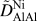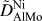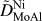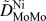20 results
The global disease burden attributable to a diet low in fibre in 204 countries and territories from 1990 to 2019
-
- Journal:
- Public Health Nutrition / Volume 26 / Issue 4 / April 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 September 2022, pp. 854-865
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
SAED and HREM Study of Intermetallic Phases in Ni-Mn-In Alloy System
-
- Journal:
- Microscopy and Microanalysis / Volume 26 / Issue S2 / August 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 July 2020, pp. 276-278
- Print publication:
- August 2020
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Dietary supplementation with Lactobacillus plantarum modified gut microbiota, bile acid profile and glucose homoeostasis in weaning piglets
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 124 / Issue 8 / 28 October 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 May 2020, pp. 797-808
- Print publication:
- 28 October 2020
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Composted manure and straw amendments in wheat of a rice–wheat rotation system alter weed richness and abundance
-
- Journal:
- Weed Science / Volume 67 / Issue 3 / May 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 March 2019, pp. 318-326
-
- Article
- Export citation
Challenges of Treating Adenovirus Infection: Application of a Deployable Rapid-Assembly Shelter Hospital
-
- Journal:
- Disaster Medicine and Public Health Preparedness / Volume 12 / Issue 1 / February 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 March 2017, pp. 109-114
-
- Article
- Export citation
High-throughput measurements of interdiffusivity matrices in face centered cubic Ni–Al–Mo alloys at 1273–1473 K
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 32 / Issue 11 / 14 June 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 February 2017, pp. 2188-2201
- Print publication:
- 14 June 2017
-
- Article
- Export citation
Laboratory astrophysics with laser-driven strong magnetic fields in China
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 4 / 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 August 2016, e27
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Disaster Medicine in China: Present and Future
-
- Journal:
- Disaster Medicine and Public Health Preparedness / Volume 12 / Issue 2 / April 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 June 2016, pp. 157-165
-
- Article
- Export citation
Dynamic Changes in Clinical Characteristics During an Outbreak of Human Adenovirus Serotype 55 in China
-
- Journal:
- Disaster Medicine and Public Health Preparedness / Volume 12 / Issue 4 / August 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 February 2016, pp. 464-469
-
- Article
- Export citation
Nε-(carboxymethyl)-lysine, White Matter, and Cognitive Function in Diabetes Patients
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 43 / Issue 4 / July 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 February 2016, pp. 518-522
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Black muntjac fibroblast cell culture and interspecies embryo reconstruction in vitro
-
- Journal:
- Chinese Journal of Agricultural Biotechnology / Volume 4 / Issue 2 / August 2007
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 August 2007, pp. 157-162
- Print publication:
- August 2007
-
- Article
- Export citation
Stable transformation of phaC2 gene in tobacco chloroplast genome
-
- Journal:
- Chinese Journal of Agricultural Biotechnology / Volume 3 / Issue 3 / December 2006
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 March 2007, pp. 201-207
- Print publication:
- December 2006
-
- Article
- Export citation
The development of a joule level of XeF(C-A) laser by optical pumping
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 23 / Issue 4 / October 2005
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 December 2005, pp. 559-562
-
- Article
- Export citation
Monacrosporium janus sp. nov., a new nematode-trapping hyphomycete parasitizing sclerotia and hyphae of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum
-
- Journal:
- Mycological Research / Volume 107 / Issue 7 / July 2003
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 August 2003, pp. 888-894
- Print publication:
- July 2003
-
- Article
- Export citation
Uncv (uncovered): a new mutation causing hairloss on mouse chromosome 11
-
- Journal:
- Genetical Research / Volume 73 / Issue 3 / June 1999
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 June 1999, pp. 233-238
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Synthesis and characterization of Y2O3: Eu3+ powder phosphor by a hydrolysis technique
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 13 / Issue 10 / October 1998
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 January 2011, pp. 2950-2955
- Print publication:
- October 1998
-
- Article
- Export citation
Calculated phase diagrams for activated low pressure diamond growth from C–H, C–O, and C–H–O systems
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 12 / Issue 12 / December 1997
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 January 2011, pp. 3250-3253
- Print publication:
- December 1997
-
- Article
- Export citation
Thermodynamic coupling effect and catalyst effect for the artificial diamond growth
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 12 / Issue 6 / June 1997
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 January 2011, pp. 1530-1535
- Print publication:
- June 1997
-
- Article
- Export citation
A Simplified Model for a Nonlinear Tidal Effect on Accretion Disks in CVS
-
- Journal:
- International Astronomical Union Colloquium / Volume 134 / 1993
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 April 2016, p. 371
- Print publication:
- 1993
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation