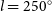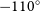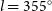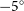74 results
The Mopra Southern Galactic Plane CO Survey – data release 4– complete survey
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 40 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 August 2023, e047
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A.1 A national eDelphi process to establish Canadian quality indicators for the care of adults hospitalized for neurological problems
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 50 / Issue s2 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 June 2023, p. S48
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Allowing Captive Marmosets to Choose the Size and Position of Their Nest Box
-
- Journal:
- Animal Welfare / Volume 8 / Issue 3 / August 1999
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 January 2023, pp. 281-285
-
- Article
- Export citation
Salience and central executive networks track overgeneralization of conditioned-fear in post-traumatic stress disorder
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 51 / Issue 15 / November 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 May 2020, pp. 2610-2619
-
- Article
- Export citation
Connecting the ISM to TeV PWNe and PWN candidates
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 36 / 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 April 2019, e014
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Aliphatic hydrocarbon content of interstellar dust
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the International Astronomical Union / Volume 15 / Issue S350 / April 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 October 2020, pp. 241-244
- Print publication:
- April 2019
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
The Mopra Southern Galactic Plane CO Survey—Data Release 3
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 35 / 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 August 2018, e029
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
A Study of the Interstellar Medium Towards the Unidentified Dark TeV γ-Ray Sources HESS J1614–518 and HESS J1616–508
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 34 / 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 December 2017, e064
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
The Behavioral Revolution and International Relations
-
- Journal:
- International Organization / Volume 71 / Issue S1 / April 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 April 2017, pp. S1-S31
- Print publication:
- April 2017
-
- Article
- Export citation
Altered weed reproduction and maternal effects under low-nitrogen fertility
-
- Journal:
- Weed Science / Volume 54 / Issue 5 / October 2006
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 January 2017, pp. 847-853
-
- Article
- Export citation
Bushkiller (Cayratia japonica) Growth in Interspecific and Intraspecific Competition
-
- Journal:
- Weed Science / Volume 58 / Issue 3 / September 2010
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 January 2017, pp. 195-198
-
- Article
- Export citation
Temperature Response of Benghal Dayflower (Commelina benghalensis): Implications for Geographic Range
-
- Journal:
- Weed Science / Volume 56 / Issue 5 / October 2008
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 January 2017, pp. 707-713
-
- Article
- Export citation
Tropical Spiderwort (Commelina benghalensis): A Tropical Invader Threatens Agroecosystems of the Southern United States
-
- Journal:
- Weed Technology / Volume 19 / Issue 3 / September 2005
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 January 2017, pp. 501-508
-
- Article
- Export citation
Dallisgrass (Paspalum Dilatatum) Control with Foramsulfuron in Bermudagrass Turf
-
- Journal:
- Weed Technology / Volume 21 / Issue 3 / September 2007
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 January 2017, pp. 759-762
-
- Article
- Export citation
Benghal Dayflower (Commelina benghalensis) Seed Viability in Soil
-
- Journal:
- Weed Science / Volume 60 / Issue 4 / December 2012
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 January 2017, pp. 589-592
-
- Article
- Export citation
Effect of Mowing on Lateral Spread and Rhizome Growth of Troublesome Paspalum Species
-
- Journal:
- Weed Science / Volume 55 / Issue 5 / October 2007
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 January 2017, pp. 486-490
-
- Article
- Export citation
Predictability Versus Flexibility: Secrecy in International Investment Arbitration
-
- Journal:
- World Politics / Volume 68 / Issue 3 / July 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 May 2016, pp. 413-453
- Print publication:
- July 2016
-
- Article
- Export citation
The Scientific Potential for Astronomy from the Antarctic Plateau: A Report prepared by the Australian Working Group for Antarctic Astronomy
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 11 / Issue 2 / August 1994
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 April 2016, pp. 127-150
-
- Article
- Export citation
An Automated Astrophysical Observatory for Antarctica
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 13 / Issue 1 / January 1996
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 April 2016, pp. 35-38
-
- Article
- Export citation
A case-control study to identify risk factors for acute salmonellosis in New Zealand dairy herds, 2011–2012
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 144 / Issue 10 / July 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 March 2016, pp. 2154-2164
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation