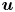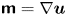152 results
Characterization and Prognosis of Biological Microenvironment in Lung Adenocarcinoma through a Disulfidptosis-Related lncRNAs Signature
-
- Journal:
- Genetics Research / Volume 2023 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e2
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Compact Thomson Scattering Source Based on a Mixed Injection Assisted Laser Wakefield Accelerator
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 2022 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e9
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Dual-band transmissive linear to circular polarization converter with angular-stable and orthogonal polarizations
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Microwave and Wireless Technologies , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 December 2023, pp. 1-9
-
- Article
- Export citation
Upregulation of miR-21-5p rescues the inhibition of cardiomyocyte proliferation induced by high glucose through negative regulation of Rhob
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Developmental Origins of Health and Disease / Volume 14 / Issue 5 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 December 2023, pp. 670-677
-
- Article
- Export citation
Clinical and genetic characteristics of catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia combined with left ventricular non-compaction
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 November 2023, pp. 1-8
-
- Article
- Export citation
Aligning values to labels: A best-worst analysis of food labels
-
- Journal:
- Agricultural and Resource Economics Review / Volume 53 / Issue 1 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 August 2023, pp. 20-44
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A diagnostic model based on routine blood examination for serious bacterial infections in neonates–a cross-sectional study
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 151 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 July 2023, e137
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Measurements of plasma density profile evolutions with a channel-guided laser
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 11 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 July 2023, e85
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Accelerated protons with energies up to 70 MeV based on the optimized SG-II Peta-watt laser facility
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 11 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 June 2023, e63
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Can ship travel contain COVID-19 outbreak after re-opening: a Bayesian meta-analysis
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 151 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 May 2023, e99
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Cooperative trajectory shaping guidance law for multiple anti-ship missiles
-
- Journal:
- The Aeronautical Journal / Volume 128 / Issue 1319 / January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 May 2023, pp. 73-91
-
- Article
- Export citation
ARITHMETICITY OF
 $\mathbb {C}$-FUCHSIAN SUBGROUPS OF SOME NONARITHMETIC LATTICES
$\mathbb {C}$-FUCHSIAN SUBGROUPS OF SOME NONARITHMETIC LATTICES
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 109 / Issue 1 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 April 2023, pp. 77-88
- Print publication:
- February 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Observations of dust fragmentations in the Experimental Advanced Superconducting Tokamak
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Plasma Physics / Volume 89 / Issue 2 / April 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 April 2023, 175890202
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Penta-band rectangular slot antenna for multi-function wireless communication with linear and circular polarizations
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Microwave and Wireless Technologies / Volume 15 / Issue 8 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 January 2023, pp. 1382-1391
-
- Article
- Export citation
New evidence from heavy minerals and detrital zircons in Quaternary fluvial sediments for the evolution of the upper Yangtze River, South China
-
- Journal:
- Quaternary Research / Volume 113 / May 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 December 2022, pp. 162-181
-
- Article
- Export citation
Molecular cloning and sequence analysis of 1Dx-type HMW-GS genes from different wheat varieties
-
- Journal:
- Plant Genetic Resources / Volume 20 / Issue 2 / April 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 October 2022, pp. 137-144
-
- Article
- Export citation
The global disease burden attributable to a diet low in fibre in 204 countries and territories from 1990 to 2019
-
- Journal:
- Public Health Nutrition / Volume 26 / Issue 4 / April 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 September 2022, pp. 854-865
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Low-order moments of the velocity gradient in homogeneous compressible turbulence
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 947 / 25 September 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 August 2022, R1
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation