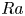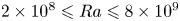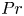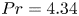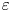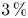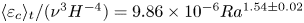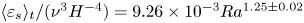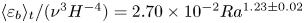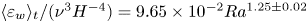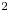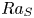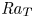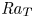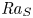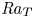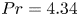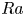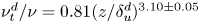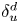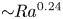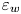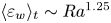47 results
Experimental measurement of spatio-temporally resolved energy dissipation rate in turbulent Rayleigh–Bénard convection
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 984 / 10 April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 March 2024, A8
-
- Article
- Export citation
Upregulation of miR-21-5p rescues the inhibition of cardiomyocyte proliferation induced by high glucose through negative regulation of Rhob
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Developmental Origins of Health and Disease / Volume 14 / Issue 5 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 December 2023, pp. 670-677
-
- Article
- Export citation
Effects of the geothermal gradient on the convective dissolution in CO2 sequestration
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 963 / 25 May 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 May 2023, A23
-
- Article
- Export citation
Measurement of electron beam transverse slice emittance using a focused beamline
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 11 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 March 2023, e36
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Peripartum women’s perspectives on research study participation in the OneFlorida Clinical Research Consortium during COVID-19 pandemic
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 7 / Issue 1 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 October 2022, e24
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Three-dimensional properties of the viscous boundary layer in turbulent Rayleigh–Bénard convection
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 947 / 25 September 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 August 2022, A15
-
- Article
- Export citation
Epidemiologic characteristics and influencing factors of cluster infection of COVID-19 in Jiangsu Province
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 149 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 February 2021, e48
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Temperature and humidity associated with increases in tuberculosis notifications: a time-series study in Hong Kong
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 149 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 December 2020, e8
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Effects of resistant starch on glycaemic control: a systematic review and meta-analysis
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 125 / Issue 11 / 14 June 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 September 2020, pp. 1260-1269
- Print publication:
- 14 June 2021
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Evaluation of gray matter reduction in patients with typhoon-related posttraumatic stress disorder using causal network analysis of structural MRI
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 52 / Issue 8 / June 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 September 2020, pp. 1481-1490
-
- Article
- Export citation
Increased vegetable and fruit intake is associated with reduced failure rate of tuberculosis treatment: a hospital-based cohort study in China
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 125 / Issue 8 / 28 April 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 September 2020, pp. 926-933
- Print publication:
- 28 April 2021
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Associations of early-life exposure to famine with abdominal fat accumulation are independent of family history of diabetes and physical activity
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 125 / Issue 8 / 28 April 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 September 2020, pp. 943-950
- Print publication:
- 28 April 2021
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3 over cerium–tungsten–titanium mixed oxide catalyst: Synergistic promotional effect of H2O2 and Ce4+
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 35 / Issue 16 / 28 August 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 August 2020, pp. 2218-2229
- Print publication:
- 28 August 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation
In-situ Observation of Magnetic Skyrmion Crystal Growth from the Conical Phase
-
- Journal:
- Microscopy and Microanalysis / Volume 26 / Issue S2 / August 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 July 2020, pp. 1764-1765
- Print publication:
- August 2020
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Damage behavior of heterogeneous magnesium matrix nanocomposites
-
- Journal:
- MRS Communications / Volume 10 / Issue 2 / June 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 May 2020, pp. 359-364
- Print publication:
- June 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation
Materials Data Science for Microstructural Characterization of Archaeological Concrete
-
- Journal:
- MRS Advances / Volume 5 / Issue 7 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 February 2020, pp. 305-318
- Print publication:
- 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation
Influenza activity prediction using meteorological factors in a warm temperate to subtropical transitional zone, Eastern China
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 147 / 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 December 2019, e325
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Multilocus sequence typing and clonal population genetic structure of Cyclospora cayetanensis in humans
-
- Journal:
- Parasitology / Volume 144 / Issue 14 / December 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 July 2017, pp. 1890-1897
-
- Article
- Export citation