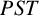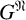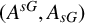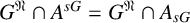663 results
Mendelian randomization: causal inference leveraging genetic data
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 April 2024, pp. 1-14
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A CHARACTERISATION OF SOLUBLE
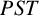 ${PST}$-GROUPS
${PST}$-GROUPS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 March 2024, pp. 1-8
-
- Article
- Export citation
Family risk, parental cortisol contagion, and parenting: A process-oriented approach to spillover
-
- Journal:
- Development and Psychopathology , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 March 2024, pp. 1-15
-
- Article
- Export citation
FC40: Social health and subsequent cognitive capability: examining the potential mediating roles of depression symptoms and inflammatory biomarker
-
- Journal:
- International Psychogeriatrics / Volume 35 / Issue S1 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 February 2024, pp. 102-103
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Longitudinal Beam Dynamics for the Heavy-Ion Synchrotron Booster Ring at HIAF
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 2021 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e4
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Introduction to a Special Issue on Molecular Computer Simulations of Clays and Clay-Water Interfaces: Recent Progress, Challenges, and Opportunities
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 64 / Issue 4 / August 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 335-336
-
- Article
- Export citation
F.6 Cranial neurosurgery medicolegal cases in Canada: a ten-year analysis of Canadian Medical Protective Association (CMPA) data
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 50 / Issue s2 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 June 2023, p. S57
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
F.3 Comprehensive multiplatform analysis of CDKN2A alterations in meningiomas
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 50 / Issue s2 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 June 2023, p. S56
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Polymer-coated urea application can increase both grain yield and nitrogen use efficiency in japonica-indica hybrid rice
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Agricultural Science / Volume 161 / Issue 1 / January 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 November 2022, pp. 51-59
-
- Article
- Export citation
An ex-Gaussian analysis of eye movements in L2 reading
-
- Journal:
- Bilingualism: Language and Cognition / Volume 26 / Issue 2 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 November 2022, pp. 330-344
-
- Article
- Export citation
Normalizing Diversity in Merit Review Forms
-
- Journal:
- PS: Political Science & Politics / Volume 56 / Issue 1 / January 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 October 2022, pp. 123-127
- Print publication:
- January 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
UAV swarm collaborative coverage control using GV division and planning algorithm
-
- Journal:
- The Aeronautical Journal / Volume 127 / Issue 1309 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 September 2022, pp. 446-465
-
- Article
- Export citation
Prediction and copy number variation identification of ZNF146 gene related to growth traits in Chinese cattle
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Agricultural Science / Volume 160 / Issue 5 / October 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 August 2022, pp. 404-412
-
- Article
- Export citation
Cryogenic Electron Microscopy Combined with Energy-Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy Tomography for Materials Science
-
- Journal:
- Microscopy and Microanalysis / Volume 28 / Issue S1 / August 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 July 2022, pp. 328-330
- Print publication:
- August 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Data Synchronization in Operando Gas and Heating TEM
-
- Journal:
- Microscopy and Microanalysis / Volume 28 / Issue S1 / August 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 July 2022, pp. 1872-1873
- Print publication:
- August 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Integration of Gas-Cell TEM, Nano-calorimetry and RGA on Oscillating Phenomena at High Temperatures in Catalysis
-
- Journal:
- Microscopy and Microanalysis / Volume 28 / Issue S1 / August 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 July 2022, pp. 2118-2119
- Print publication:
- August 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Responding to Repeated Disasters: Time to Recovery in Public Health Workers
-
- Journal:
- Disaster Medicine and Public Health Preparedness / Volume 17 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 June 2022, e172
-
- Article
- Export citation
GP.5 Identifying clinically relevant prognostic epigenetic subtypes of chordoma and their non-invasive detection in plasma
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 49 / Issue s1 / June 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 June 2022, p. S2
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
340 Machine Learning Segmentation of Amyloid Load in Ligamentum Flavum Specimens From Spinal Stenosis Patients
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 6 / Issue s1 / April 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 April 2022, p. 63
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Cooperative guidance law for intercepting a hypersonic target with impact angle constraint
-
- Journal:
- The Aeronautical Journal / Volume 126 / Issue 1300 / June 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 January 2022, pp. 1026-1044
-
- Article
- Export citation