mortality and the Foundations of Human Society: Sedentism and the Collective
-
-
- Book:
- Death Rituals, Social Order and the Archaeology of Immortality in the Ancient World
- Published online:
- 05 November 2015
- Print publication:
- 19 November 2015, pp 65-81
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
The power of confocal raman-AFM and raman-SEM (RISE) imaging in polymer research
-
- Journal:
- Microscopy and Microanalysis / Volume 21 / Issue S3 / August 2015
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 September 2015, pp. 2189-2190
- Print publication:
- August 2015
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Notes on contributors
-
-
- Book:
- The Cambridge History of Fifteenth-Century Music
- Published online:
- 05 July 2015
- Print publication:
- 16 July 2015, pp xix-xxvi
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Contributors
-
-
- Book:
- Cerebral Small Vessel Disease
- Published online:
- 05 June 2014
- Print publication:
- 01 May 2014, pp ix-xii
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Contributors
-
-
- Book:
- GIs in Germany
- Published online:
- 05 October 2013
- Print publication:
- 02 September 2013, pp ix-x
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Circle maps and
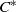 ${C}^{\ast } $-algebras
${C}^{\ast } $-algebras
-
- Journal:
- Ergodic Theory and Dynamical Systems / Volume 35 / Issue 2 / April 2015
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 August 2013, pp. 546-584
- Print publication:
- April 2015
-
- Article
- Export citation
A presumably benign human ether-a-go-go-related gene mutation (R176W) with a malignant primary manifestation of long QT syndrome – CORRIGENDUM
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 23 / Issue 1 / February 2013
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 September 2012, p. 158
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Homoclinic points, atoral polynomials, and periodic points of algebraic
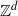 $\mathbb {Z}^d$-actions
$\mathbb {Z}^d$-actions
-
- Journal:
- Ergodic Theory and Dynamical Systems / Volume 33 / Issue 4 / August 2013
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 May 2012, pp. 1060-1081
- Print publication:
- August 2013
-
- Article
- Export citation
A presumably benign human ether-a-go-go-related gene mutation (R176W) with a malignant primary manifestation of long QT syndrome
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 22 / Issue 3 / June 2012
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 November 2011, pp. 360-363
-
- Article
- Export citation
5 - Inflation targeting twenty years on: where, when, why, with what effects and what lies ahead?
-
-
- Book:
- Twenty Years of Inflation Targeting
- Published online:
- 05 October 2010
- Print publication:
- 16 September 2010, pp 57-89
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Algebraic Polymorphisms– ERRATUM
-
- Journal:
- Ergodic Theory and Dynamical Systems / Volume 29 / Issue 4 / August 2009
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 August 2009, pp. 1369-1370
- Print publication:
- August 2009
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Decompositions of vector measures in Riesz spaces and Banach lattices
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society / Volume 29 / Issue 1 / February 1986
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 January 2009, pp. 23-39
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Functional Fatigue of Shape-Memory Polymers
-
- Journal:
- MRS Online Proceedings Library Archive / Volume 1190 / 2009
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 January 2011, 1190-NN03-02
- Print publication:
- 2009
-
- Article
- Export citation