135 results
76 Lessons learned during implementation of OMOP common data model across multiple health systems
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 8 / Issue s1 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 April 2024, p. 20
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Head and Neck Cancer: United Kingdom National Multidisciplinary Guidelines, Sixth Edition
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Laryngology & Otology / Volume 138 / Issue S1 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 March 2024, pp. S1-S224
- Print publication:
- April 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Call-Outs and Call-Ins
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the American Philosophical Association , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 March 2024, pp. 1-20
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Empowering the Participant Voice (EPV): Design and implementation of collaborative infrastructure to collect research participant experience feedback at scale
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 8 / Issue 1 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 February 2024, e40
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
27 Assessing Differences in Academic Achievement Among a National Sample of Children with Epilepsy Before and During the COVID-19 Pandemic
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 29 / Issue s1 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 December 2023, pp. 28-29
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
3 Emotional Expression in Infants with Agenesis of the Corpus Callosum: The Role of Callosal Connectivity in Early Temperament
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 29 / Issue s1 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 December 2023, pp. 403-404
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
4 Language Development in Infants and Toddlers (12 to 24 months) with Agenesis of the Corpus Callosum
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 29 / Issue s1 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 December 2023, pp. 404-405
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
1 Early Development of Adaptive Skills in Young Children with Agenesis of the Corpus Callosum: A Comparison to Monogenetic and Neurodevelopmental Conditions
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 29 / Issue s1 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 December 2023, pp. 401-402
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
3 Latent Wechsler Profiles in Presurgical Pediatric Epilepsy
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 29 / Issue s1 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 December 2023, pp. 308-310
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
26 The Importance of Executive Functioning for Academic Achievement Among a National Sample of Children with Epilepsy
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 29 / Issue s1 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 December 2023, pp. 26-27
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
38 Fine Motor Skills in Pediatric Frontal Lobe Epilepsy are Associated with Executive Dysfunction and ADHD Symptomatology
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 29 / Issue s1 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 December 2023, pp. 37-38
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Testing a conceptual Hierarchy of Effects model of food marketing exposure and associations with children and adolescents’ diet-related outcomes
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Public Health Nutrition / Volume 27 / Issue 1 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 December 2023, e10
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Investigating the association between characteristics of local crisis care systems and service use in an English national survey – CORRIGENDUM
-
- Journal:
- BJPsych Open / Volume 10 / Issue 1 / January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 December 2023, e6
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Temperate pasture- or concentrate-beef production systems: steer performance, meat nutritional value, land-use, food–feed competition, economic and environmental sustainability
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Agricultural Science / Volume 161 / Issue 5 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 November 2023, pp. 704-719
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Investigating the association between characteristics of local crisis care systems and service use in an English national survey
-
- Journal:
- BJPsych Open / Volume 9 / Issue 6 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 November 2023, e209
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Partula tree snail conservation back on track
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
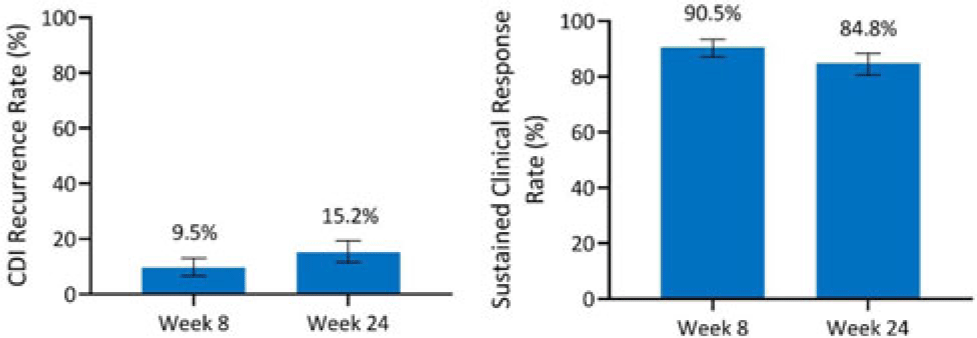
Integrated efficacy analysis from phase 3 studies of investigational microbiome therapeutic, SER-109, in recurrent Clostridioides difficile infection
-
- Journal:
- Antimicrobial Stewardship & Healthcare Epidemiology / Volume 3 / Issue S2 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 September 2023, p. s5
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Integrated safety analysis of phase 3 studies for investigational microbiome therapeutic, SER-109, in recurrent CDI
-
- Journal:
- Antimicrobial Stewardship & Healthcare Epidemiology / Volume 3 / Issue S2 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 September 2023, pp. s44-s45
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Reducing the rate of guideline-discordant therapy for inpatients with community-acquired pneumonia
-
- Journal:
- Antimicrobial Stewardship & Healthcare Epidemiology / Volume 3 / Issue S2 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 September 2023, p. s24
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
A communication intervention to improve prognostic understanding and engagement in advance care planning among diverse advanced cancer patient–caregiver dyads: A pilot study
-
- Journal:
- Palliative & Supportive Care / Volume 22 / Issue 1 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 August 2023, pp. 10-18
-
- Article
- Export citation