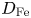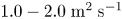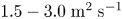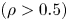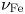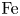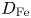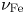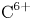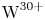86 results
Shared genetic basis and causality between schizophrenia and inflammatory bowel disease: evidence from a comprehensive genetic analysis
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 April 2024, pp. 1-11
-
- Article
- Export citation
Airfoil response to periodic vertical and longitudinal gusts
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 979 / 25 January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 January 2024, A35
-
- Article
- Export citation
Inverse association between maternal serum concentrations of trace elements and risk of spontaneous preterm birth: a nested case–control study in China
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 131 / Issue 8 / 28 April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 January 2024, pp. 1425-1435
- Print publication:
- 28 April 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Voltage-gated sodium channel gene mutation and P450 gene expression are associated with the resistance of Aphis spiraecola Patch (Hemiptera: Aphididae) to lambda-cyhalothrin
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of Entomological Research / Volume 114 / Issue 1 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 January 2024, pp. 49-56
-
- Article
- Export citation
Advanced Glycation End Products’ Receptor DNA Methylation Associated with Immune Infiltration and Prognosis of Lung Adenocarcinoma and Lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma
-
- Journal:
- Genetics Research / Volume 2023 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e4
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Dispersion and Swellability of Ternary Surfactant Co-Modified Montmorillonites
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 69 / Issue 6 / December 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 759-771
-
- Article
- Export citation
Comprehensive Multiomics Analysis of Monozygotic Twin Discordant for Double Outlet Right Ventricle
-
- Journal:
- Twin Research and Human Genetics / Volume 26 / Issue 6 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 December 2023, pp. 370-378
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Genetic and Environmental Influences on Blood Pressure and Serum Lipids Across Age-Groups
-
- Journal:
- Twin Research and Human Genetics / Volume 26 / Issue 3 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 August 2023, pp. 223-230
-
- Article
- Export citation
The complete mitochondrial genome of Ogmocotyle ailuri: gene content, composition and rearrangement and phylogenetic implications
-
- Journal:
- Parasitology / Volume 150 / Issue 8 / July 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 April 2023, pp. 661-671
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Re-exploration of dietary iodine intake in Chinese adult males using a modified iodine balance study
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 130 / Issue 8 / 28 October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 March 2023, pp. 1308-1315
- Print publication:
- 28 October 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Exploring the Genetic Association between Obesity and Serum Lipid Levels Using Bivariate Methods
-
- Journal:
- Twin Research and Human Genetics / Volume 25 / Issue 6 / December 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 January 2023, pp. 234-244
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
The green lacewing Chrysopa formosa as a potential biocontrol agent for managing Spodoptera frugiperda and Spodoptera litura
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of Entomological Research / Volume 113 / Issue 1 / February 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 July 2022, pp. 49-62
-
- Article
- Export citation
Geometric morphometric analysis for the systematic elucidation of new Hylicellidae from the Jurassic of China (Hemiptera: Cicadomorpha)
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Paleontology / Volume 96 / Issue 5 / September 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 May 2022, pp. 1119-1131
-
- Article
- Export citation
A Comparison of Preterm Birth Rate and Growth from Birth to 18 Years Old between in Vitro Fertilization and Spontaneous Conception of Twins
-
- Journal:
- Twin Research and Human Genetics / Volume 24 / Issue 4 / August 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 September 2021, pp. 228-233
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Individual SFA intake and risk of overweight/obesity: findings from a population-based nationwide cohort study
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 128 / Issue 1 / 14 July 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 August 2021, pp. 75-83
- Print publication:
- 14 July 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Associations of Obesity Measurements with Serum Metabolomic Profile: A Chinese Twin Study
-
- Journal:
- Twin Research and Human Genetics / Volume 24 / Issue 1 / February 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 April 2021, pp. 14-21
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Experimental and simulation study of impurity transport response to RMPs in RF-heated H-mode plasmas at EAST
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Plasma Physics / Volume 87 / Issue 2 / April 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 March 2021, 905870213
-
- Article
- Export citation