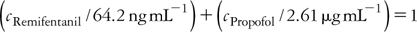31 results
Annual bluegrass weevil (Listronotus maculicollis) and paclobutrazol control annual bluegrass (Poa annua) in creeping bentgrass fairways
-
- Journal:
- Weed Technology / Volume 36 / Issue 1 / February 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 January 2022, pp. 137-144
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Reductions in inpatient fluoroquinolone use and postdischarge Clostridioides difficile infection (CDI) from a systemwide antimicrobial stewardship intervention
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Antimicrobial Stewardship & Healthcare Epidemiology / Volume 1 / Issue 1 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 October 2021, e32
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Two faces of rem sleep in normal and psychopathological development
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 26 / Issue S2 / March 2011
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 April 2020, pp. 422-423
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
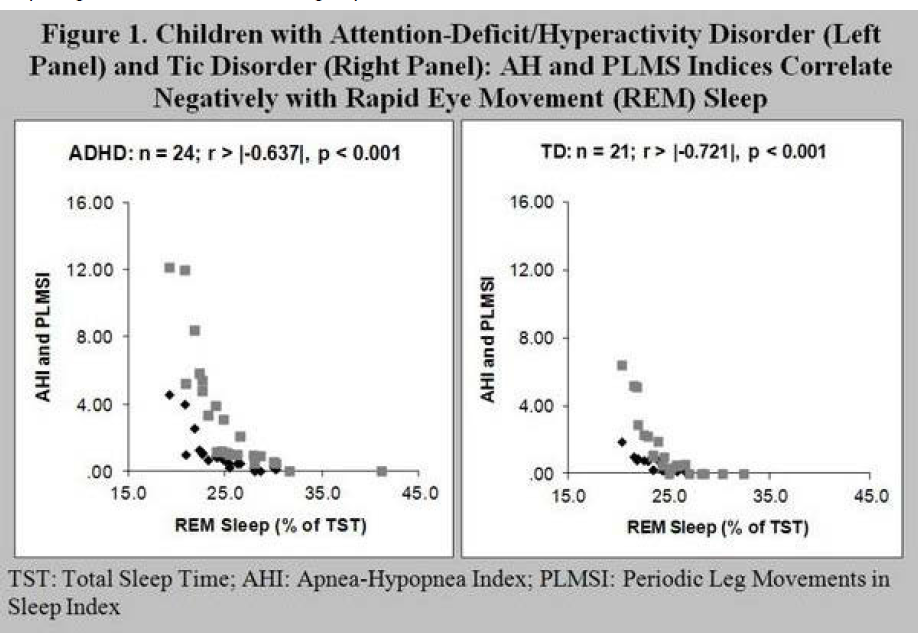
922 – Increased Frequency Of Sdb And Plms Is Associated With Lower Rem-sleep Amount In Common Child Psychopathology And Normally Developing Children
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 28 / Issue S1 / 2013
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 April 2020, 28-E365
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
The impact of an electronic medical record nudge on reducing testing for hospital-onset Clostridioides difficile infection
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 41 / Issue 4 / April 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 February 2020, pp. 411-417
- Print publication:
- April 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation
Abundance of beige and brown adipocyte markers in different adipose depots of cattle at 26 months of age
-
- Journal:
- Advances in Animal Biosciences / Volume 8 / Issue s1 / October 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 October 2017, pp. s38-s41
- Print publication:
- October 2017
-
- Article
- Export citation
Resolution-dependent performance of grounding line motion in a shallow model compared with a full-Stokes model according to the MISMIP3d intercomparison
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Glaciology / Volume 60 / Issue 220 / 2014
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 July 2017, pp. 353-360
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Triadic resonances in precessing rapidly rotating cylinder flows
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 778 / 10 September 2015
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 July 2015, R1
-
- Article
- Export citation
Methods for Scanning Transmission Electron Microscopy High Angle Annular Dark Field Based for Three Dimensional Analysis of the Local Composition in Solid Alloys
-
- Journal:
- Microscopy and Microanalysis / Volume 20 / Issue S3 / August 2014
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 August 2014, pp. 594-595
- Print publication:
- August 2014
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Ambulatory-treated Clostridium difficile infection: a comparison of community-acquired vs. nosocomial infection
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 143 / Issue 6 / April 2015
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 July 2014, pp. 1225-1235
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Wafer-Scale Ion Beam Lithography of Nanopore Devices
-
- Journal:
- Microscopy and Microanalysis / Volume 19 / Issue S2 / August 2013
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 October 2013, pp. 912-913
- Print publication:
- August 2013
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Contributors
-
-
- Book:
- Scanning Electron Microscopy for the Life Sciences
- Published online:
- 05 January 2013
- Print publication:
- 06 December 2012, pp ix-xii
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Familiality of neural preparation and response control in childhood attention deficit-hyperactivity disorder
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 43 / Issue 9 / September 2013
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 December 2012, pp. 1997-2011
-
- Article
- Export citation
Assessment of the effectiveness of South Africa's marine protected areas at representing ichthyofaunal communities
-
- Journal:
- Environmental Conservation / Volume 39 / Issue 3 / September 2012
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 April 2012, pp. 259-270
-
- Article
- Export citation
Contributors
-
-
- Book:
- The Cambridge Dictionary of Christianity
- Published online:
- 05 August 2012
- Print publication:
- 20 September 2010, pp xi-xliv
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
The relationship between ADHD and key cognitive phenotypes is not mediated by shared familial effects with IQ
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 41 / Issue 4 / April 2011
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 June 2010, pp. 861-871
-
- Article
- Export citation
Duration discrimination in the range of milliseconds and seconds in children with ADHD and their unaffected siblings
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 39 / Issue 10 / October 2009
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 March 2009, pp. 1745-1751
-
- Article
- Export citation
Post-resuscitation haemodynamics in a novel acute myocardial infarction cardiac arrest model in the pig
-
- Journal:
- European Journal of Anaesthesiology / Volume 24 / Issue 7 / July 2007
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 July 2007, pp. 580-588
- Print publication:
- July 2007
-
- Article
- Export citation
Functionalized Porous Silicon in a Simulated Gastrointestinal Tract: Modeling the Biocompatibility of a Monolayer Protected Nanostructured Material
-
- Journal:
- MRS Online Proceedings Library Archive / Volume 1063 / 2007
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 February 2011, 1063-OO06-01
- Print publication:
- 2007
-
- Article
- Export citation
Modelling the pharmacodynamic interaction between remifentanil and propofol by EEG-controlled dosing
-
- Journal:
- European Journal of Anaesthesiology / Volume 20 / Issue 5 / May 2003
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 June 2005, pp. 373-379
- Print publication:
- May 2003
-
- Article
- Export citation