147 results
Quality Improvement Project on Standardising GP Discharge Summaries in Liaison Psychiatry Services for Older People in Nottinghamshire Healthcare NHS Trust
-
- Journal:
- BJPsych Open / Volume 10 / Issue S1 / June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 August 2024, pp. S173-S174
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
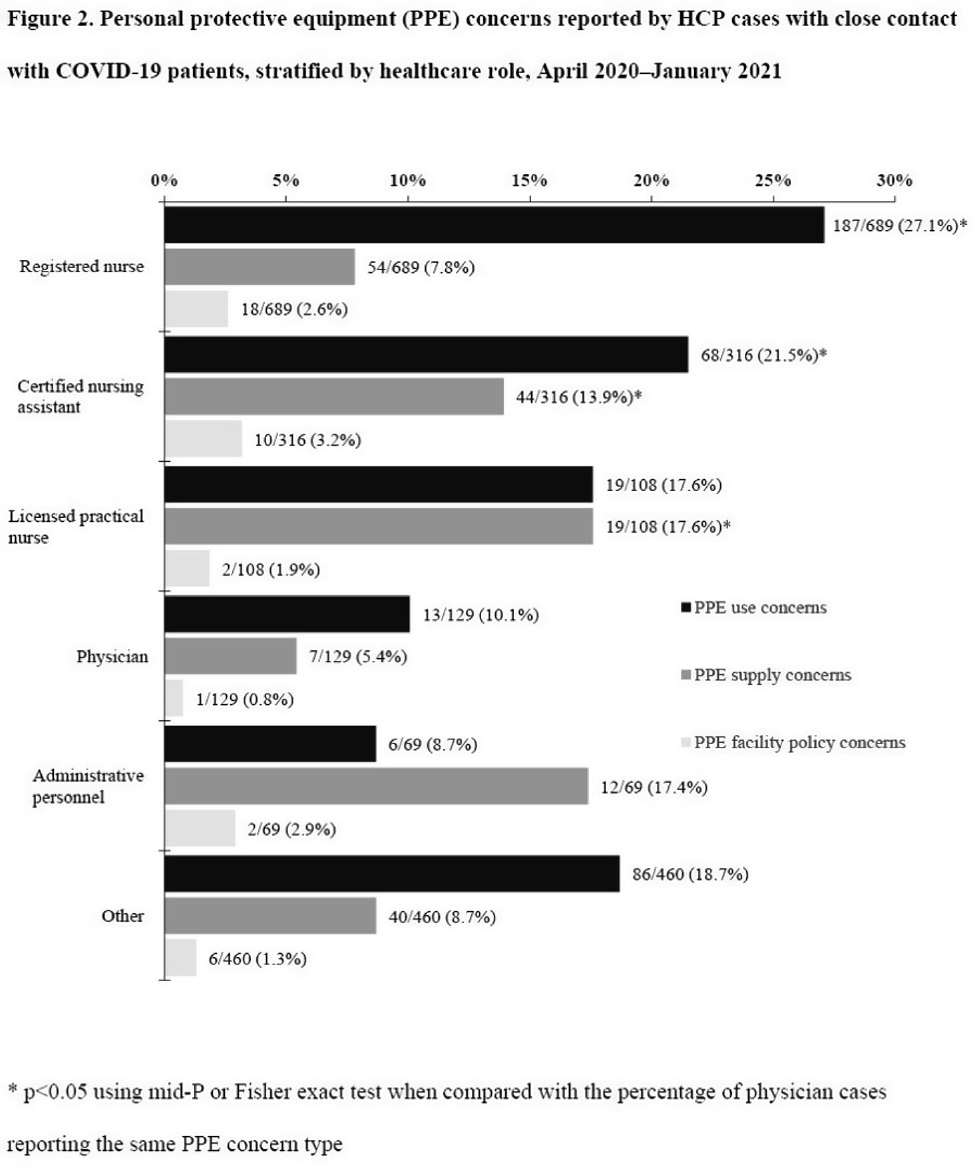
Characteristics of healthcare personnel with SARS-CoV-2 infection: 10 emerging infections program sites in the United States, April 2020–December 2021
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 May 2024, pp. 1-9
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
11 - Community Leadership Development
- from Part III - Civil Society and Coalitions
-
-
- Book:
- The Cambridge Handbook of Community Empowerment
- Published online:
- 18 April 2024
- Print publication:
- 25 April 2024, pp 289-312
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Detection of and response to gender-based violence: a quality improvement project across three secondary mental health services in London
-
- Journal:
- BJPsych Bulletin , FirstView
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 April 2024, pp. 1-6
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The Trial Innovation Network Liaison Team: building a national clinical and translational community of practice
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 7 / Issue 1 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 November 2023, e249
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The Impact of Chemical, Biological, Radiological, Nuclear and Explosive Events on Emergency Departments: An Integrative Review
-
- Journal:
- Prehospital and Disaster Medicine / Volume 38 / Issue S1 / May 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 July 2023, p. s3
- Print publication:
- May 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Learning Together: Experimental Evidence on Promoting Connections in Remote Classes
-
- Journal:
- PS: Political Science & Politics / Volume 56 / Issue 3 / July 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 March 2023, pp. 438-443
- Print publication:
- July 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Cracking the Nest Egg: Comparing Pension Politics in Post-Communist Russia and Hungary – ERRATUM
-
- Journal:
- Social Policy and Society / Volume 22 / Issue 3 / July 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 February 2023, p. 471
- Print publication:
- July 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Cracking the Nest Egg: Comparing Pension Politics in Post-Communist Russia and Hungary
-
- Journal:
- Social Policy and Society / Volume 22 / Issue 2 / April 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 January 2023, pp. 338-354
- Print publication:
- April 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
An outbreak of Cryptosporidium parvum linked to pasteurised milk from a vending machine in England: a descriptive study, March 2021
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 150 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 October 2022, e185
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
13 - Inequality and Social Policy in Russia
- from Part II - Political Economy
-
-
- Book:
- Russian Politics Today
- Published online:
- 28 October 2022
- Print publication:
- 27 October 2022, pp 293-317
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
A pilot randomized trial to evaluate the efficacy of oral and nasal povidone iodine in reducing the burden of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 RNA in patients with coronavirus disease 2019
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 44 / Issue 4 / April 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 October 2022, pp. 679-681
- Print publication:
- April 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Templated microbiology comments with candiduria to enhance antimicrobial stewardship
-
- Journal:
- Antimicrobial Stewardship & Healthcare Epidemiology / Volume 2 / Issue 1 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 September 2022, e156
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A randomized trial to determine whether wearing slippers reduces transfer of bacteriophage MS2 from floors to patients and surfaces in hospital rooms
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 44 / Issue 4 / April 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 August 2022, pp. 670-673
- Print publication:
- April 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Investigating the Relationship Between Childhood Music Practice and Pitch-Naming Ability in Professional Musicians and a Population-Based Twin Sample
-
- Journal:
- Twin Research and Human Genetics / Volume 25 / Issue 3 / June 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 August 2022, pp. 140-148
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
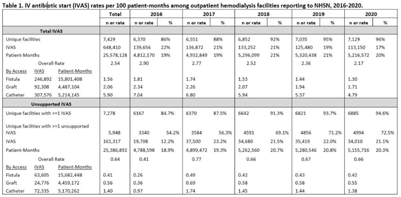
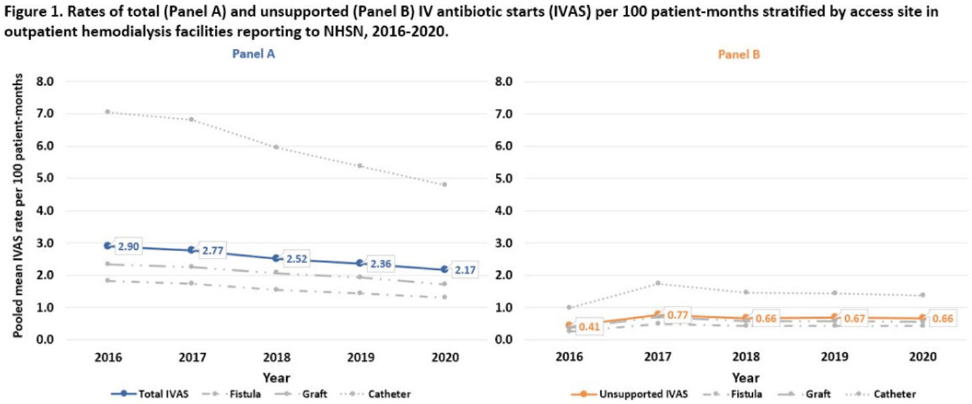
Rates of intravenous antibiotic starts among outpatient hemodialysis patients using NHSN dialysis event reporting, 2016–2020
-
- Journal:
- Antimicrobial Stewardship & Healthcare Epidemiology / Volume 2 / Issue S1 / July 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 May 2022, pp. s71-s72
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
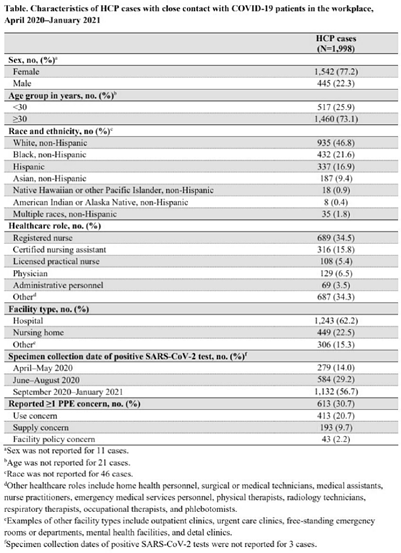
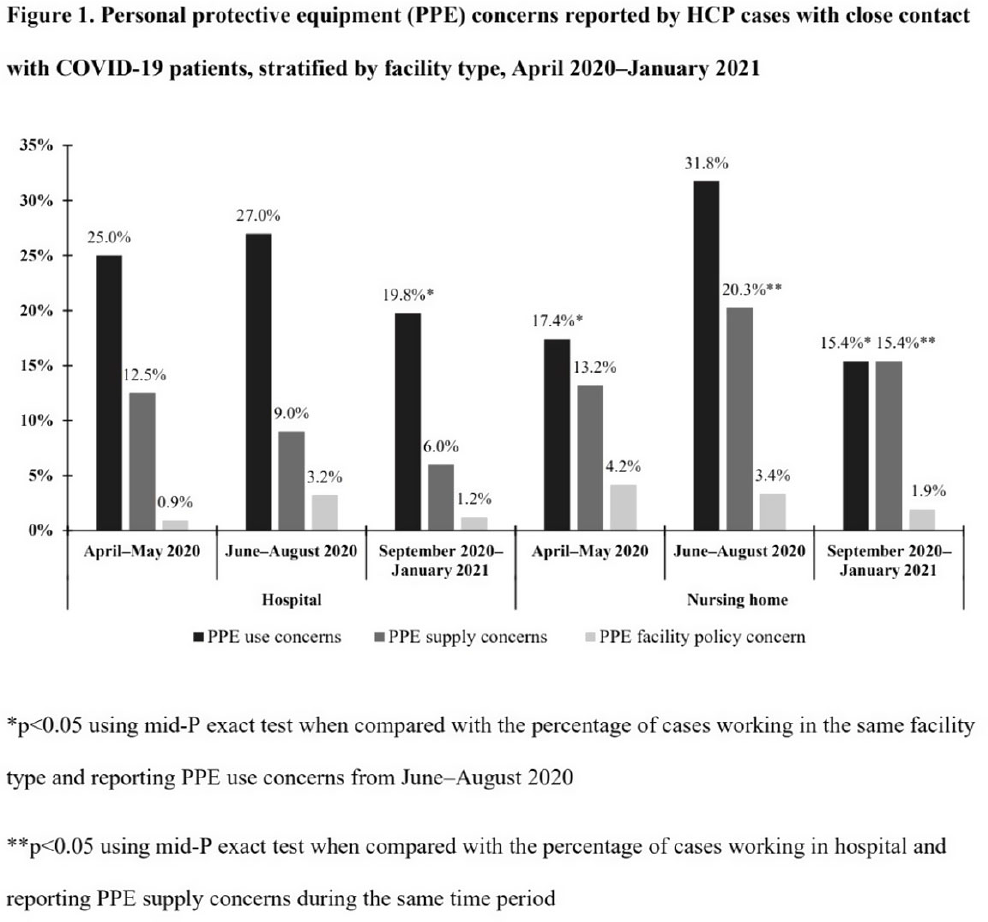
Characteristics of healthcare personnel who reported concerns related to PPE use during care of COVID-19 patients
-
- Journal:
- Antimicrobial Stewardship & Healthcare Epidemiology / Volume 2 / Issue S1 / July 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 May 2022, pp. s8-s9
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Learning by Doing: Using an Undergraduate Research Lab to Promote Diversity and Inclusion
-
- Journal:
- PS: Political Science & Politics / Volume 55 / Issue 2 / April 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 January 2022, pp. 413-418
- Print publication:
- April 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Compounding and complementary carnivores: Australian bird species eaten by the introduced European red fox Vulpes vulpes and domestic cat Felis catus
-
- Journal:
- Bird Conservation International / Volume 32 / Issue 3 / September 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 December 2021, pp. 506-522
-
- Article
- Export citation
Frequent detection of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) RNA on hands and skin of patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 43 / Issue 12 / December 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 September 2021, pp. 1976-1977
- Print publication:
- December 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation