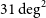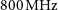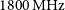75 results
53 2-Back Performance Does Not Differ Between Cognitive Training Groups in Older Adults Without Dementia
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 29 / Issue s1 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 December 2023, pp. 360-361
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
78 BVMT-R Learning Ratio Moderates Cognitive Training Gains in Useful Field of View Task in Healthy Older Adults
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 29 / Issue s1 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 December 2023, pp. 180-181
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
6 Adjunctive Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation and Cognitive Training Alters Default Mode and Frontoparietal Control Network Connectivity in Older Adults
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 29 / Issue s1 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 December 2023, pp. 675-676
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
9 Connecting memory and functional brain networks in older adults: a resting state fMRI study
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 29 / Issue s1 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 December 2023, pp. 527-528
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Characterisation of age and polarity at onset in bipolar disorder
-
- Journal:
- The British Journal of Psychiatry / Volume 219 / Issue 6 / December 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 August 2021, pp. 659-669
- Print publication:
- December 2021
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Hospital-acquired infections among adult patients admitted for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 43 / Issue 8 / August 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 April 2021, pp. 1054-1057
- Print publication:
- August 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
Australian square kilometre array pathfinder: I. system description
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 38 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 March 2021, e009
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Infant temperament prospectively predicts general psychopathology in childhood
-
- Journal:
- Development and Psychopathology / Volume 34 / Issue 3 / August 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 January 2021, pp. 774-783
-
- Article
- Export citation
Does smoking cause lower educational attainment and general cognitive ability? Triangulation of causal evidence using multiple study designs
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 52 / Issue 8 / June 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 October 2020, pp. 1578-1586
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Effects of genomic copy number variants penetrant for schizophrenia on cortical thickness and surface area in healthy individuals: analysis of the UK Biobank
-
- Journal:
- The British Journal of Psychiatry / Volume 218 / Issue 2 / February 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 August 2020, pp. 104-111
- Print publication:
- February 2021
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Examining pathways between genetic liability for schizophrenia and patterns of tobacco and cannabis use in adolescence
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 52 / Issue 1 / January 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 June 2020, pp. 132-139
-
- Article
- Export citation
Examining the effect of smoking on suicidal ideation and attempts: triangulation of epidemiological approaches
-
- Journal:
- The British Journal of Psychiatry / Volume 217 / Issue 6 / December 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 April 2020, pp. 701-707
- Print publication:
- December 2020
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Evidence for causal effects of lifetime smoking on risk for depression and schizophrenia: a Mendelian randomisation study
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 50 / Issue 14 / October 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 November 2019, pp. 2435-2443
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
High-repetition-rate (
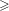 ${\geqslant}$ kHz) targets and optics from liquid microjets for high-intensity laser–plasma interactions
${\geqslant}$ kHz) targets and optics from liquid microjets for high-intensity laser–plasma interactions
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 7 / 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 August 2019, e50
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Meta-analysis across Cohorts for Heart and Aging Research in Genomic Epidemiology (CHARGE) consortium provides evidence for an association of serum vitamin D with pulmonary function
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 120 / Issue 10 / 28 November 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 September 2018, pp. 1159-1170
- Print publication:
- 28 November 2018
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
31 Intracranial growing teratoma syndrome (IGTS): An international retrospective study
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 45 / Issue S3 / June 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 July 2018, p. S13
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Monitoring the Vela Pulsar with a Phased Array Feed (PAF) Receiver
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the International Astronomical Union / Volume 13 / Issue S337 / September 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 June 2018, pp. 408-409
- Print publication:
- September 2017
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
One Year of Monitoring the Vela Pulsar Using a Phased Array Feed
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 34 / 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 July 2017, e027
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Growth and Yield of Flax (Linum usitatissimum) Injured by Trifluralin
-
- Journal:
- Weed Science / Volume 40 / Issue 3 / September 1992
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 June 2017, pp. 460-464
-
- Article
- Export citation
Recovery of Spring Wheat (Triticum aestivum) Injured by Trifluralin
-
- Journal:
- Weed Science / Volume 37 / Issue 6 / November 1989
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 June 2017, pp. 784-789
-
- Article
- Export citation