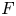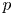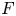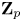274 results
Completed prismatic F-crystals and crystalline Zp-local systems
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Compositio Mathematica / Volume 160 / Issue 5 / May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 April 2024, pp. 1101-1166
- Print publication:
- May 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Evaluation of the psychometrics of the Social Impact Scale and its association with depression among asymptomatic COVID-19 carriers
-
- Journal:
- BJPsych Open / Volume 10 / Issue 2 / March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 February 2024, e41
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The Clinical Relevance and Functional Implications of Thymosin Beta-10 in Glioma
-
- Journal:
- Genetics Research / Volume 2023 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e35
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Plasma Spectroscopy on Hydrogen-Carbon-Oxygen Foam Targets Driven by Laser-Generated Hohlraum Radiation
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 2022 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e15
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Upregulated Solute Carrier SLC39A1 Promotes Gastric Cancer Proliferation and Indicates Unfavorable Prognosis
-
- Journal:
- Genetics Research / Volume 2022 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e12
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Gray matter atrophy is constrained by normal structural brain network architecture in depression
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 54 / Issue 7 / May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 November 2023, pp. 1318-1328
-
- Article
- Export citation
Moser's theorem with frequency-preserving
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 August 2023, pp. 1-31
-
- Article
- Export citation
Validation of inductively coupled plasma simulation model by laser Thomson scattering experiment
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Plasma Physics / Volume 89 / Issue 4 / August 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 July 2023, 905890409
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
5 - Fundamentals of Computational Thermodynamics and the CALPHAD Method
-
- Book:
- Computational Design of Engineering Materials
- Published online:
- 29 June 2023
- Print publication:
- 29 June 2023, pp 113-197
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
10 - Case Studies on Cemented Carbide Design
-
- Book:
- Computational Design of Engineering Materials
- Published online:
- 29 June 2023
- Print publication:
- 29 June 2023, pp 342-369
-
- Chapter
- Export citation

Computational Design of Engineering Materials
- Fundamentals and Case Studies
-
- Published online:
- 29 June 2023
- Print publication:
- 29 June 2023
3 - Fundamentals of Mesoscale Simulation Methods
-
- Book:
- Computational Design of Engineering Materials
- Published online:
- 29 June 2023
- Print publication:
- 29 June 2023, pp 46-94
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Index
-
- Book:
- Computational Design of Engineering Materials
- Published online:
- 29 June 2023
- Print publication:
- 29 June 2023, pp 469-478
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Preface
-
- Book:
- Computational Design of Engineering Materials
- Published online:
- 29 June 2023
- Print publication:
- 29 June 2023, pp xvii-xviii
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Appendix A - Ancillary Materials
-
- Book:
- Computational Design of Engineering Materials
- Published online:
- 29 June 2023
- Print publication:
- 29 June 2023, pp 457-460
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Dedication
-
- Book:
- Computational Design of Engineering Materials
- Published online:
- 29 June 2023
- Print publication:
- 29 June 2023, pp v-vi
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Contents
-
- Book:
- Computational Design of Engineering Materials
- Published online:
- 29 June 2023
- Print publication:
- 29 June 2023, pp vii-xiv
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
8 - Case Studies on Light Alloy Design
-
- Book:
- Computational Design of Engineering Materials
- Published online:
- 29 June 2023
- Print publication:
- 29 June 2023, pp 295-322
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
11 - Case Studies on Hard Coating Design
-
- Book:
- Computational Design of Engineering Materials
- Published online:
- 29 June 2023
- Print publication:
- 29 June 2023, pp 370-401
-
- Chapter
- Export citation