338 results
South East Asian Nutrition Surveys (SEANUTS) II - a multi-country evaluation of nutrition and lifestyle indicators in children aged 12 years and below: Rationale and Design
-
- Journal:
- Public Health Nutrition / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 April 2024, pp. 1-29
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
VaTEST III: Validation of 8 Potential Super-Earths from TESS Data
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 April 2024, pp. 1-22
-
- Article
- Export citation
Delivery of a telehealth supported home exercise program with dietary advice to increase plant-based protein intake in people with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a 12-week randomised controlled feasibility trial
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 January 2024, pp. 1-11
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
ResearchMatch on FHIR: Development and evaluation of a recruitment registry and electronic health record system interface for volunteer profile completion
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 7 / Issue 1 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 October 2023, e222
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
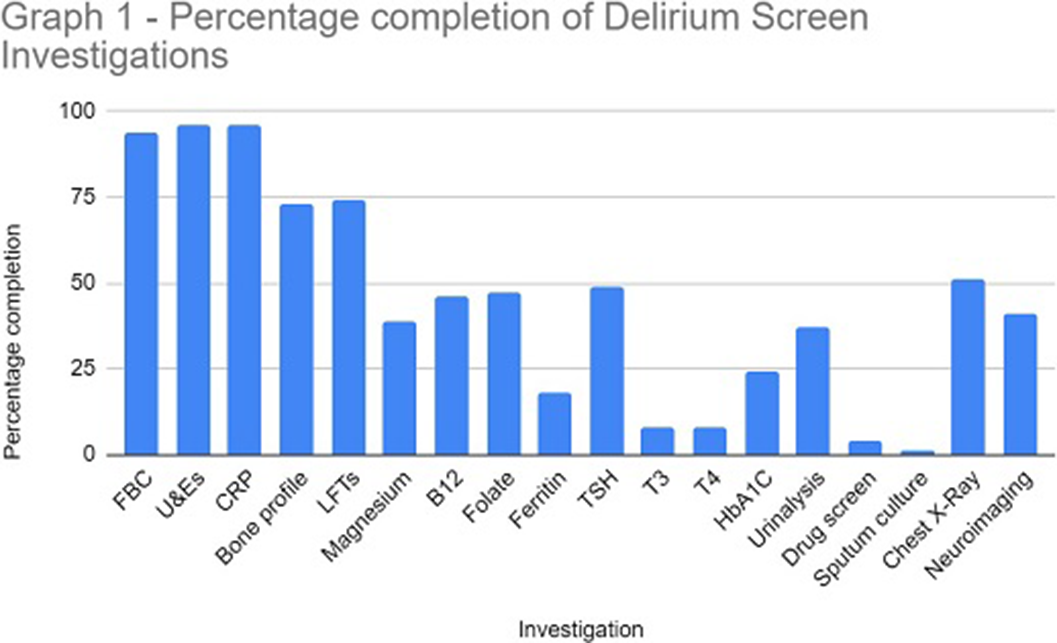
Are We Adequately Assessing Delirium? An Analysis Of Liaison Psychiatry Referrals
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 66 / Issue S1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 July 2023, pp. S518-S519
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Facing the COVID-19 pandemic – an assessment of students’ mental health and major coping strategies during the COVID-19 pandemic – an international study
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 66 / Issue S1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 July 2023, pp. S152-S153
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
P.017 Convergent and contrasting modulation of saccade and pupil responses by several neurodegenerative diseases during free viewing of video clips
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 50 / Issue s2 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 June 2023, p. S62
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
The impact of strict lockdowns on the mental health and well-being of people living in Australia during the first year of the COVID-19 pandemic
-
- Journal:
- BJPsych Open / Volume 9 / Issue 3 / May 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 May 2023, e90
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Examining the impact of racial disparities on Clostridioides difficile infection outcomes at a Southern California academic teaching hospital
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 44 / Issue 11 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 May 2023, pp. 1861-1865
- Print publication:
- November 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
39 Prenatal antibiotic exposure and risk of childhood asthma among children with Down syndrome
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 7 / Issue s1 / April 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 April 2023, p. 10
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Dietary resistant starch alters gut microbiota, microbially produced metabolites and albuminuria in diabetic mice
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Nutrition Society / Volume 82 / Issue OCE2 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 March 2023, E183
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Screen to Intervene; establishing a dedicated metabolic clinic for patients with chronic mental illness in an Irish Metal Health Service
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 65 / Issue S1 / June 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 September 2022, pp. S198-S199
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Resting-state EEG networks characterized by intramodular and global hyperconnectivity in depressive sample
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 65 / Issue S1 / June 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 September 2022, pp. S213-S214
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Beta-band network modularity in resting-state EEG negatively correlates with level of intelligence
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 65 / Issue S1 / June 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 September 2022, p. S639
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Stability of Fe Electrode in Alkaline Electrolyte
-
- Journal:
- Microscopy and Microanalysis / Volume 28 / Issue S1 / August 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 July 2022, pp. 830-832
- Print publication:
- August 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Beyond In Situ ETEM Imaging: Unveiling the Size-dependent Oxidation Mechanism of Metallic Nanoparticles by Individual Nanoparticle-level Oxidation Kinetic Analysis
-
- Journal:
- Microscopy and Microanalysis / Volume 28 / Issue S1 / August 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 July 2022, pp. 160-161
- Print publication:
- August 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Convolutional Neural Network as a Solution to Segment and Classify High Resolution TEM Images to Obtain 3D Information
-
- Journal:
- Microscopy and Microanalysis / Volume 28 / Issue S1 / August 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 July 2022, pp. 3024-3026
- Print publication:
- August 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Field Experiments in the Global South: Assessing Risks, Localizing Benefits, and Addressing Positionality—ADDENDUM
-
- Journal:
- PS: Political Science & Politics / Volume 55 / Issue 4 / October 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 July 2022, p. 835
- Print publication:
- October 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
P.002 Saccade parameters reveal cognitive impairment and differentially associate with cognitive domains across neurodegenerative diseases
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 49 / Issue s1 / June 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 June 2022, p. S8
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Frontal sinus obliteration with beta-tricalcium phosphate putty: case series with long-term radiological follow up
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Laryngology & Otology / Volume 137 / Issue 2 / February 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 June 2022, pp. 163-168
- Print publication:
- February 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation



 R
R R
R R
R R
R R
R R
R R
R R
R