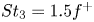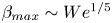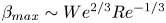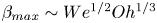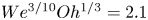98 results

Web3
- Blockchain, the New Economy, and the Self-Sovereign Internet
- Coming soon
-
- Expected online publication date:
- August 2024
- Print publication:
- 31 August 2024
-
- Book
- Export citation
The Composition and Growth Mechanism of Coexisting 4M2 and 4A8 Biotite Polytypes from Rhyolite of Long Valley Caldera, California
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 70 / Issue 1 / February 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 48-61
-
- Article
- Export citation
Thermal Characterization of Surfactant-Modified Montmorillonites
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 53 / Issue 3 / June 2005
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 287-293
-
- Article
- Export citation
The Protective Effect of Trichosanthes kirilowii Peel Polysaccharide on the Oxidative Damaged HepG2 and HUASMC Cells
-
- Journal:
- Genetics Research / Volume 2022 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e49
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
An outbreak of nosocomial infection of neonatal aseptic meningitis caused by echovirus 18
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 151 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 June 2023, e107
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Neural habituation during acute stress signals a blunted endocrine response and poor resilience
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 53 / Issue 16 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 June 2023, pp. 7735-7745
-
- Article
- Export citation
New trilobite assemblage from the lower Cambrian (upper Stage 4) of the Lake Zone, western Mongolia
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Paleontology / Volume 97 / Issue 3 / May 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 June 2023, pp. 577-590
-
- Article
- Export citation
Aerodynamics and fluid–structure interaction of an airfoil with actively controlled flexible leeward surface
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 954 / 10 January 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 January 2023, A34
-
- Article
- Export citation
China’s Employment Contract Law: Does it deliver employment security?
-
- Journal:
- The Economic and Labour Relations Review / Volume 30 / Issue 1 / March 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2023, pp. 99-119
-
- Article
- Export citation
Investigation of a Fused in Sarcoma Splicing Mutation in a Chinese Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Patient
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 50 / Issue 6 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 December 2022, pp. 891-896
-
- Article
- Export citation
Dietary fat quantity and quality in early pregnancy and risk of gestational diabetes mellitus in Chinese women: a prospective cohort study
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 129 / Issue 9 / 14 May 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 August 2022, pp. 1481-1490
- Print publication:
- 14 May 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Timing of gestational weight gain in association with birth weight outcomes: a prospective cohort study
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 129 / Issue 6 / 28 March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 July 2022, pp. 1058-1065
- Print publication:
- 28 March 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Association between hyperhomocysteinaemia and the risk of all-cause and cause-specific mortality among adults in the USA
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 129 / Issue 6 / 28 March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 July 2022, pp. 1046-1057
- Print publication:
- 28 March 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Mid-Neoproterozoic magmatism in the South Qilian Belt, NE Tibetan Plateau and its tectonic implications
-
- Journal:
- Geological Magazine / Volume 159 / Issue 8 / August 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 May 2022, pp. 1384-1396
-
- Article
- Export citation
Scaling laws of the maximum spreading factor for impact of nanodroplets on solid surfaces
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 937 / 25 April 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 February 2022, A12
-
- Article
- Export citation
CYP4CJ6-mediated resistance to two neonicotinoid insecticides in Sitobion miscanthi (Takahashi)
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of Entomological Research / Volume 112 / Issue 5 / October 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2022, pp. 646-655
-
- Article
- Export citation
A new small soft-bodied non-trilobite artiopod from the Cambrian Stage 4 Guanshan Biota
-
- Journal:
- Geological Magazine / Volume 159 / Issue 5 / May 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 December 2021, pp. 730-734
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Vortex dynamics and hydrodynamic performance enhancement mechanism in batoid fish oscillatory swimming
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 930 / 10 January 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 November 2021, A28
-
- Article
- Export citation
Glucosamine use, smoking and risk of incident chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a large prospective cohort study
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 128 / Issue 4 / 28 August 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 September 2021, pp. 721-732
- Print publication:
- 28 August 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Silencing of CYP6AS160 in Solenopsis invicta Buren by RNA interference enhances worker susceptibility to fipronil
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of Entomological Research / Volume 112 / Issue 2 / April 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 August 2021, pp. 171-178
-
- Article
- Export citation