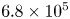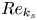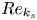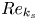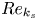113 results
The influence of surface roughness on postcritical flow over circular cylinders revisited – CORRIGENDUM
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 979 / 25 January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 January 2024, E1
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The influence of surface roughness on postcritical flow over circular cylinders revisited
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 975 / 25 November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 November 2023, A36
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
International Comparison of Ambulance Times Terminology and Definitions: A Benchmarking Study
-
- Journal:
- Prehospital and Disaster Medicine / Volume 38 / Issue S1 / May 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 July 2023, pp. s168-s169
- Print publication:
- May 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Temporal Trends of Ambulance Times for Suspected Stroke/Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA) Before and During the COVID-19 Pandemic in Ireland: A Retrospective Cohort Study
-
- Journal:
- Prehospital and Disaster Medicine / Volume 38 / Issue S1 / May 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 July 2023, p. s40
- Print publication:
- May 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
The double backward-facing step: effect of forcing on interacting separated flow regions
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 946 / 10 September 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 August 2022, A9
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The double backward-facing step: interaction of multiple separated flow regions
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 936 / 10 April 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 February 2022, A29
-
- Article
- Export citation
8 - Religious Experience in Buddhism
- from Part III - Religious Experience Outside Traditional Monotheism
-
-
- Book:
- The Cambridge Companion to Religious Experience
- Published online:
- 20 June 2020
- Print publication:
- 16 July 2020, pp 187-207
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Planning for patient-reported outcome implementation: Development of decision tools and practical experience across four clinics
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 4 / Issue 6 / December 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 April 2020, pp. 498-507
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Avoiding the white elephants: A new approach to infrastructure planning at the 2018 Gold Coast Commonwealth Games?
-
- Journal:
- Queensland Review / Volume 26 / Issue 1 / June 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 June 2019, pp. 128-146
- Print publication:
- June 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation
Nanoscale Chemical Variations at Boundaries in a BaCe0.8Y0.2O3-δ – Ce0.8Y0.2O3-δ Dual Phase Hydrogen Separation Membrane
-
- Journal:
- Microscopy and Microanalysis / Volume 23 / Issue S1 / July 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 August 2017, pp. 684-685
- Print publication:
- July 2017
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Utilizing Atom Probe Tomography for 3-D Quantification of Point Defects
-
- Journal:
- Microscopy and Microanalysis / Volume 23 / Issue S1 / July 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 August 2017, pp. 1574-1575
- Print publication:
- July 2017
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Effect of Sethoxydim and Haloxyfop on Acetyl-Coenzyme a Carboxylase Activity in Festuca Species
-
- Journal:
- Weed Science / Volume 37 / Issue 4 / July 1989
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 June 2017, pp. 512-516
-
- Article
- Export citation
Effect of BAS 145 138, CGA 154 281, and Naphthalic Anhydride Seed Treatments on Sweet Corn (Zea mays) Tolerance to Nicosulfuron
-
- Journal:
- Weed Science / Volume 42 / Issue 4 / December 1994
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 June 2017, pp. 614-617
-
- Article
- Export citation
Safening Influence of LAB 145 138 on Nicosulfuron, Terbufos and Bentazon Interactions in Sweet Corn (Zea mays)
-
- Journal:
- Weed Science / Volume 44 / Issue 2 / June 1996
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 June 2017, pp. 339-344
-
- Article
- Export citation
The Behavioral Revolution and International Relations
-
- Journal:
- International Organization / Volume 71 / Issue S1 / April 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 April 2017, pp. S1-S31
- Print publication:
- April 2017
-
- Article
- Export citation
20 - Contraception, pregnancy, the puerperium and breastfeeding
- from Section II - Medical specialties
-
-
- Book:
- Essentials of Physical Health in Psychiatry
- Published by:
- Royal College of Psychiatrists
- Published online:
- 25 February 2017, pp 265-281
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
19 - Sexual health
- from Section II - Medical specialties
-
-
- Book:
- Essentials of Physical Health in Psychiatry
- Published by:
- Royal College of Psychiatrists
- Published online:
- 25 February 2017, pp 250-264
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Altered weed reproduction and maternal effects under low-nitrogen fertility
-
- Journal:
- Weed Science / Volume 54 / Issue 5 / October 2006
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 January 2017, pp. 847-853
-
- Article
- Export citation
Doveweed (Murdannia nudiflora) germination and emergence as affected by temperature and seed burial depth
-
- Journal:
- Weed Science / Volume 54 / Issue 6 / December 2006
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 January 2017, pp. 1000-1003
-
- Article
- Export citation
Interference and Control of Glyphosate-Resistant and -Susceptible Palmer Amaranth (Amaranthus palmeri) Populations under Greenhouse Conditions
-
- Journal:
- Weed Science / Volume 61 / Issue 2 / June 2013
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 January 2017, pp. 259-266
-
- Article
- Export citation