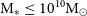127 results
Annual risk of hepatitis E virus infection and seroreversion: Insights from a serological cohort in Sitakunda, Bangladesh
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 152 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 March 2024, e52
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
EMU/GAMA: A technique for detecting active galactic nuclei in low mass systems
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 41 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 February 2024, e016
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Jurassic Trigoniida (Bivalvia) from Gebel Maghara, northern Sinai, Egypt
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Paleontology / Volume 97 / Issue 6 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 January 2024, pp. 1206-1232
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
EMU/GAMA: Radio-detected galaxies are more obscured than optically selected galaxies
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 41 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 January 2024, e021
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Conceptual Dissonance in Peacebuilding Research: Lessons from a Somali Diaspora
-
- Journal:
- PS: Political Science & Politics , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 November 2023, pp. 1-6
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Atrial septal defect-associated pulmonary hypertension with decompensated heart failure: outcomes after fenestrated device closure – CORRIGENDUM
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 34 / Issue 2 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 September 2023, p. 467
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Effect of an initial specimen diversion device on blood-culture contamination rates and vancomycin usage: A quasi-experimental study
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 45 / Issue 1 / January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 August 2023, pp. 100-102
- Print publication:
- January 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Atrial septal defect-associated pulmonary hypertension with decompensated heart failure: outcomes after fenestrated device closure
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 34 / Issue 2 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 July 2023, pp. 395-400
-
- Article
- Export citation
Revision of Jurassic Protobranch Bivalves from Gebel Maghara, northern Sinai, Egypt
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Paleontology / Volume 97 / Issue S93 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 June 2023, pp. 1-45
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Versatile tape-drive target for high-repetition-rate laser-driven proton acceleration – CORRIGENDUM
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 11 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 June 2023, e43
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Automated control and optimization of laser-driven ion acceleration
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 11 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 March 2023, e35
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Versatile tape-drive target for high-repetition-rate laser-driven proton acceleration
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 11 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 March 2023, e23
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The prognostic role of liver volumetry in Fontan patients
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 33 / Issue 10 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 October 2022, pp. 1834-1839
-
- Article
- Export citation
P.153 Traumatic spinal cord injuries among indigenous and non-indigenous peoples of Canada
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 49 / Issue s1 / June 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 June 2022, p. S47
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Feasibility of a school-based mental health program implementation to improve the status of depression and quality of life of mothers of children with autism spectrum disorders in urban Bangladesh: MENTHOL study
-
- Journal:
- Global Mental Health / Volume 9 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 March 2022, pp. 146-156
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Outbreak of severe acute respiratory coronavirus virus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) in hospitalized hemodialysis patients: An epidemiologic and genomic investigation
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 44 / Issue 2 / February 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 December 2021, pp. 332-334
- Print publication:
- February 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Intergenerational differences in dietary acculturation among Ghanaian immigrants living in New York City: a qualitative study
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Nutritional Science / Volume 10 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 September 2021, e80
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Nasal chondromesenchymal hamartoma: an update
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Laryngology & Otology / Volume 136 / Issue 12 / December 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 August 2021, pp. 1140-1147
- Print publication:
- December 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
An online forum to support consultant psychiatrists in their first five years of practice, introduced during the COVID-19 pandemic
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 64 / Issue S1 / April 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 August 2021, p. S471
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Enhancing a nutrition and self-management: An intervention program via teletherapy for teenager with ADHD. A pilot case study
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 64 / Issue S1 / April 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 August 2021, p. S790
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation