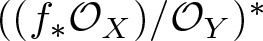32 results
Pushforward of structure sheaf and virtual global generation
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 April 2024, pp. 1-11
-
- Article
- Export citation
Micronutrient diversity in pole and bush type Dolichos bean germplasm: identification of gene sources from biofortification perspectives
-
- Journal:
- Plant Genetic Resources / Volume 22 / Issue 1 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 January 2024, pp. 50-52
-
- Article
- Export citation
Detection of the β-lactoglobulin genotype in zebu cattle (Gangatiri) milk using high-resolution accurate mass spectroscopy
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Dairy Research / Volume 90 / Issue 3 / August 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 August 2023, pp. 287-291
- Print publication:
- August 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Glacier retreat, dynamics and bed overdeepenings of Parkachik Glacier, Ladakh Himalaya, India
-
- Journal:
- Annals of Glaciology , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 July 2023, pp. 1-14
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Probing of alpha, beta and kappa-caseins polymorphic variants in Gangatiri cow milk with the use of polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and HRAMS
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Dairy Research / Volume 90 / Issue 1 / February 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2023, pp. 54-57
- Print publication:
- February 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Design of a flower shaped compact printed antenna for ultra-wideband communication
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Microwave and Wireless Technologies / Volume 15 / Issue 7 / September 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 October 2022, pp. 1172-1178
-
- Article
- Export citation
Geochronology and oxygen fugacity of the pelitic granulite from the Diwani hills, NE Gujarat (NW India)
-
- Journal:
- Geological Magazine / Volume 160 / Issue 1 / January 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 August 2022, pp. 22-34
-
- Article
- Export citation
Public health implications of plasmid-mediated quinolone and aminoglycoside resistance genes in Escherichia coli inhabiting a major anthropogenic river of India
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 150 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 March 2022, e78
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A compact ultra-wideband square and circular slot ground plane planar antenna with a modified circular patch
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Microwave and Wireless Technologies / Volume 14 / Issue 8 / October 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 August 2021, pp. 989-994
-
- Article
- Export citation
Microstructural Evolution of Chessboard like Nanodomains in Mn-doped ZnGaO4 Spinel
-
- Journal:
- Microscopy and Microanalysis / Volume 27 / Issue S1 / August 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 July 2021, pp. 2418-2419
- Print publication:
- August 2021
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
TEM Studies of Nanoscale Phase Transformation during in-situ reaction of Li with 2D Materials (MoS2, WS2, Graphite)
-
- Journal:
- Microscopy and Microanalysis / Volume 27 / Issue S1 / August 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 July 2021, pp. 338-340
- Print publication:
- August 2021
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Stagnation of the Pensilungpa glacier, western Himalaya, India: causes and implications
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Glaciology / Volume 68 / Issue 268 / April 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 July 2021, pp. 221-235
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Subjective global nutritional assessment as a nutritional tool in childhood chronic liver disease
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 127 / Issue 6 / 28 March 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 May 2021, pp. 904-913
- Print publication:
- 28 March 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Direct Visualization of the Earliest Stages of Crystallization
-
- Journal:
- Microscopy and Microanalysis / Volume 27 / Issue 4 / August 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 May 2021, pp. 659-665
- Print publication:
- August 2021
-
- Article
- Export citation
Origin of the long-ranged attraction or repulsion between intruders in a confined granular medium
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 886 / 10 March 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 January 2020, A23
-
- Article
- Export citation
Evaluation of an alcohol-based antiseptic for nasal decolonization of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in colonized patients
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 40 / Issue 12 / December 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 September 2019, pp. 1436-1437
- Print publication:
- December 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation
Yartsagunbu: transforming people's livelihoods in the Western Himalaya
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Needs Assessment for Simulation Training for Prehospital Providers in Botswana
-
- Journal:
- Prehospital and Disaster Medicine / Volume 33 / Issue 6 / December 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 November 2018, pp. 621-626
- Print publication:
- December 2018
-
- Article
- Export citation
Room temperature deformation mechanisms of Mg/Nb nanolayered composites
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 33 / Issue 10 / 28 May 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 May 2018, pp. 1311-1332
- Print publication:
- 28 May 2018
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation