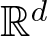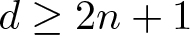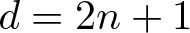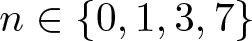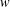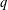102 results
Unit sphere fibrations in Euclidean space
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 March 2024, pp. 1-12
-
- Article
- Export citation
Use of narratives to communicate organics with commodity grain farmers
-
- Journal:
- Renewable Agriculture and Food Systems / Volume 38 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 August 2023, e39
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Narrow-windrow burning to control seeds of Italian ryegrass (Lolium perenne ssp. multiflorum) in wheat and Palmer amaranth (Amaranthus palmeri) in soybean
-
- Journal:
- Weed Technology / Volume 36 / Issue 5 / October 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 September 2022, pp. 716-722
-
- Article
- Export citation
Modeling clinical trajectory status of critically ill COVID-19 patients over time: A method for analyzing discrete longitudinal and ordinal outcomes
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 6 / Issue 1 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 April 2022, e61
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Seed-shattering phenology at soybean harvest of economically important weeds in multiple regions of the United States. Part 3: Drivers of seed shatter
-
- Journal:
- Weed Science / Volume 70 / Issue 1 / January 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 November 2021, pp. 79-86
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Risk for depression tripled during the COVID-19 pandemic in emerging adults followed for the last 8 years
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 53 / Issue 5 / April 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 November 2021, pp. 2156-2163
-
- Article
- Export citation
Staffing in a Level 1 Trauma Center: Quantifying Capacity for Preparedness
-
- Journal:
- Disaster Medicine and Public Health Preparedness / Volume 16 / Issue 5 / October 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 September 2021, pp. 1990-1996
-
- Article
- Export citation
Potential wheat yield loss due to weeds in the United States and Canada
-
- Journal:
- Weed Technology / Volume 35 / Issue 6 / December 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 September 2021, pp. 916-923
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
COMPARING DIRECT CARBONATE AND STANDARD GRAPHITE 14C DETERMINATIONS OF BIOGENIC CARBONATES
-
- Journal:
- Radiocarbon / Volume 63 / Issue 2 / April 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 January 2021, pp. 387-403
- Print publication:
- April 2021
-
- Article
- Export citation
Hairy buttercup (Ranunculus sardous) and cutleaf evening primrose (Oenothera laciniata) control using halauxifen-methyl based programs in Mississippi and Oklahoma winter wheat
-
- Journal:
- Weed Technology / Volume 35 / Issue 4 / August 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 November 2020, pp. 644-650
-
- Article
- Export citation
Seed-shattering phenology at soybean harvest of economically important weeds in multiple regions of the United States. Part 1: Broadleaf species
-
- Journal:
- Weed Science / Volume 69 / Issue 1 / January 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 November 2020, pp. 95-103
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Seed-shattering phenology at soybean harvest of economically important weeds in multiple regions of the United States. Part 2: Grass species
-
- Journal:
- Weed Science / Volume 69 / Issue 1 / January 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 October 2020, pp. 104-110
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A Guide for Caring for Patients Amidst the Novel Coronavirus Pandemic
-
- Journal:
- Disaster Medicine and Public Health Preparedness / Volume 15 / Issue 4 / August 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 October 2020, p. e19
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
RANK GENERATING FUNCTIONS FOR ODD-BALANCED UNIMODAL SEQUENCES, QUANTUM JACOBI FORMS, AND MOCK JACOBI FORMS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 109 / Issue 2 / October 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 January 2020, pp. 157-175
- Print publication:
- October 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation
ATLAS probe: Breakthrough science of galaxy evolution, cosmology, Milky Way, and the Solar System
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 36 / 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 April 2019, e015
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
4 - The Promise of Vervet Genomics
- from Part II - Taxonomy
-
-
- Book:
- Savanna Monkeys
- Published online:
- 08 March 2019
- Print publication:
- 21 March 2019, pp 55-59
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
EXPLORATION–EXPLOITATION POLICIES WITH ALMOST SURE, ARBITRARILY SLOW GROWING ASYMPTOTIC REGRET
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Probability in the Engineering and Informational Sciences / Volume 34 / Issue 3 / July 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 January 2019, pp. 406-428
-
- Article
- Export citation
Solar on the rise: How cost declines and grid integration shape solar’s growth potential in the United States
-
- Journal:
- MRS Energy & Sustainability / Volume 5 / 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 April 2018, E4
- Print publication:
- 2018
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Evolutionary Adaptations of Palmer Amaranth (Amaranthus palmeri) to Nitrogen Fertilization and Crop Rotation History Affect Morphology and Nutrient-Use Efficiency
-
- Journal:
- Weed Science / Volume 66 / Issue 2 / March 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 December 2017, pp. 180-189
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
5 - Patient Monitoring, Equipment, and Intravenous Fluids
-
-
- Book:
- Moderate and Deep Sedation in Clinical Practice
- Published online:
- 22 November 2017
- Print publication:
- 12 October 2017, pp 61-76
-
- Chapter
- Export citation