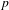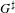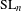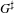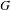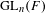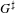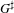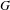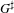76 results
Empowering the Participant Voice (EPV): Design and implementation of collaborative infrastructure to collect research participant experience feedback at scale
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 8 / Issue 1 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 February 2024, e40
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The association between symptom burden and processing speed and executive functioning at 4 and 12 weeks following pediatric concussion
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 January 2024, pp. 1-13
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Racial and ethnic disparities in COVID-19 diagnosis and adherence to mitigation behaviours in a national United States older adult sample
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 151 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 October 2023, e175
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Optimising motor development in the hospitalised infant with CHD: factors contributing to early motor challenges and recommendations for assessment and intervention
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 33 / Issue 10 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 September 2023, pp. 1800-1812
-
- Article
- Export citation
Identifying structural brain markers of resilience to adversity in young people using voxel-based morphometry
-
- Journal:
- Development and Psychopathology / Volume 35 / Issue 5 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 July 2023, pp. 2302-2314
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Evaluating the feasibility and acceptability of the Mood Assessment Post-Stroke (MAPS) mood screening training
-
- Journal:
- Brain Impairment / Volume 24 / Issue 3 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 December 2022, pp. 679-695
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Has the COVID-19 pandemic influenced suicide rates differentially according to socioeconomic indices and ethnicity? More evidence is needed globally
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology and Psychiatric Sciences / Volume 31 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 October 2022, e72
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on presentations to health services following self-harm: systematic review
-
- Journal:
- The British Journal of Psychiatry / Volume 221 / Issue 4 / October 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 July 2022, pp. 603-612
- Print publication:
- October 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The mental health of NHS staff during the COVID-19 pandemic: two-wave Scottish cohort study
-
- Journal:
- BJPsych Open / Volume 8 / Issue 1 / January 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 January 2022, e23
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Chapter 5 - A Sociological Perspective on Psychiatric Epidemiology in Britain
- from Part I - Social and Institutional Contexts
-
-
- Book:
- Mind, State and Society
- Published online:
- 17 June 2021
- Print publication:
- 24 June 2021, pp 41-48
-
- Chapter
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Positive and negative parenting in conduct disorder with high versus low levels of callous–unemotional traits
-
- Journal:
- Development and Psychopathology / Volume 33 / Issue 3 / August 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 June 2020, pp. 980-991
-
- Article
- Export citation
Two-month consumption of bread enriched with a fiber mix: impact on gut microbiota and cardiometabolic profile in at cardiometabolic-risk subjects.
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Nutrition Society / Volume 79 / Issue OCE2 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 June 2020, E135
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Chapter 3 - A Sociological View of Mental Health and Illness
- from Section 1 - Conceptual Basis and Overarching Themes
-
-
- Book:
- Primary Care Mental Health
- Published online:
- 10 September 2018
- Print publication:
- 20 September 2018, pp 24-38
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
VP88 Transient Ischaemic Attack Referral (TIER) Intervention Development
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Technology Assessment in Health Care / Volume 33 / Issue S1 / 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 January 2018, pp. 189-190
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Leafy Spurge (Euphorbia esula) Control and Grass Injury with Sulfometuron
-
- Journal:
- Weed Technology / Volume 7 / Issue 1 / March 1993
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 June 2017, pp. 212-215
-
- Article
- Export citation
Older men's perceptions of the need for and access to male-focused community programmes such as Men's Sheds
-
- Journal:
- Ageing & Society / Volume 38 / Issue 4 / April 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 December 2016, pp. 794-816
- Print publication:
- April 2018
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A study of the effects of prenatal alcohol exposure on white matter microstructural integrity at birth
-
- Journal:
- Acta Neuropsychiatrica / Volume 27 / Issue 4 / August 2015
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 May 2015, pp. 197-205
-
- Article
- Export citation
HECKE ALGEBRAS FOR INNER FORMS OF
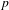 $p$-ADIC SPECIAL LINEAR GROUPS
$p$-ADIC SPECIAL LINEAR GROUPS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Institute of Mathematics of Jussieu / Volume 16 / Issue 2 / April 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 May 2015, pp. 351-419
- Print publication:
- April 2017
-
- Article
- Export citation
Contributors
-
-
- Book:
- The Cambridge Dictionary of Philosophy
- Published online:
- 05 August 2015
- Print publication:
- 27 April 2015, pp ix-xxx
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Contributors
-
-
- Book:
- Clinical Gynecology
- Published online:
- 05 April 2015
- Print publication:
- 23 April 2015, pp viii-xiv
-
- Chapter
- Export citation