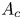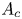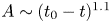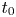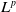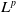185 results
Quantifying stakeholders’ preference for implantable medical devices in China: a discrete choice experiment
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Technology Assessment in Health Care / Volume 40 / Issue 1 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 January 2024, e8
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Serum Levels of VWF, t-PA, TNF-α, and ICAM-1 in Patients Receiving Hemocoagulase Combined with Platelet-Rich Plasma during Total Hip Replacement
-
- Journal:
- Genetics Research / Volume 2022 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e80
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Compact Thomson Scattering Source Based on a Mixed Injection Assisted Laser Wakefield Accelerator
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 2022 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e9
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A tunable balanced phase shifter with wide operating bandwidth
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Microwave and Wireless Technologies , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 November 2023, pp. 1-9
-
- Article
- Export citation
Edge-driven collapse of fluid holes
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 973 / 25 October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 October 2023, A18
-
- Article
- Export citation
5 - Deep Learning for CT Image Reconstruction
- from Part II - Deep-Learning Architecture for Various Imaging Architectures
-
-
- Book:
- Deep Learning for Biomedical Image Reconstruction
- Published online:
- 15 September 2023
- Print publication:
- 12 October 2023, pp 89-113
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
FINITE BASIS PROBLEM FOR INVOLUTION MONOIDS OF ORDER FIVE
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 109 / Issue 2 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 October 2023, pp. 350-364
- Print publication:
- April 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Dissociation between neuroanatomical and symptomatic subtypes in schizophrenia
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 66 / Issue 1 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 September 2023, e78
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
High-energy and high-peak-power GHz burst-mode all-fiber laser with a uniform envelope and tunable intra-burst pulses
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 11 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 August 2023, e81
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Automatic detection of cataclysmic variables from SDSS images
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 40 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 June 2023, e033
-
- Article
- Export citation
45 Senolytic Therapy Transiently Reduces Inflammatory Markers in Primary Blood Mononuclear Cells of Individuals with Early Alzheimer’s Disease: Exploring the Conserved Transcriptional Response to Adversity as a Biomarker for Disease State
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 7 / Issue s1 / April 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 April 2023, p. 12
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
The complete mitochondrial genome of Ogmocotyle ailuri: gene content, composition and rearrangement and phylogenetic implications
-
- Journal:
- Parasitology / Volume 150 / Issue 8 / July 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 April 2023, pp. 661-671
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Pre-treatment functional connectivity of the cingulate cortex predicts anti-suicidal effects of serial ketamine infusions
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 66 / Issue 1 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 March 2023, e31
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
2.1
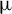 $\unicode{x3bc}$m, high-energy dissipative soliton resonance from a holmium-doped fiber laser system
$\unicode{x3bc}$m, high-energy dissipative soliton resonance from a holmium-doped fiber laser system
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 11 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 January 2023, e12
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Reduced cerebral cortex thickness is related to overexpression of exosomal miR-146a-5p in medication-free patients with major depressive disorder
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 53 / Issue 13 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 November 2022, pp. 6253-6260
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
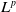 $L^p$ harmonic 1-forms on hypersurfaces with finite index
$L^p$ harmonic 1-forms on hypersurfaces with finite index
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Glasgow Mathematical Journal / Volume 65 / Issue 2 / May 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 November 2022, pp. 310-323
- Print publication:
- May 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Record power and efficient mid-infrared supercontinuum generation in germania fiber with high stability
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 10 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 September 2022, e36
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Facilitating timelier research with a novel classification of workplace technology
-
- Journal:
- Industrial and Organizational Psychology / Volume 15 / Issue 3 / September 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 September 2022, pp. 475-478
-
- Article
- Export citation