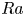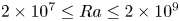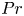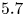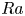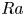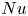515 results
Coffee intake leads to preeclampsia-like syndromes in susceptible pregnant rats
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Nutritional Science / Volume 13 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 September 2024, e34
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Real-world effectiveness of fidaxomicin in patients at high risk of Clostridioides difficile recurrence
-
- Journal:
- Antimicrobial Stewardship & Healthcare Epidemiology / Volume 4 / Issue 1 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 September 2024, e127
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Improving social cognition following theta burst stimulation over the right inferior frontal gyrus in autism spectrum: an 8-week double-blind sham-controlled trial
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 September 2024, pp. 1-12
-
- Article
- Export citation
Impact of total parenteral nutrition v. exclusive enteral nutrition on postoperative adverse outcomes in patients with penetrating Crohn’s disease undergoing surgical resection: a retrospective cohort study
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 June 2024, pp. 1-10
-
- Article
- Export citation
Posterior cingulate and medial prefrontal excitation-inhibition balance in euthymic bipolar disorder
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 June 2024, pp. 1-9
-
- Article
- Export citation
Determining cut-off values and predictors for the Snaith–Hamilton Pleasure Scale: comparison between clinical and school settings
-
- Journal:
- BJPsych Open / Volume 10 / Issue 3 / May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 May 2024, e106
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
One-stage thyroid cartilage laryngotracheal reconstruction for children less than one year old with congenital subglottic stenosis
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Laryngology & Otology , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 April 2024, pp. 1-5
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Association between cortical thickness or surface area and divergent thinking in patients with bipolar disorder
-
- Journal:
- Acta Neuropsychiatrica , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 April 2024, pp. 1-8
-
- Article
- Export citation
An acceleration method employing sparse sensing matrix for fast analysis of the wide-angle electromagnetic problems based on compressive sensing
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Microwave and Wireless Technologies , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 March 2024, pp. 1-6
-
- Article
- Export citation
Enhanced heat transfer and reduced flow reversals in turbulent thermal convection with an obstructed centre
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 981 / 25 February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 February 2024, A16
-
- Article
- Export citation
P199: Cluster analysis dissecting cognitive deficits in older adults with major depressive disorder and the association between neurofilament light chain
-
- Journal:
- International Psychogeriatrics / Volume 35 / Issue S1 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 February 2024, pp. 188-189
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
P30: Neuro-therapeutic play with Asian older adults: a qualitative analysis.
-
- Journal:
- International Psychogeriatrics / Volume 35 / Issue S1 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 February 2024, p. 238
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Coulomb-driven electroconvection turbulence in two-dimensional cavity
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 980 / 10 February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 January 2024, A22
-
- Article
- Export citation
Voltage-gated sodium channel gene mutation and P450 gene expression are associated with the resistance of Aphis spiraecola Patch (Hemiptera: Aphididae) to lambda-cyhalothrin
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of Entomological Research / Volume 114 / Issue 1 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 January 2024, pp. 49-56
-
- Article
- Export citation
Assessment of Combined Karyotype Analysis and Chromosome Microarray Analysis in Prenatal Diagnosis: A Cohort Study of 3710 Pregnancies
-
- Journal:
- Genetics Research / Volume 2022 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e1
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Effect of Viscosity on Stopping Power for a Charged Particle Moving above Two-Dimensional Electron Gas
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 2022 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e19
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Upregulated Solute Carrier SLC39A1 Promotes Gastric Cancer Proliferation and Indicates Unfavorable Prognosis
-
- Journal:
- Genetics Research / Volume 2022 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e12
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Effect of the SiO2/Al2O3 Molar Ratio on the Microstructure and Properties of Clay-based Geopolymers: A Comparative Study of Kaolinite-based and Halloysite-based Geopolymers
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 70 / Issue 6 / December 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 882-902
-
- Article
- Export citation
Overexpressed Histocompatibility Minor 13 was Associated with Liver Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression and Prognosis
-
- Journal:
- Genetics Research / Volume 2022 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e23
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
17 Emotional and Instrumental Support as Protective Factors in Cognitive Aging Among Black and Hispanic/Latinx Older Adults
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 29 / Issue s1 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 December 2023, pp. 330-331
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation