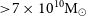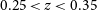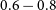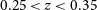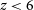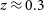182 results
Study of the pellet ablation cloud using the tomography technique for two-directional simultaneous photography in GAMMA 10/PDX
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Plasma Physics / Volume 90 / Issue 2 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 April 2024, 905900208
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
3 Harmonized Memory and Language Function in the Harmonized Cognitive Assessment Protocol (HCAP) Across the United States and Mexico
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 29 / Issue s1 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 December 2023, pp. 87-88
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Potential analytical interferences when measuring Tmax during temperature programmed pyrolysis of hydrothermally altered volcanoclastic sediment
-
- Journal:
- Experimental Results / Volume 4 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 February 2023, e5
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The Missing Fingerprints: U.S. Women Legislators and International Development Aid
-
- Journal:
- Politics & Gender / Volume 19 / Issue 2 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 September 2022, pp. 585-610
-
- Article
- Export citation
P.111 In vivo hippocampal mGluR5 abnormalities predict MTLE post-surgical outcome
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 49 / Issue s1 / June 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 June 2022, p. S37
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
‘Losing the illusion of control and predictability of life’: experiences of grief and loss among ageing US adults during the COVID-19 pandemic
-
- Journal:
- Ageing & Society / Volume 43 / Issue 12 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 February 2022, pp. 2821-2844
- Print publication:
- December 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A.7 In vivo hippocampal mGluR5 abnormalities predict MTLE post-surgical outcome
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 48 / Issue s3 / November 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 January 2022, p. S15
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Evaluation of point-of-care thumb-size bispectral electroencephalography device to quantify delirium severity and predict mortality
-
- Journal:
- The British Journal of Psychiatry / Volume 220 / Issue 6 / June 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 August 2021, pp. 322-329
- Print publication:
- June 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
The MAGPI survey: Science goals, design, observing strategy, early results and theoretical framework
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 38 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 July 2021, e031
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) incidence after exposures in shared patient rooms in a tertiary-care center in Iowa, July 2020–May 2021
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 43 / Issue 12 / December 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 July 2021, pp. 1910-1913
- Print publication:
- December 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
Ketonuria and Seizure Control in the Medium Chain Triglyceride and Classic Ketogenic Diets
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 49 / Issue 3 / May 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 June 2021, pp. 433-436
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Repair of a mixed form of supracardiac total anomalous pulmonary venous connection
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 31 / Issue 2 / February 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 November 2020, pp. 300-302
-
- Article
- Export citation
Addressing decontaminated respirators: Some methods appear to damage mask integrity and protective function
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 41 / Issue 12 / December 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 July 2020, pp. 1446-1448
- Print publication:
- December 2020
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A rare case of primary cardiac Hodgkin lymphoma in a child
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 30 / Issue 6 / June 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 June 2020, pp. 866-868
-
- Article
- Export citation
Self-recovery in schizophrenia: Insight from autobiographical narratives of patients
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 30 / Issue S2 / November 2015
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 April 2020, p. S26
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
760 – Cognitive and Affective Impairments of a Novel SCA/MND Crossroad Mutation Asidan
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 28 / Issue S1 / 2013
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 April 2020, 28-E255
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Creation of micro and macro spaces by electrospinning and application to electrode materials of energy devices
-
- Journal:
- MRS Advances / Volume 5 / Issue 27-28 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 January 2020, pp. 1423-1431
- Print publication:
- 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation
Impact of space weather on climate and habitability of terrestrial-type exoplanets
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Astrobiology / Volume 19 / Issue 2 / April 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 July 2019, pp. 136-194
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
The role of frozen section biopsy for parotid gland tumour with benign fine-needle aspiration cytology
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Laryngology & Otology / Volume 133 / Issue 3 / March 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 February 2019, pp. 227-229
- Print publication:
- March 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation
Experimental investigations of piping phenomena in bentonite-based buffer materials for an HLW repository
-
- Journal:
- Clay Minerals / Volume 48 / Issue 2 / May 2013
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 July 2018, pp. 363-382
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation