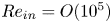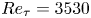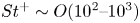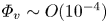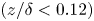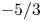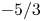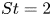430 results
The ameliorative and neuroprotective effects of dietary fibre on hyperuricaemia mice: a perspective from microbiome and metabolome
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 June 2024, pp. 1-14
-
- Article
- Export citation
Characterizing the distinct imaging phenotypes, clinical behavior, and genetic vulnerability of brain maturational subtypes in mood disorders
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 May 2024, pp. 1-11
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The long-term spatio-temporal trends in burden and attributable risk factors of major depressive disorder at global, regional and national levels during 1990–2019: a systematic analysis for GBD 2019
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology and Psychiatric Sciences / Volume 33 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 May 2024, e28
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
High-efficiency tandem Ho:YAG single-crystal fiber laser delivering more than 100 W output power
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 12 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 May 2024, e41
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Development and characterization of novel EST-SSR markers for Gentiana straminea Maxim., a traditional Tibetan herb in China and cross-amplification in related species
-
- Journal:
- Plant Genetic Resources , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 May 2024, pp. 1-6
-
- Article
- Export citation
Flow–acoustic resonance mechanism in tandem deep cavities coupled with acoustic eigenmodes in turbulent shear layers
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 984 / 10 April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 April 2024, A19
-
- Article
- Export citation
Relationship between syncopal symptoms and head-up tilt test modes
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 April 2024, pp. 1-6
-
- Article
- Export citation
Experimental study of the effect of particle–wall interactions on inertial particle dynamics in wall turbulence
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 984 / 10 April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 March 2024, A4
-
- Article
- Export citation
Modulations of turbulent/non-turbulent interfaces by particles in turbulent boundary layers
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 983 / 25 March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 March 2024, A15
-
- Article
- Export citation
Epidemiology of tuberculosis among children in Beijing, China, 2012–2021
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 152 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 March 2024, e44
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Effectiveness of a WHO self-help psychological intervention to alleviate stress among healthcare workers in the context of COVID-19 in China: a randomised controlled trial
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology and Psychiatric Sciences / Volume 33 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 March 2024, e11
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Modulational instability of the interacting electron whistlers and magnetosonic perturbations
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Plasma Physics / Volume 90 / Issue 1 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 February 2024, 905900121
-
- Article
- Export citation
Binary collision dynamics of equal-sized nanodroplets
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 979 / 25 January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 January 2024, A25
-
- Article
- Export citation
Life history and mitochondrial genomes of Salassinae and Agliinae (Insecta, Lepidoptera): New insights into the loss of cocooning behaviour and phylogeny of Saturniidae
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of Entomological Research / Volume 114 / Issue 1 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 January 2024, pp. 107-123
-
- Article
- Export citation
Evaluation of suitable reference genes for expression profile analyses of target genes in the coffee berry borer, Hypothenemus hampei (Ferrari) (Coleoptera: Curculionidae)
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of Entomological Research / Volume 114 / Issue 1 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 January 2024, pp. 57-66
-
- Article
- Export citation
Sialic acid in human milk and infant formulas in China: concentration, distribution and type
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 131 / Issue 9 / 14 May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 January 2024, pp. 1506-1512
- Print publication:
- 14 May 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Dynamic Adsorption of Cd2+ Onto Acid-Modified Attapulgite From Aqueous Solution
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 62 / Issue 5 / October 2014
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 415-424
-
- Article
- Export citation
LncRNA HOXA-AS2 Promotes Temozolomide Resistance in Glioblastoma by Regulated miR-302a-3p/IGF1 Axis
-
- Journal:
- Genetics Research / Volume 2022 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e9
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Hsa-let-7c-5p, hsa-miR-130b-3p, and hsa-miR-142-3p as Novel miRNA Biomarkers for Melanoma Progression
-
- Journal:
- Genetics Research / Volume 2022 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e53
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Advanced Glycation End Products’ Receptor DNA Methylation Associated with Immune Infiltration and Prognosis of Lung Adenocarcinoma and Lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma
-
- Journal:
- Genetics Research / Volume 2023 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e4
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation