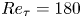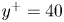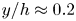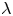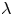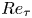380 results
Improving social cognition following theta burst stimulation over the right inferior frontal gyrus in autism spectrum: an 8-week double-blind sham-controlled trial
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 September 2024, pp. 1-12
-
- Article
- Export citation
Childhood socio-economic disadvantages versus adverse care experiences: Mediation and moderation impacts on late-life depressive symptoms
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 67 / Issue 1 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 August 2024, e47
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Asymptotic profiles of a nonlocal dispersal SIS epidemic model with saturated incidence
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 May 2024, pp. 1-33
-
- Article
- Export citation
Exploring the differential effects of psychological resilience and social support in mitigating post-traumatic psychiatric symptoms: real-world network analysis of front-line rescuers
-
- Journal:
- BJPsych Open / Volume 10 / Issue 3 / May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 May 2024, e109
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Impacts of environmental factors on the aetiological diagnosis and disease severity of community-acquired pneumonia in China: a multicentre, hospital-based, observational study
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 152 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 May 2024, e80
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Religious Institutional Environment and Executive Pay Dispersion
-
- Journal:
- Management and Organization Review / Volume 20 / Issue 2 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 May 2024, pp. 265-295
-
- Article
- Export citation
Temporal trend analysis of acute hepatitis B virus infection in China, 1990–2019
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 152 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 March 2024, e48
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Impact of primary care triage using the Head and Neck Cancer Risk Calculator version 2 on tertiary head and neck services in the post-coronavirus disease 2019 period
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Laryngology & Otology , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 January 2024, pp. 1-6
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Creating shared goals and experiences as a pathway to peace
-
- Journal:
- Behavioral and Brain Sciences / Volume 47 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 January 2024, e5
-
- Article
- Export citation
Inverse association between maternal serum concentrations of trace elements and risk of spontaneous preterm birth: a nested case–control study in China
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 131 / Issue 8 / 28 April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 January 2024, pp. 1425-1435
- Print publication:
- 28 April 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Cloning and spatio-temporal expression of CsKr-h1 encoding the juvenile hormone response gene in Coccinella septempunctata L
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of Entomological Research / Volume 114 / Issue 1 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 January 2024, pp. 99-106
-
- Article
- Export citation
Alpha-Particle Generation from H-11B Fusion Initiated by Laser-Accelerated Boron Ions
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 2022 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e7
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Downregulated miR-150-5p in the Tissue of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma
-
- Journal:
- Genetics Research / Volume 2022 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e34
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Identification of Key Biomarkers and Candidate Molecules in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer by Integrated Bioinformatics Analysis
-
- Journal:
- Genetics Research / Volume 2023 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e29
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Overexpressed Histocompatibility Minor 13 was Associated with Liver Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression and Prognosis
-
- Journal:
- Genetics Research / Volume 2022 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e23
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
17 The Chinese Version of Craft Story Recall: A Preliminary Study on the Diagnostic Values of Mild Cognitive Impairment and Dementia.
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 29 / Issue s1 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 December 2023, pp. 700-701
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
The egg ribonuclease SjCP1412 accelerates liver fibrosis caused by Schistosoma japonicum infection involving damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs)
-
- Journal:
- Parasitology / Volume 151 / Issue 3 / March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 December 2023, pp. 260-270
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Comprehensive Multiomics Analysis of Monozygotic Twin Discordant for Double Outlet Right Ventricle
-
- Journal:
- Twin Research and Human Genetics / Volume 26 / Issue 6 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 December 2023, pp. 370-378
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
OP62 Development Of The Oral Health Risk Adjustment Model To Predict The Outpatient Dental Expenditure In Children With Autism
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Technology Assessment in Health Care / Volume 39 / Issue S1 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 December 2023, pp. S17-S18
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
A resolvent-based prediction framework for incompressible turbulent channel flow with limited measurements
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 976 / 10 December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 December 2023, A31
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation