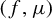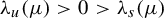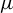102 results
The melanin pigment gene black mediates body pigmentation and courtship behaviour in the German cockroach Blattella germanica
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of Entomological Research , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 April 2024, pp. 1-10
-
- Article
- Export citation
Molecular mechanisms of cytochrome P450-mediated detoxification of tetraniliprole, spinetoram, and emamectin benzoate in the fall armyworm, Spodoptera frugiperda (J.E. Smith)
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of Entomological Research , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 April 2024, pp. 1-13
-
- Article
- Export citation
Association of consumption of sugar-sweetened beverages with elevated blood pressure among college students in Yunnan Province, China
-
- Journal:
- Public Health Nutrition / Volume 27 / Issue 1 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 February 2024, e85
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Dimension estimates and approximation in non-uniformly hyperbolic systems
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Ergodic Theory and Dynamical Systems , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 February 2024, pp. 1-27
-
- Article
- Export citation
1 - China’s Reform and Opening-Up and Its Move to International Institutions
- from Part I - Taking Centre Stage in Global Governance and the International Legal Order
-
-
- Book:
- The Cambridge Handbook of China and International Law
- Published online:
- 04 January 2024
- Print publication:
- 18 January 2024, pp 15-30
-
- Chapter
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Quantifying stakeholders’ preference for implantable medical devices in China: a discrete choice experiment
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Technology Assessment in Health Care / Volume 40 / Issue 1 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 January 2024, e8
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Instability evolution of a shock-accelerated thin heavy fluid layer in cylindrical geometry
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 969 / 25 August 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 August 2023, A6
-
- Article
- Export citation
Reduced-order variational mode decomposition to reveal transient and non-stationary dynamics in fluid flows
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 966 / 10 July 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 June 2023, A7
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Early-initiated childhood reading for pleasure: associations with better cognitive performance, mental well-being and brain structure in young adolescence
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 54 / Issue 2 / January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 June 2023, pp. 359-373
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Dimension approximation in smooth dynamical systems
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Ergodic Theory and Dynamical Systems / Volume 44 / Issue 2 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 April 2023, pp. 383-407
- Print publication:
- February 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Measures of maximal and full dimension for smooth maps
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Ergodic Theory and Dynamical Systems / Volume 44 / Issue 1 / January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 March 2023, pp. 31-49
- Print publication:
- January 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Bubble re-acceleration behaviours in compressible Rayleigh–Taylor instability with isothermal stratification
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 954 / 10 January 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 January 2023, A16
-
- Article
- Export citation
Blastocyst Stage Affects the Isolation and Culture of Buffalo Naive/Primed Embryonic Stem-Like Cells
-
- Journal:
- Microscopy and Microanalysis / Volume 28 / Issue 6 / December 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 September 2022, pp. 2093-2104
- Print publication:
- December 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
NEW SAMPLE PREPARATION LINE FOR RADIOCARBON MEASUREMENTS AT THE GXNU LABORATORY
-
- Journal:
- Radiocarbon / Volume 64 / Issue 6 / December 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 May 2022, pp. 1501-1511
- Print publication:
- December 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
14C-AMS TECHNOLOGY AND ITS APPLICATIONS TO AN OIL FIELD TRACER EXPERIMENT
-
- Journal:
- Radiocarbon / Volume 64 / Issue 5 / October 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 May 2022, pp. 1159-1169
- Print publication:
- October 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
Compositional and functional features of the gut microbiota of the intertidal snail Nerita yoldii along China's coast
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom / Volume 101 / Issue 8 / December 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 April 2022, pp. 1103-1110
-
- Article
- Export citation
Interparental conflict and depressive symptoms among Chinese adolescents: A longitudinal moderated mediation model
-
- Journal:
- Development and Psychopathology / Volume 35 / Issue 2 / May 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 March 2022, pp. 972-981
-
- Article
- Export citation
AlepPBP2, but not AlepPBP3, may involve in the recognition of sex pheromones and maize volatiles in Athetis lepigone
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of Entomological Research / Volume 112 / Issue 4 / August 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 February 2022, pp. 536-545
-
- Article
- Export citation
ATP-binding cassette transporters ABCF2 and ABCG9 regulate rice black-streaked dwarf virus infection in its insect vector, Laodelphax striatellus (Fallén)
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of Entomological Research / Volume 112 / Issue 3 / June 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 September 2021, pp. 327-334
-
- Article
- Export citation