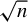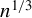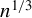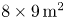549 results
Intelligence in robotics for computer, engineering, and applied sciences
-
- Journal:
- Robotica , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 September 2024, pp. 1-4
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Complete mitochondrial genome of Scathophaga stercoraria (Diptera: Scathophagidae) in wild plateau pika: Genome descriptions and Phylogenetic evolution
-
- Journal:
- Parasitology / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 May 2024, pp. 1-27
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
A HOMEMADE SEMIAUTOMATIC GRAPHITIZATION DEVICE FOR AMS 14C DATING AT NTUAMS LAB
-
- Journal:
- Radiocarbon , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 April 2024, pp. 1-9
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Macrolide resistance of Mycoplasma pneumoniae in several regions of China from 2013 to 2019
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 152 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 April 2024, e75
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Relationship between syncopal symptoms and head-up tilt test modes
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 April 2024, pp. 1-6
-
- Article
- Export citation
Excess mortality among patients with severe mental disorders and effects of community-based mental healthcare: A community-based prospective study in Sichuan, China – RETRACTION
-
- Journal:
- BJPsych Open / Volume 10 / Issue 2 / March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 March 2024, e64
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Does an antihypertensive diet cost more? Analysis from the Chinese Heart-Healthy diet trial
-
- Journal:
- Public Health Nutrition / Volume 27 / Issue 1 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 March 2024, e73
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Morphology, genetic characterization and phylogeny of Moniliformis tupaia n. sp. (Acanthocephala: Moniliformidae) from the northern tree shrew Tupaia belangeri chinensis Anderson (Mammalia: Scandentia)
-
- Journal:
- Parasitology / Volume 151 / Issue 4 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 March 2024, pp. 440-448
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
RATE-ADAPTIVE BOOTSTRAP FOR POSSIBLY MISSPECIFIED GMM
-
- Journal:
- Econometric Theory , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 January 2024, pp. 1-51
-
- Article
- Export citation
AMS 14C DATING AND STABLE ISOTOPE ANALYSIS ON AN 8-KYR OYSTER SHELL FROM TAIPEI BASIN: SEA LEVEL AND SST CHANGES
-
- Journal:
- Radiocarbon , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 January 2024, pp. 1-15
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Stochastic modelling of the instantaneous velocity profile in rough-wall turbulent boundary layers
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 979 / 25 January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 January 2024, A12
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Inverse association between maternal serum concentrations of trace elements and risk of spontaneous preterm birth: a nested case–control study in China
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 131 / Issue 8 / 28 April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 January 2024, pp. 1425-1435
- Print publication:
- 28 April 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
In Silico Analysis of the Gene Expression Patterns between Aldosterone-Producing Adenoma and Nonfunctional Adrenocortical Adenoma
-
- Journal:
- Genetics Research / Volume 2021 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e9
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Clay Mineralogy of the Zhada Sediments: Evidence for Climatic and Tectonic Evolution Since ~9 Ma in Zhada, Southwestern Tibet
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 60 / Issue 3 / June 2012
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 240-253
-
- Article
- Export citation
Oligocene clay mineralogy of the linxia basin: evidence of paleoclimatic evolution subsequent to the initial-stage uplift of the Tibetan Plateau
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 55 / Issue 5 / October 2007
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 491-503
-
- Article
- Export citation
FTIR and XRD Investigations of Tetracycline Intercalation in Smectites
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 58 / Issue 4 / August 2010
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 462-474
-
- Article
- Export citation
Creep Mechanical Properties and Constitutive Model of Hard Brittle Mud Shale
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 70 / Issue 3 / June 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 307-327
-
- Article
- Export citation
Clay Mineralogy Along the Laterite Profile in Hubei, South China: Mineral Evolution and Evidence for Eolian Origin
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 57 / Issue 5 / October 2009
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 602-615
-
- Article
- Export citation
Compact Thomson Scattering Source Based on a Mixed Injection Assisted Laser Wakefield Accelerator
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 2022 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e9
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Clay mineralogy across the P-T boundary of the Xiakou section, China: Evidence of clay provenance and environment
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 56 / Issue 2 / April 2008
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 131-143
-
- Article
- Export citation