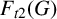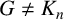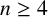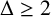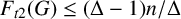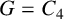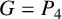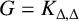183 results
Relationship between syncopal symptoms and head-up tilt test modes
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 April 2024, pp. 1-6
-
- Article
- Export citation
Numerical study on the mechanism of drag modulation by dispersed drops in two-phase Taylor–Couette turbulence
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 984 / 10 April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 April 2024, R3
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Effect of gender identity on the association between gender dysphoria and suicidality via appearance anxiety among transgender and gender-diverse young people: moderated mediation study
-
- Journal:
- BJPsych Open / Volume 10 / Issue 2 / March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 March 2024, e66
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Preparation and Properties of Sepiolite-Based 3D Flame-Retardant Aerogel
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 70 / Issue 6 / December 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 865-881
-
- Article
- Export citation
Prediction of swelling characteristics of compacted GMZ bentonite in salt solution incorporating ion-exchange reactions
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 67 / Issue 2 / 15 April 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 163-172
-
- Article
- Export citation
Overexpressed Histocompatibility Minor 13 was Associated with Liver Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression and Prognosis
-
- Journal:
- Genetics Research / Volume 2022 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e23
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
6 Why Do Cultures Affect Facial Emotion Perception? - A Systematic Review
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 29 / Issue s1 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 December 2023, p. 520
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Dietary chenodeoxycholic acid attenuates high-fat diet-induced growth retardation, lipid accumulation and bile acid metabolism disorder in the liver of yellow catfish Pelteobagrus fulvidraco
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 131 / Issue 6 / 28 March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 October 2023, pp. 921-934
- Print publication:
- 28 March 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Fat-free mass may play a dominant role in the association between systolic blood pressure and body composition in children and adolescents
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 131 / Issue 4 / 28 February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 September 2023, pp. 622-629
- Print publication:
- 28 February 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Geochemistry, zircon U–Pb geochronology and Hf isotope of the early Permian gabbro and high-Mg diorites from the Zhusileng–Hangwula Belt in the northern Alxa area: Petrogenesis and tectonic implications
-
- Journal:
- Geological Magazine / Volume 160 / Issue 7 / July 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 August 2023, pp. 1417-1427
-
- Article
- Export citation
UPPER BOUNDS ON THE SEMITOTAL FORCING NUMBER OF GRAPHS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 109 / Issue 2 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 June 2023, pp. 177-185
- Print publication:
- April 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Measurement of electron beam transverse slice emittance using a focused beamline
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 11 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 March 2023, e36
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The first discovery of Lochkovian (Lower Devonian) conodonts in central Guangxi, South China and its geological implications
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Paleontology / Volume 97 / Issue 2 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 February 2023, pp. 421-433
-
- Article
- Export citation
Ultra-broadband pulse generation via hollow-core fiber compression and frequency doubling for ultra-intense lasers
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 11 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 January 2023, e5
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Foreground-background salience effect in traffic risk communication
-
- Journal:
- Judgment and Decision Making / Volume 9 / Issue 1 / January 2014
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2023, pp. 83-89
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Dispersion management for a 100 PW level laser using a mismatched-grating compressor
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 10 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 November 2022, e38
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
13 - Tonal Processes Defined as Articulatory-based Contextual Tonal Variation
- from Part Three - Phonetic-phonological Issues in Chinese
-
-
- Book:
- The Cambridge Handbook of Chinese Linguistics
- Published online:
- 04 August 2022
- Print publication:
- 18 August 2022, pp 275-290
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Forty-five terawatt vortex ultrashort laser pulses from a chirped-pulse amplification system
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 10 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 August 2022, e32
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Attitudes and Factors Associated With Intention to the Third Dose of COVID-19 Vaccine Among Adolescents: A Cross-Sectional Survey in 3 Provinces of China
-
- Journal:
- Disaster Medicine and Public Health Preparedness / Volume 17 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 July 2022, e201
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Effect of cloud-based information systems on the agile development of industrial business process management
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Management & Organization / Volume 29 / Issue 4 / July 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 June 2022, pp. 614-631
-
- Article
- Export citation