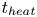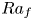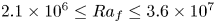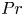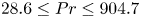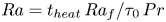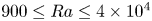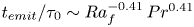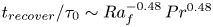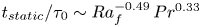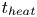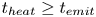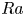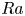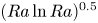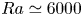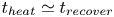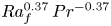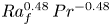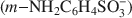478 results
Global, regional and national burdens of depression in adolescents and young adults aged 10–24 years, from 1990 to 2019: findings from the 2019 Global Burden of Disease study
-
- Journal:
- The British Journal of Psychiatry , FirstView
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 April 2024, pp. 1-10
-
- Article
- Export citation
Macrolide-Resistance of Mycoplasma pneumoniae in Several Regions of China from 2013 to 2019
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 April 2024, pp. 1-18
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Antimicrobial peptide cecropin B functions in pathogen resistance of Mythimna separata
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of Entomological Research , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 April 2024, pp. 1-12
-
- Article
- Export citation
Formation and evolution of laminar thermal structures: correlation to the thermal boundary layer and effects of heating time
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 984 / 10 April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 April 2024, A60
-
- Article
- Export citation
Unified gas-kinetic wave–particle method for polydisperse gas–solid particle multiphase flow
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 983 / 25 March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 March 2024, A37
-
- Article
- Export citation
Chinese stalagmite δ18O records reveal the diverse moisture trajectories during the middle to late last glacial period
-
- Journal:
- Geological Magazine , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 February 2024, pp. 1-13
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A single-layer band-stop frequency selective surface with wide angular stability property
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Microwave and Wireless Technologies , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 January 2024, pp. 1-8
-
- Article
- Export citation
Clinical parameter-based prediction model for neurosyphilis risk stratification
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 152 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 January 2024, e21
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Numerical investigation of mixed-phase turbulence induced by a plunging jet
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 979 / 25 January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 January 2024, A27
-
- Article
- Export citation
Cross-Section Measurements of the 11B(p,α)2α Reaction near the First Resonant Energy
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 2023 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e12
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Stopping Power Modulation by Pump Waves of Charged Particles Moving above Two-Dimensional Electron Gases
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 2021 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e14
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Association between the PLTP rs4810479 SNP and Serum Lipid Traits in the Chinese Maonan and Han Populations
-
- Journal:
- Genetics Research / Volume 2021 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e14
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Controlled Polymerization of Metanilic Anion within the Interlayer of NiAl Layered Double Hydroxide
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 54 / Issue 4 / August 2006
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 418-425
-
- Article
- Export citation
Effect of Viscosity on Stopping Power for a Charged Particle Moving above Two-Dimensional Electron Gas
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 2022 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e19
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Comparison and Analysis on the Existing Single-Herbal Strategies against Viral Myocarditis
-
- Journal:
- Genetics Research / Volume 2021 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e11
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The Composition and Growth Mechanism of Coexisting 4M2 and 4A8 Biotite Polytypes from Rhyolite of Long Valley Caldera, California
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 70 / Issue 1 / February 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 48-61
-
- Article
- Export citation
Bioinformatics Analysis Identifies TNFRSF1A as a Biomarker of Liver Injury in Sepsis TNFRSF1A is a Biomarker for Septic Liver Injury
-
- Journal:
- Genetics Research / Volume 2022 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e20
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A Compact High-Power Ultra-Wideband Bipolar Pulse Generator
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 2021 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e5
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Compact Thomson Scattering Source Based on a Mixed Injection Assisted Laser Wakefield Accelerator
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 2022 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e9
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A Survival Model Based on the ASB Genes and Used to Predict the Prognosis of Kidney Renal Clear Cell Carcinoma
-
- Journal:
- Genetics Research / Volume 2023 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e22
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation