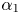137 results
Voltage-gated sodium channel gene mutation and P450 gene expression are associated with the resistance of Aphis spiraecola Patch (Hemiptera: Aphididae) to lambda-cyhalothrin
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of Entomological Research / Volume 114 / Issue 1 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 January 2024, pp. 49-56
-
- Article
- Export citation
Relationship between CYP2C19 Polymorphism and Clopidogrel Resistance in Patients with Coronary Heart Disease and Ischemic Stroke in China
-
- Journal:
- Genetics Research / Volume 2022 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e17
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
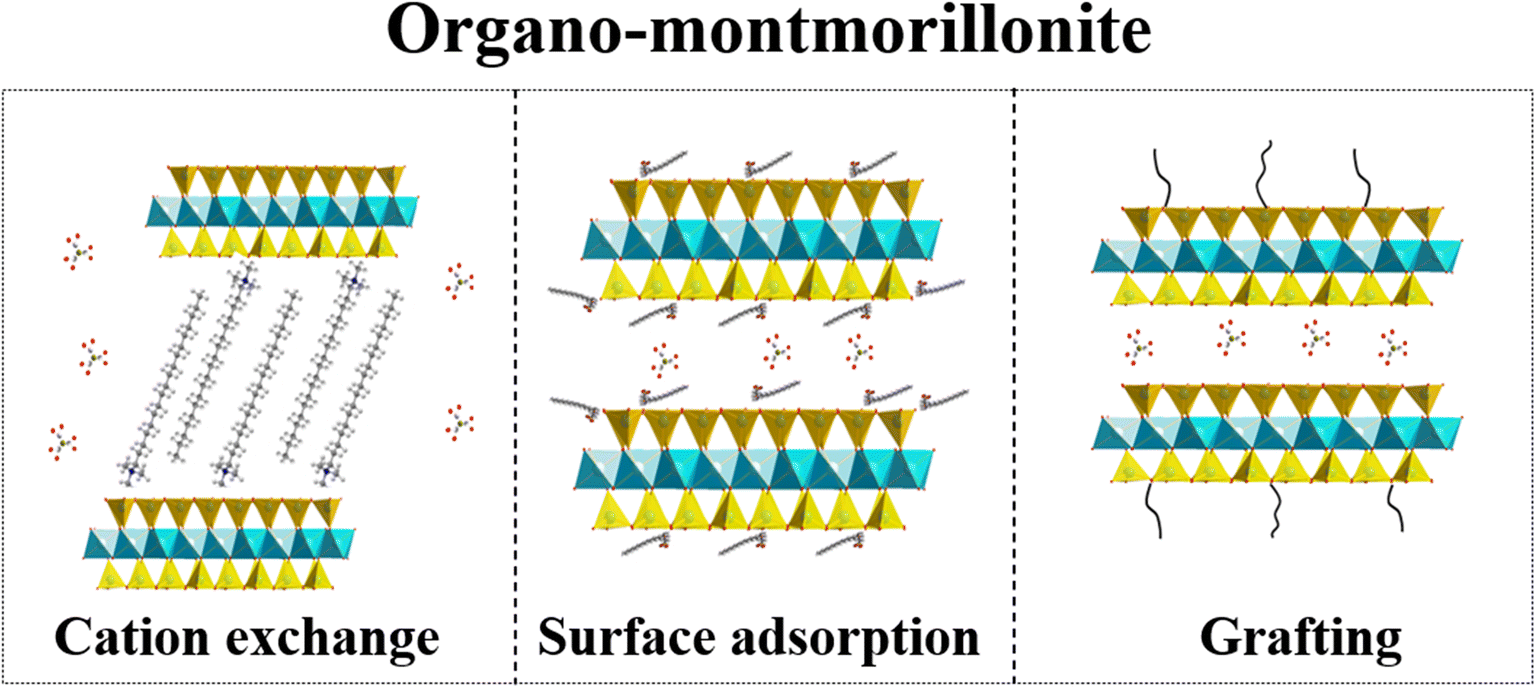
Organo-Modification of Montmorillonite
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 68 / Issue 6 / December 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 601-622
-
- Article
- Export citation
Operational impact of decreased turnaround times for Candida auris screening tests in a tertiary academic medical center
-
- Journal:
- Antimicrobial Stewardship & Healthcare Epidemiology / Volume 3 / Issue 1 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 October 2023, e176
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Maternal and Neonatal Outcomes of Twin Pregnant Women With Anemia
-
- Journal:
- Twin Research and Human Genetics / Volume 26 / Issue 4-5 / August 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 August 2023, pp. 313-318
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Separation length scaling for dual-incident shock wave–turbulent boundary layer interactions with different shock wave distances
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 960 / 10 April 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 March 2023, A9
-
- Article
- Export citation
SG-APSIC1199: Evaluation of a pooling strategy using Xpert Carba-R assay for screening for carbapenemase-producing organisms in rectal swabs
-
- Journal:
- Antimicrobial Stewardship & Healthcare Epidemiology / Volume 3 / Issue S1 / February 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 March 2023, pp. s26-s27
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
SG-APSIC1203: Detection of carbapenemase genes in donor lungs at the point of care before transplantation reduces the risk of carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae–associated donor-derived infection in lung-transplant recipients
-
- Journal:
- Antimicrobial Stewardship & Healthcare Epidemiology / Volume 3 / Issue S1 / February 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 March 2023, p. s25
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Characteristics of patients with SARS-COV-2 PCR re-positivity after recovering from COVID-19
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 151 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2023, e34
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Serum levels of n-3 PUFA and colorectal cancer risk in Chinese population
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 130 / Issue 7 / 14 October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 February 2023, pp. 1239-1249
- Print publication:
- 14 October 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Why and When Narcissistic Employees Are More Creative in the Workplace? A Social Cognitive Perspective
-
- Journal:
- Management and Organization Review / Volume 19 / Issue 3 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 January 2023, pp. 567-593
-
- Article
- Export citation
Comparison of ventricular synchrony in children with left bundle branch area pacing and right ventricular septal pacing
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 33 / Issue 10 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 January 2023, pp. 2078-2086
-
- Article
- Export citation
Plasma image classification using cosine similarity constrained convolutional neural network
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Plasma Physics / Volume 88 / Issue 6 / December 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 December 2022, 895880603
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Investigation of a Fused in Sarcoma Splicing Mutation in a Chinese Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Patient
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 50 / Issue 6 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 December 2022, pp. 891-896
-
- Article
- Export citation
Transverse mode instability mitigation in a high-power confined-doped fiber amplifier with good beam quality through seed laser control
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 10 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 November 2022, e44
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The application of nature-inspired optimization algorithms on the modern management: A systematic literature review and bibliometric analysis
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Management & Organization / Volume 29 / Issue 4 / July 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 October 2022, pp. 655-678
-
- Article
- Export citation
Effectiveness of enhancing contact model on reducing family caregiving burden and improving psychological wellbeing among caregivers of persons with schizophrenia in rural China
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 53 / Issue 12 / September 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 September 2022, pp. 5756-5766
-
- Article
- Export citation
The global disease burden attributable to a diet low in fibre in 204 countries and territories from 1990 to 2019
-
- Journal:
- Public Health Nutrition / Volume 26 / Issue 4 / April 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 September 2022, pp. 854-865
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Mechanisms of inkjet printing in a liquid environment
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 948 / 10 October 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 September 2022, A40
-
- Article
- Export citation