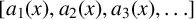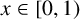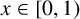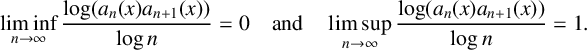12487 results

Web3
- Blockchain, the New Economy, and the Self-Sovereign Internet
- Coming soon
-
- Expected online publication date:
- August 2024
- Print publication:
- 31 August 2024
-
- Book
- Export citation

Laws of Physics
- Coming soon
-
- Expected online publication date:
- July 2024
- Print publication:
- 31 July 2024
-
- Element
- Export citation

Algebraic Varieties: Minimal Models and Finite Generation
- Coming soon
-
- Expected online publication date:
- May 2024
- Print publication:
- 31 May 2024
-
- Book
- Export citation

Charting America's Cold War Waters in East Asia
- Sovereignty, Local Interests, and International Security
- Coming soon
-
- Expected online publication date:
- May 2024
- Print publication:
- 31 May 2024
-
- Book
- Export citation
The design and optimization methods towards 10 kW high beam quality fiber laser based on counter tandem pumping scheme
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 April 2024, pp. 1-19
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Precise mode control of mid-infrared high-power laser diode using on-chip advanced sawtooth waveguide designs
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 April 2024, pp. 1-14
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
The role of psychosis and clozapine load in excessive checking in treatment-resistant schizophrenia: longitudinal observational study
-
- Journal:
- The British Journal of Psychiatry / Volume 224 / Issue 5 / May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 April 2024, pp. 164-169
- Print publication:
- May 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Spectral proper orthogonal decomposition of time-resolved three-dimensional flow measurements in the turbulent wake of the Ahmed body
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 985 / 25 April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 April 2024, A19
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Lateralised courtship behaviour and its impact on mating success in Ostrinia furnacalis (Lepidoptera: Crambidae)
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of Entomological Research , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 April 2024, pp. 1-9
-
- Article
- Export citation
Mendelian randomization: causal inference leveraging genetic data
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 April 2024, pp. 1-14
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Letter from the Editor
-
- Journal:
- Management and Organization Review , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 April 2024, pp. 1-2
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Toward standardization, harmonization, and integration of social determinants of health data: A Texas Clinical and Translational Science Award institutions collaboration – CORRIGENDUM
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 8 / Issue 1 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 April 2024, e62
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Genetic Causal Relationship Between Alanine Aminotransferase Levels and Risk of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: Mendelian Randomization Analysis Based on Two Samples
-
- Journal:
- Twin Research and Human Genetics , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 April 2024, pp. 1-5
-
- Article
- Export citation
ASYMPTOTIC BEHAVIOUR FOR PRODUCTS OF CONSECUTIVE PARTIAL QUOTIENTS IN CONTINUED FRACTIONS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 April 2024, pp. 1-12
-
- Article
- Export citation
Effectiveness of GLIM and SGA for diagnosing malnutrition and predicting wound healing in patients with diabetic foot ulcers
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 April 2024, pp. 1-30
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Case 2: - The man who is confused about his identity
-
-
- Book:
- Case Studies: Stahl's Essential Psychopharmacology
- Published online:
- 03 April 2024
- Print publication:
- 18 April 2024, pp 21-38
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Population and contact tracer uptake of New Zealand’s QR-code-based digital contact tracing app for Covid-19
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 April 2024, pp. 1-20
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
THE WARING PROBLEM FOR UPPER TRIANGULAR MATRIX ALGEBRAS
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Mathematics / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 April 2024, pp. 1-25
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Effects of retrieval schedules on the acquisition of explicit, automatized-explicit, and implicit knowledge of L2 collocations
-
- Journal:
- Studies in Second Language Acquisition , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 April 2024, pp. 1-23
-
- Article
- Export citation