98 results
Validation of resonance Raman spectroscopy-measured skin carotenoid status as a biomarker for fruit and vegetable intake in Korean adults
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 130 / Issue 11 / 14 December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 May 2023, pp. 1993-2001
- Print publication:
- 14 December 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Application of Deep Learning to Solar and Space Weather Data
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the International Astronomical Union / Volume 18 / Issue S372 / August 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 September 2023, pp. 131-149
- Print publication:
- August 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
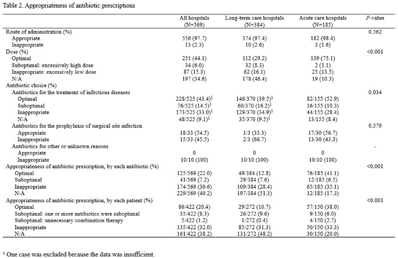
Prescriptions patterns and appropriateness of usage of antibiotics in small and medium- sized hospitals in Korea
-
- Journal:
- Antimicrobial Stewardship & Healthcare Epidemiology / Volume 2 / Issue S1 / July 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 May 2022, p. s19
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Paediatric heart transplantation recipients ≥7 years of age receiving donors with pre-existing coronary atherosclerosis showed progressive coronary artery disease
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 32 / Issue 7 / July 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 September 2021, pp. 1104-1111
-
- Article
- Export citation
LONG-TERM CHANGES IN 14C AGE DIFFERENCES BETWEEN HUMIC ACID AND PLANT FRAGMENTS AND THEIR LINKS TO PAST CLIMATE CHANGE
-
- Journal:
- Radiocarbon / Volume 63 / Issue 1 / February 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 December 2020, pp. 139-153
- Print publication:
- February 2021
-
- Article
- Export citation
Clinical impact of early reinsertion of a central venous catheter after catheter removal in patients with catheter-related bloodstream infections
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 42 / Issue 2 / February 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 September 2020, pp. 162-168
- Print publication:
- February 2021
-
- Article
- Export citation
Migraine with Aura as a Stroke Mimic
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 47 / Issue 2 / March 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 October 2019, pp. 242-244
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Alexithymia and frontal–amygdala functional connectivity in North Korean refugees
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 50 / Issue 2 / January 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 February 2019, pp. 334-341
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene):sulfonated poly(diphenylacetylene) complex as a hole injection material in organic light-emitting diodes
-
- Journal:
- MRS Communications / Volume 7 / Issue 3 / September 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 August 2017, pp. 701-708
- Print publication:
- September 2017
-
- Article
- Export citation
Distress and body image due to altered appearance in posttreatment and active treatment of breast cancer patients and in general population controls
-
- Journal:
- Palliative & Supportive Care / Volume 16 / Issue 2 / April 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 March 2017, pp. 137-145
-
- Article
- Export citation
Effects of the Saemangeum Reclamation Project on migratory shorebird staging in the Saemangeum and Geum Estuaries, South Korea
-
- Journal:
- Bird Conservation International / Volume 28 / Issue 2 / June 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 February 2017, pp. 238-250
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Serologic Evaluation of MERS Screening Strategy for Healthcare Personnel During a Hospital-Associated Outbreak
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 38 / Issue 2 / February 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 November 2016, pp. 234-238
- Print publication:
- February 2017
-
- Article
- Export citation
Influence of personality on depression, burden, and health-related quality of life in family caregivers of persons with dementia
-
- Journal:
- International Psychogeriatrics / Volume 29 / Issue 2 / February 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 October 2016, pp. 227-237
-
- Article
- Export citation
Do we always need gelfoam packing in the middle ear cavity during tympanoplasty?: Presenting Author: Woo Jin Kim
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Laryngology & Otology / Volume 130 / Issue S3 / May 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 June 2016, p. S191
- Print publication:
- May 2016
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
A pilot study to investigate the therapeutic effect of Valsalva maneuver on otitis media with effusion in adults: Presenting Author: Jung ju Han
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Laryngology & Otology / Volume 130 / Issue S3 / May 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 June 2016, p. S170
- Print publication:
- May 2016
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Identification of novel potential biomarkers and signaling pathways related to otitis media induced by diesel exhaust particle in in vivo system via transcriptomic analysis: Presenting Author: Moo Kyun Park
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Laryngology & Otology / Volume 130 / Issue S3 / May 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 June 2016, pp. S190-S191
- Print publication:
- May 2016
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
In-line Monitoring of Grain Size Distribution of Channel Poly Si used in 3D NAND Flash Memory Devices using Multiwavelength Raman Spectroscopy
-
- Journal:
- MRS Advances / Volume 1 / Issue 5 / 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 January 2016, pp. 339-348
- Print publication:
- 2016
-
- Article
- Export citation